|
|
All Countries Ships and Boats T‑Z
|
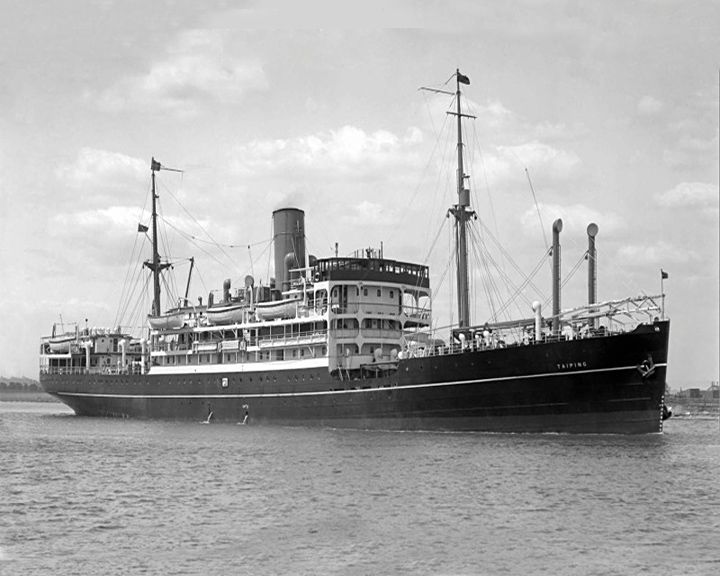 Taiping — Chinese steamship Tragically collided with another vessel killing over 1,500 people. A memorial to the ship and those who died aboard her was established at Port Keeling naval base on Taiwan. The 2014 movie The Crossing is based on the sinking. LAUNCHED: 1920, probably → FATE: Sank January 27, 1949. |
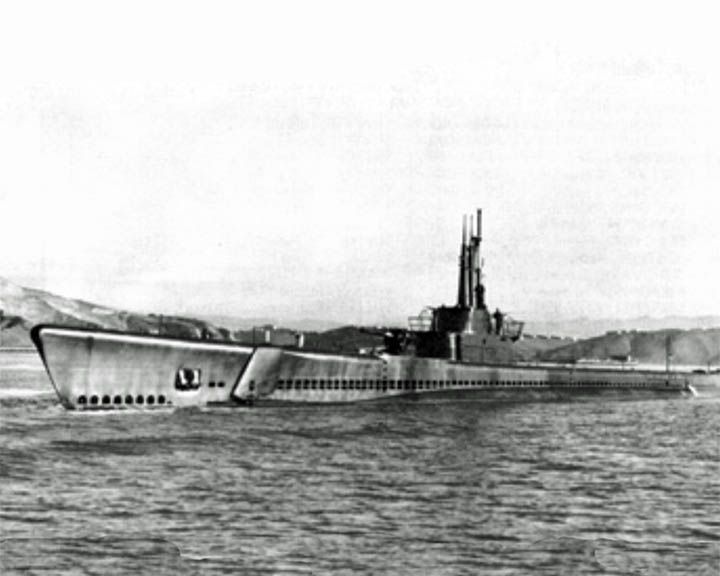 Tang, USS — American Balao class submarine Credited with sinking 31 enemy ships totaling 227,800 tons, unequaled among American submarines during World War II. When she was sunk by a circular run of her final torpedo, several crew escaped the sinking boat with a Momsen lung, the only known occasion of its use. 78 men were lost and the nine survived. LAUNCHED: 1943, August 18 → FATE: Sunk by her own torpedo in the Taiwan Strait October 24, 1944. |
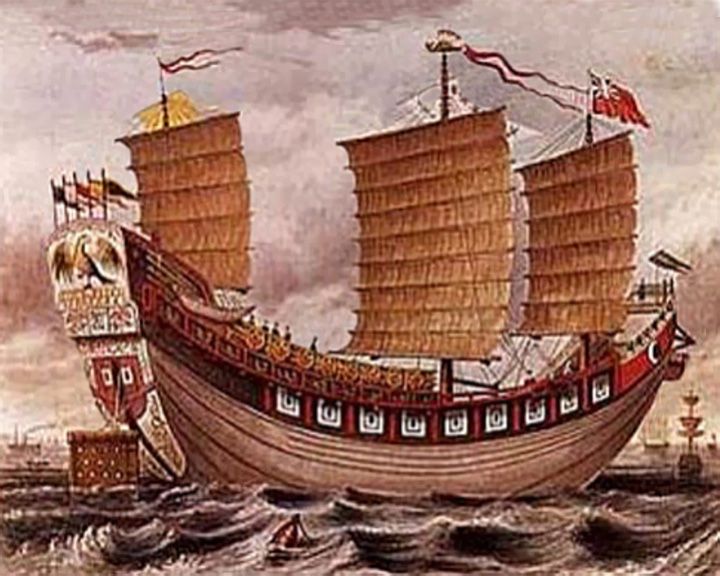 Tek Sin — Chinese ocean-going junk Called the "Titanic of the East" when it sank taking with it over 1,600 people. Only about 200 people survived, being rescued by another ship the next day. LAUNCHED: 1820, circa → FATE: Grounded on a reef, then sank on February 6, 1822. |
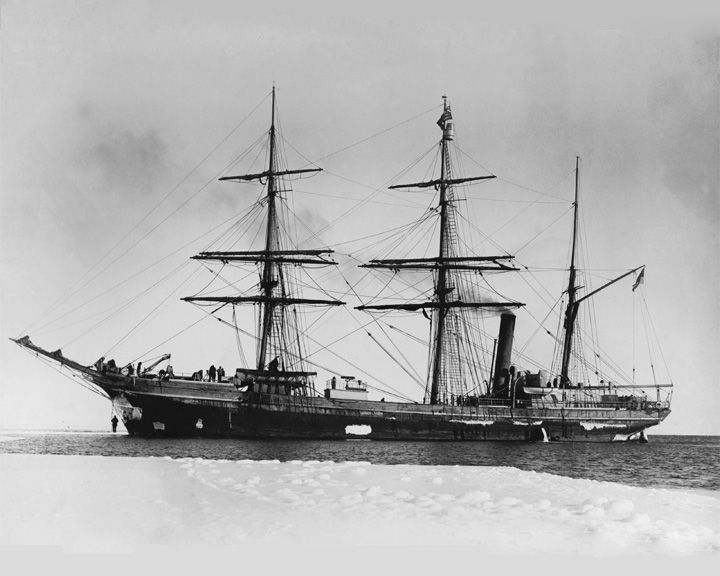 Terra Nova — British wooden-hulled barque Serving in the British Antarctic Expedition 1910, best remembered for the death of Captain Scott and four companions. She was built for the Dundee whaling and sealing fleet, working 10 years in the annual seal fishery in the Labrador Sea. LAUNCHED: 1884 → FATE: Sank off the southwestern tip of Greenland September 13, 1943. |
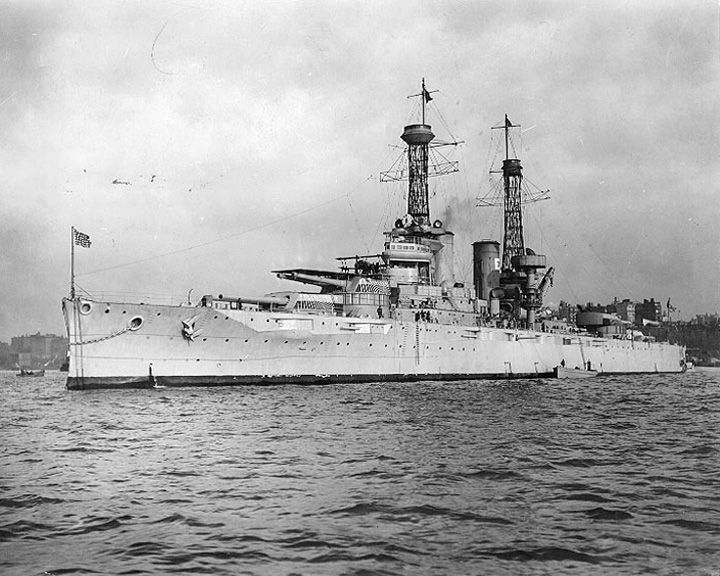 (Another (Another Texas, USS — American New York class battleship The only remaining World War I era dreadnought battleship. She is noteworthy for being one of only seven remaining ships and the only remaining capital ship to have served in both World Wars. LAUNCHED: 1912, May 18 → FATE: Museum ship at San Jacinto Battleground State Historic Site. |
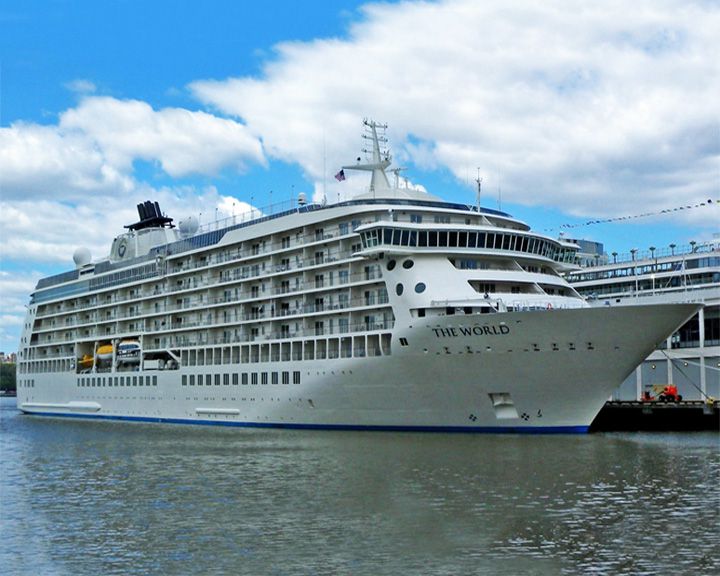 The World, MS — Swedish cruise ship A ship serving as a residential community owned by its residents. She became the largest passenger ship to transit the Northwest Passage by sailing from Nome, Alaska to Nuuk, Greenland in 25 days, August-September, 2012. LAUNCHED: 2002, March → FATE: Still in service. |
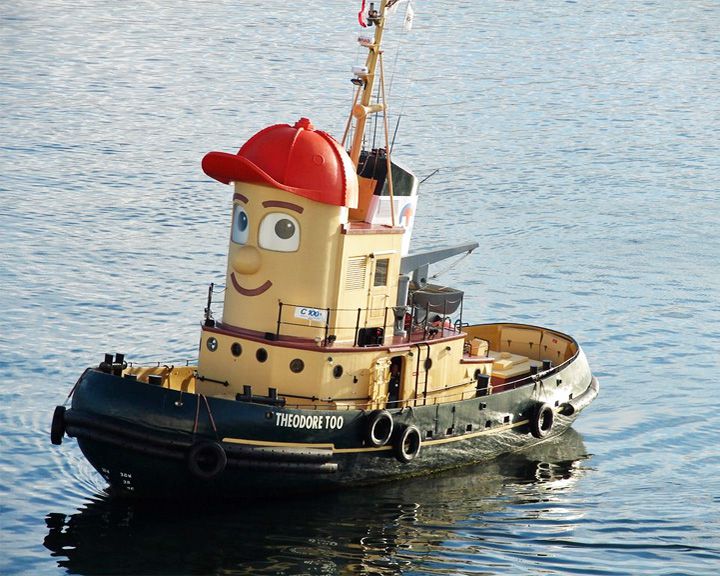 Theodore Too — Canadian tug boat Full size imitation tugboat based on the fictional tugboat Theodore from the television show Theodore Tugboat. She is the ambassador of the U.S. National Safe Boating Council and mascot to the U.S. Coast Guard participating in several tall ship events. LAUNCHED: 2000, April 18 → FATE: Still in service. |


|
Page 2
|
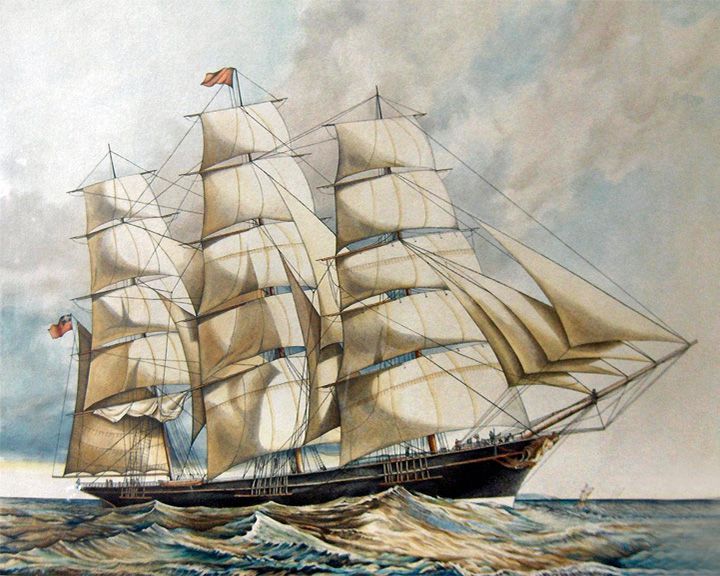 Thermopylae — English extreme clipper Raced the clipper Cutty Sark from Shanghai back to London and won by seven days. In 1897, she was sold to Portugal and renamed Pedro Nunes for used as a naval training ship. LAUNCHED: 1868, August → FATE: Sunk as target practice by the Portuguese Navy, October 13, 1907. |
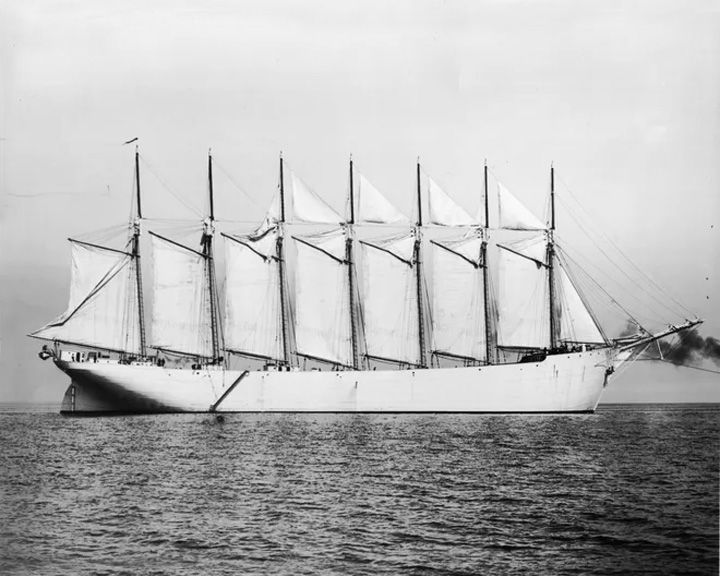 Thomas W. Lawson — American seven-masted schooner The largest schooner and largest sailing vessel without an auxiliary engine ever built. She proved problematic in the ports she was intended to operate in due to the amount of water she displaced. LAUNCHED: 1902, July, 10 → FATE: Sank in a storm while at anchor off Cornwall, England, in 1907 taking 16 of her crew with her. |
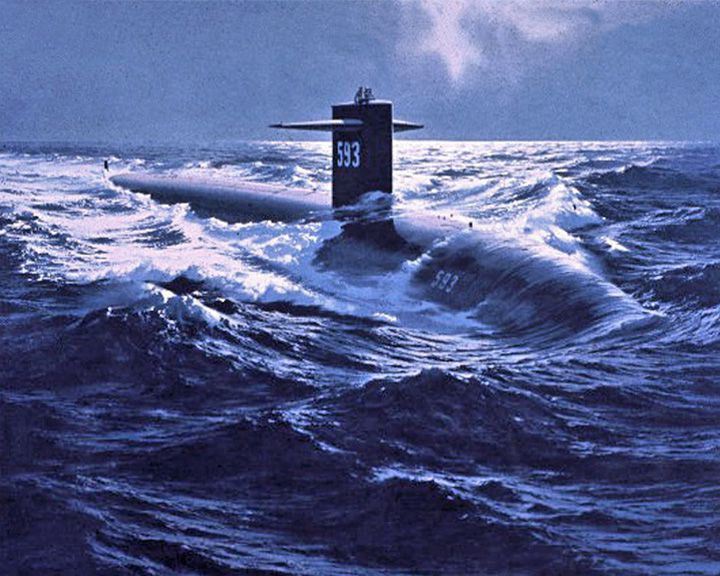 Thresher, USS — American nuclear submarine Lost at sea during deep-diving tests in 1963 with 129 crew. She was the lead ship of her class of nuclear-powered attack submarines and one of two nuclear submarines the U.S. Navy has lost, the other being USS Scorpion, SSN-589. LAUNCHED: 1960, July 18 → FATE: Sunk April 10, 1963. |
 Tigerfish, USS — American attack submarine Fictional submarine in the movie Ice Station Zebra. She was portrayed in the movie by the diesel-electric submarine USS Ronquil when seen on the surface. LAUNCHED: 1968, movie release → FATE: Inconclusive. |
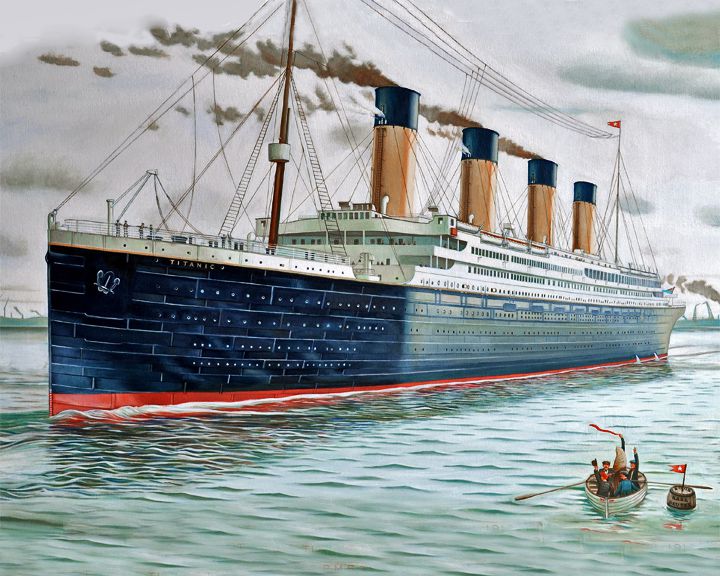 (Another (Another Titanic, RMS — British luxury ocean liner The most famous ship sinking in history, she sank after hitting iceberg in the Atlantic, claiming over 1500 lives. Believed by many to be unsinkable, her disintegrating remains lie at a depth of 3,784 meters. Many movie have been made about her sinking including the 1997 film. LAUNCHED: 1911, May 18 → FATE: Sank in the North Atlantic April 15, 1912. |
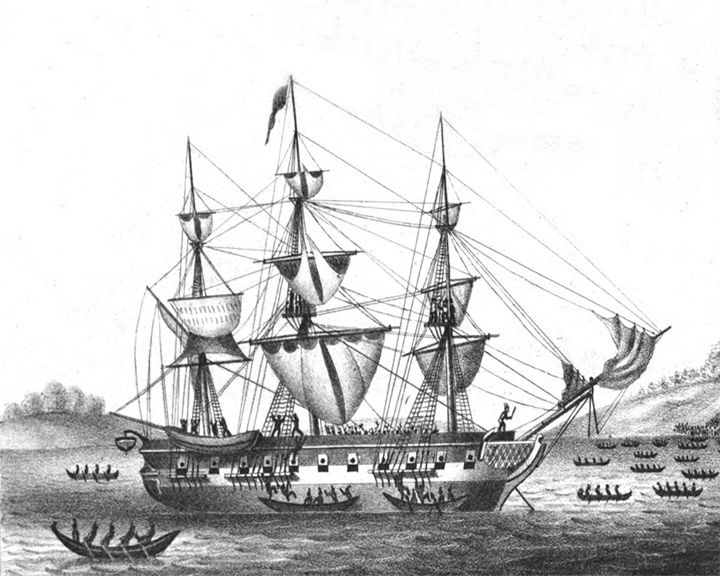 Tonquin — American merchant ship The ship was part of Astor's attempt to establish a fur trading outpost on the Pacific Northwest coast. After an angry encounter with natives, two surviving crew hid in the ship, then when the Indian natives returned to loot the ship, lit a fuse that detonated her powder magazine killing more than 100 natives and two crew. LAUNCHED: 1807, May 26 → FATE: Blown up June 16, 1811. |
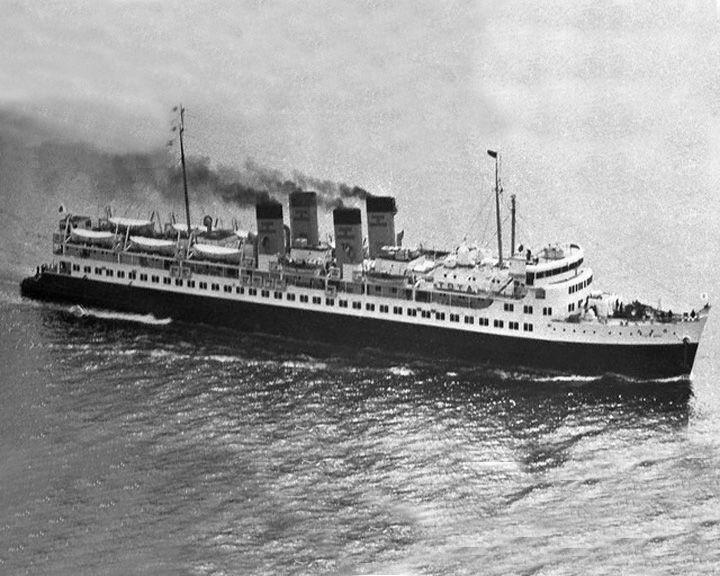 Toya Maru — Japanese train ferry Her sinking was one of the major factors behind the construction of the Seikan Tunnel between Hokkaido and Honshu. Perhaps 1,153 people were lost but the exact number is unknown because some people boarded without tickets and others cancelled just before sailing. LAUNCHED: 1947, November → FATE: Sank during a typhoon in the Tsugaru Strait September 26, 1954. |
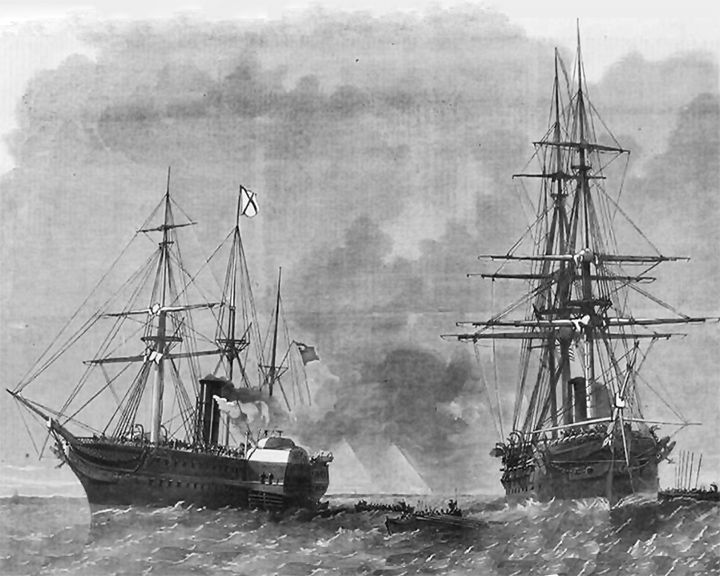 Trent, RMS — British paddle steamer serving as a packet boat Principle ship in the Trent affair in 1861 during the American Civil War. Her interception by USS San Jacinto and unlawfully capture of two Confederate diplomats almost led to war between the Britian and the United States. LAUNCHED: 1841 → FATE: Sold and broken up after 1865. |
|
Page 3
|
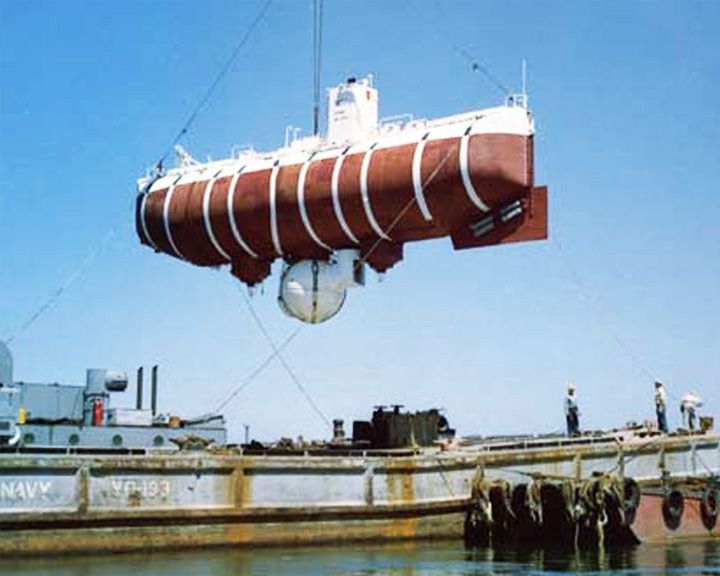 Trieste — Italian deep-diving research bathyscaphe; Swiss designed Dove to a record ocean depth of about 10,911 metres, or about 6.8 miles. She reached the ocean floor in the Mariana Trench on January 23, 1960. She found the missing submarine USS Thresher off the coast of New England in August of 1963. LAUNCHED: 1953, August 18 → FATE: On display at the U.S. Naval National Undersea Museum in Keyport, Washington. |
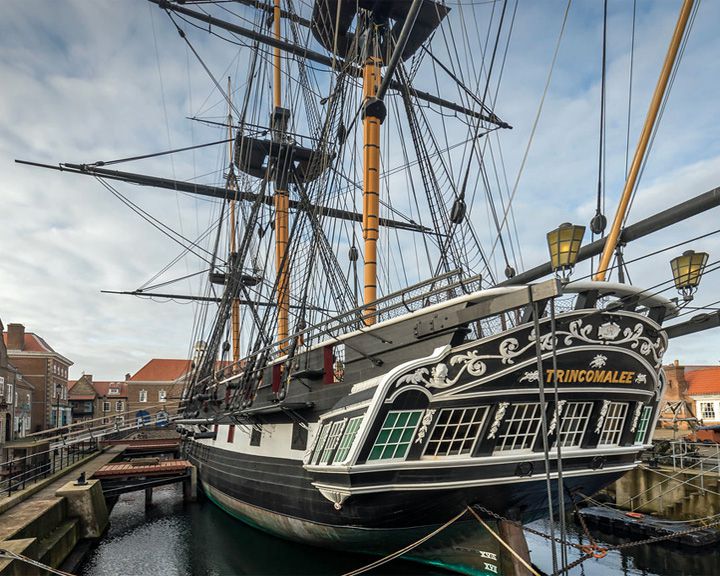 Trincomalee, HMS — British Leda-class frigate One of two surviving British frigates of her era. Holds the distinction of being the oldest British warship still afloat. LAUNCHED: 1817, October 12 → FATE: Restored made the centerpiece museum ship in Hartlepool, England. |
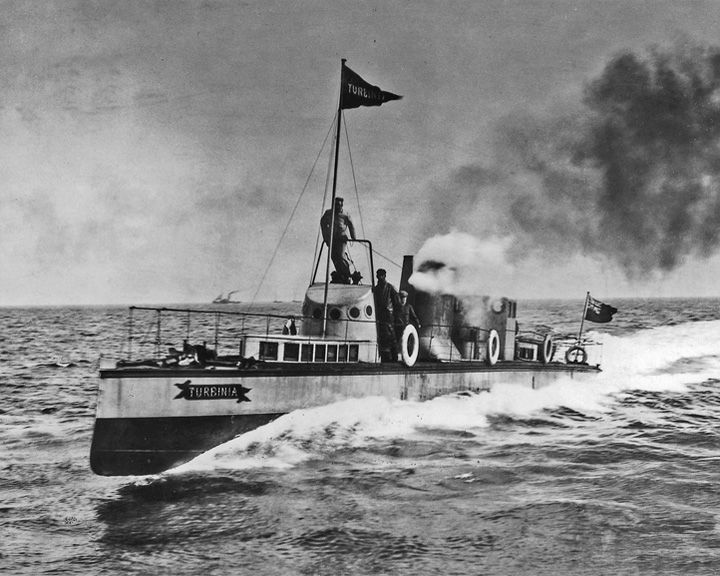 Turbinia — British steamship First steam turbine-powered steamship and the fastest ship in the world at that time at over 34 knots. She showed up unannounced at the Fleet Review for Queen Victoria's Diamond Jubilee at Spithead in 1897, racing up and down the ranks of other ships. LAUNCHED: 1894, August 18 → FATE: On display at the Discovery Museum at Newcastle upon Tyne, England. |
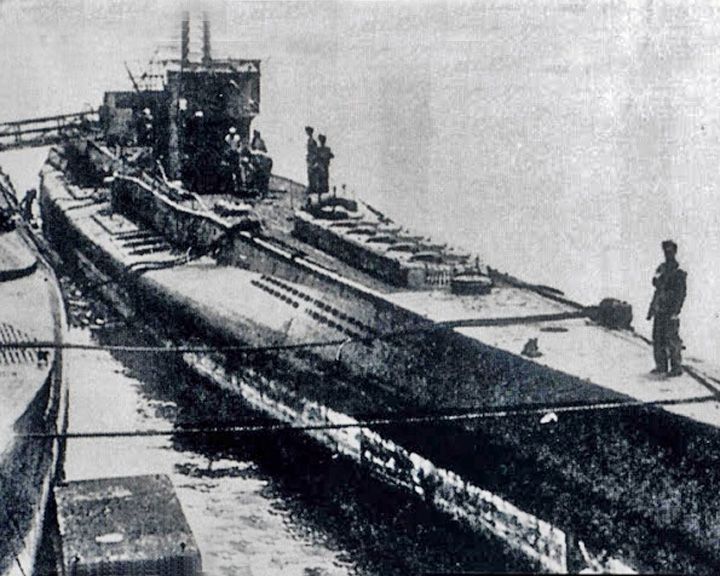 U-234 — German submarine Hitler's last submarine; ironically, there is an isotope of uranium designated U-234. While attempting to deliver uranium to Japan near the end of World War II, she surrendered to the United States on May 14, 1945. LAUNCHED: 1943, December → FATE: Sunk by torpedo November 20, 1947. |
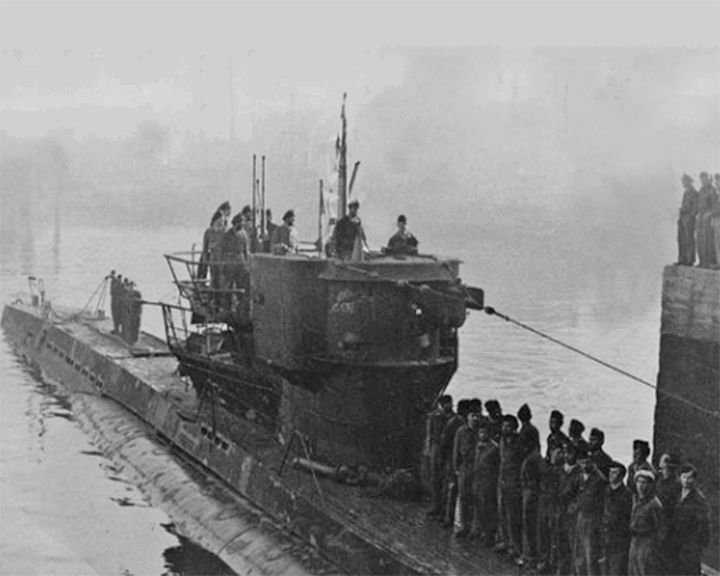 U-480 — German experimental Kriegsmarine Type VIIC submarine The first stealth submarine; she was covered with a special rubber coating making it difficult to detect with SONAR. She sank two warships and two merchantmen ships and was never detected by the British until it was discovered by divers in 1998 south of Isle of Wight. LAUNCHED: 1943, August 14 → FATE: Sunk in February 1945 in an English Channel minefield with the loss of its crew. |
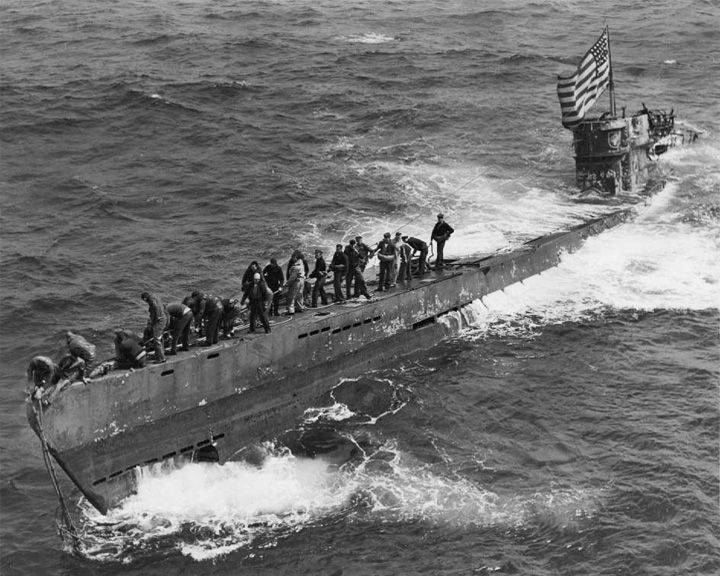 U-505 — German submarine Codebooks, an Enigma machine, and other secret materials that were found on board assisted Allied code breakers during World War II. All but one of crew were rescued from U-505. For U-110, there were casualties among the crew caused by two attacking destroyers. LAUNCHED: 1941, August → FATE: Captured in June 4, 1944. Now at Chicago museum. |
 U-96 — German German Type VIIC submarine She was made famous in the 1981 movie Das Boot, a fictional account of its adventures in the Battle of Atlantic of World War II.. During 1941, war a correspondent joined U-96 and, based on his experiences, published a novel that was made into the 1981 movie LAUNCHED: 1940, August 1 → FATE: Sunk in the Hipper Basin at Wilhelmshaven, March 30, 1945. |
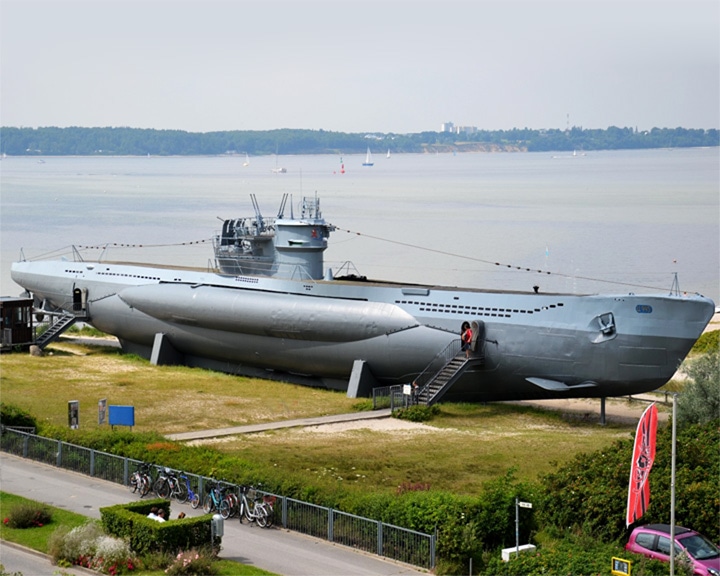 U-995 — German submarine The last existing submarine of its type, which was the workhorse for the German navy during World War II. From 1943 till 1945 the U-995 fulfilled several missions against allied convoys heading for Murmansk, Russia. LAUNCHED: 1942, November 25 → FATE: At the end of WW-II, she was surrendered to the British in December 1945 and then transferred to Norwegian ownership in October 1948. Eventually, in October 1971, she became a museum ship at Laboe Naval Memorial, in Germany. |
|
Page 4
|
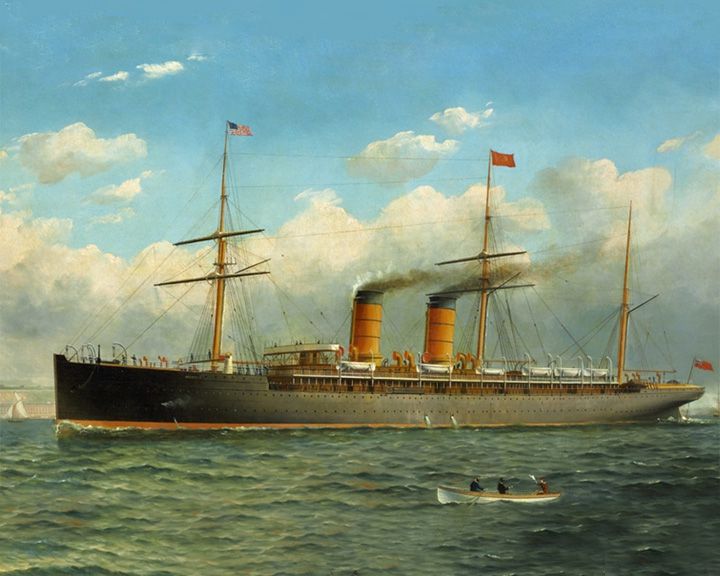 Umbria, RMS — British ocean liner With her sister ship, Etruria, the last two transatlantic ocean liners fitted with auxiliary sails. In May of 1903, the Mafia tried to blow her up but failed. LAUNCHED: 1884, June 18 → FATE: Scrapped in 1910. |
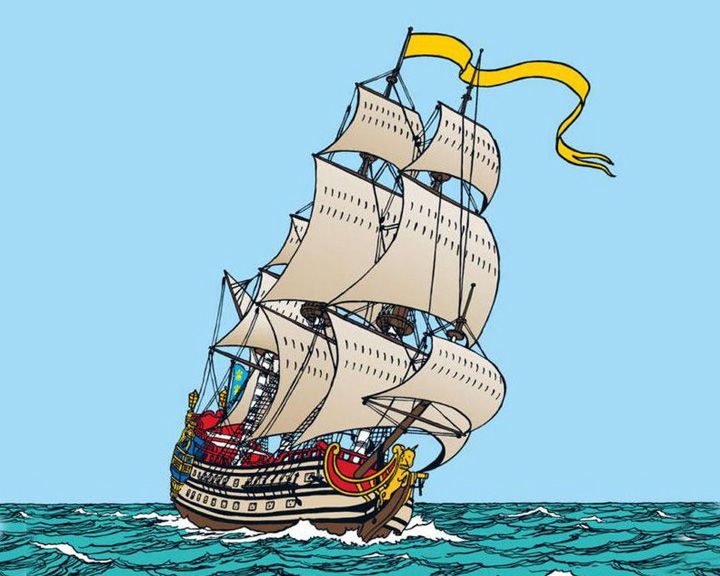 (Another (Another Unicorn — British three-masted sailing ship Royal Navy vessel appearing in the comics series by Belgian cartoonist Hergé The Adventures of Tintin, and the movie. She is the setting of a battle between pirates and sailors, then scuttled, and discovered years later by the boy Tintin and his friends. LAUNCHED: 1943, first appeared in print; movie release in 2011 → FATE: Inconclusive. |
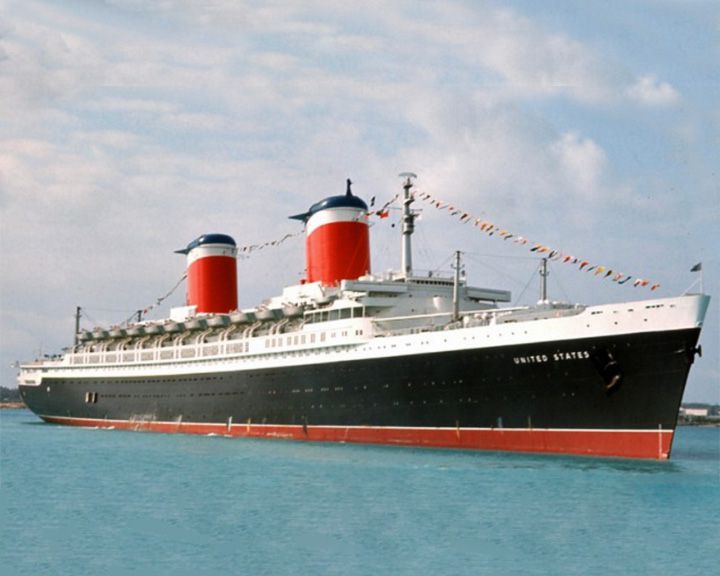 United States, SS — American ocean liner (steamship) The fastest liner ever built; virtually no wood used in her construction. On her maiden voyage she captured the Blue Riband with the fastest transatlantic crossing on record in 3 days, 10 hours, 40 minutes at an average speed of 35.59 knots. LAUNCHED: 1951, June 18 → FATE: As of February 7, 2012, work has begun on the restoration project to prepare the ship for her eventual rebuild. |
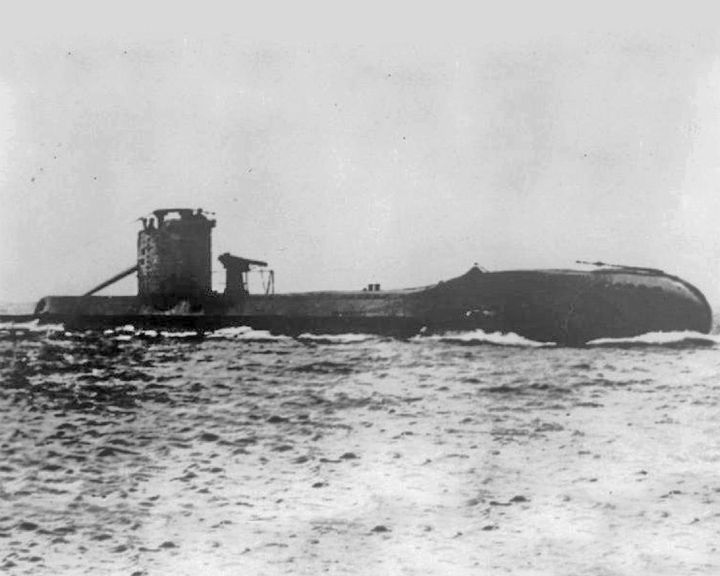 Upholder, HMS — British U-class submarine The most successful British submarine of the World War II sinking a gross tonnage of 93,031. She was one of four U-class submarines with 2 external torpedo tubes at the bows in addition to the 4 internal ones. LAUNCHED: 1940, July 8 → FATE: Lost northeast of Tripoli with all hands, probably sunk by enemy depth charges April 14, 1942. |
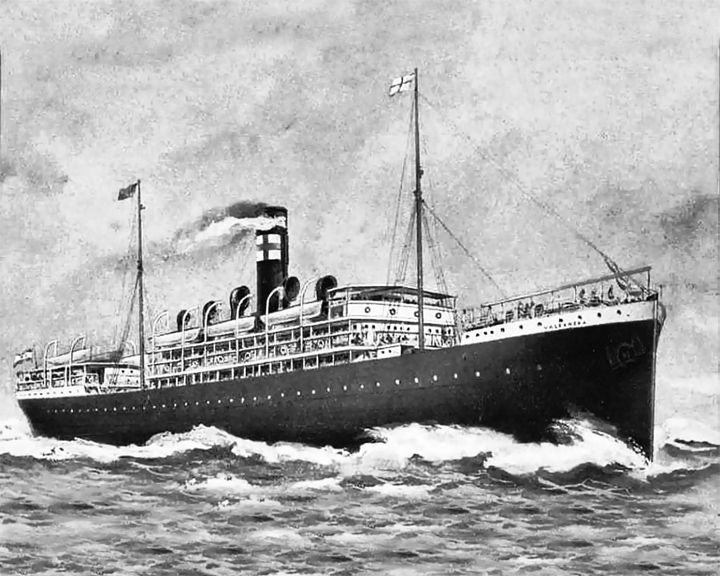 Valbanera, SS — Scotish, then Spanish passenger steamship Notable because of the mystery surrounding her disappearance during a hurricane. More than 480 passengers and crew were lost. Two empty lifeboats and the ships mast marked the spot where the ship sank. LAUNCHED: 1906 → FATE: Sank in a hurricane off Key West September of 1919. |
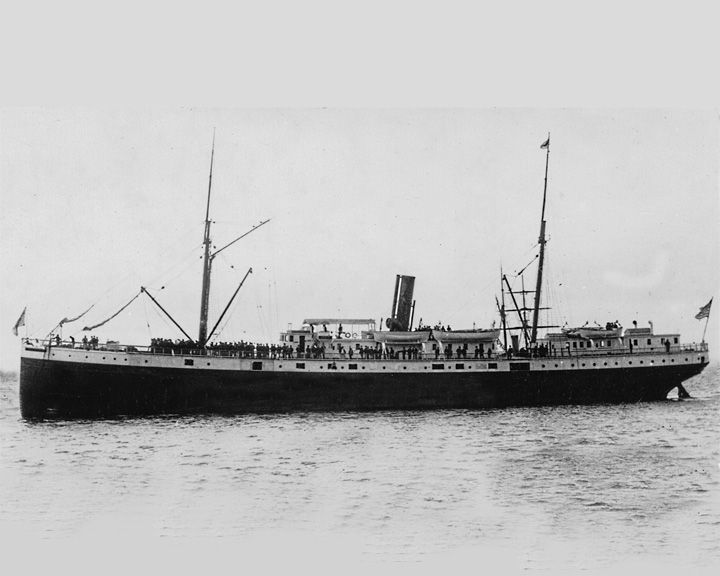 Valencia, SS — American passenger steamboat (steamship) Consider the worst maritime disaster in the Graveyard of the Pacific, a treacherous area off the southwest coast of Vancouver Island, British Columbia. 27 years after her sinking, one of her life rafts was found floating peacefully in nearby Barkley Sound. LAUNCHED: 1882, May → FATE: Wrecked January 22, 1906. |
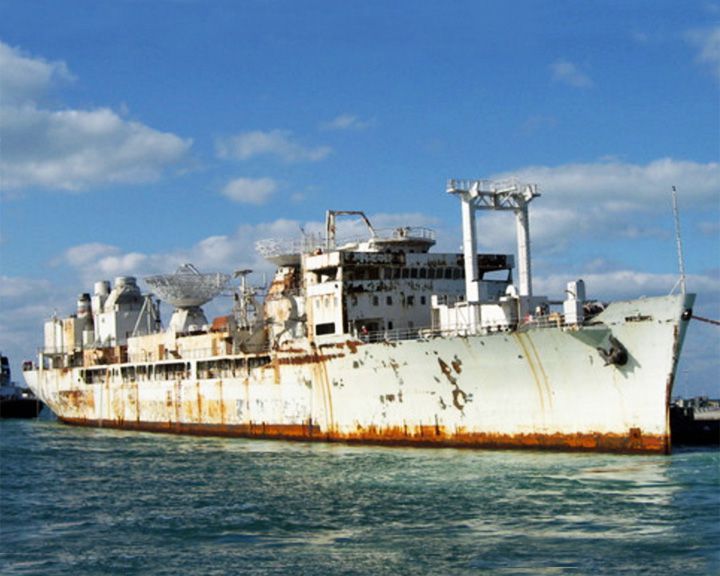 Vandenberg, USAFS — American transport ship Second-largest artificial reef in the world, after the aircraft carrier USS Oriskany. She transported troops in World War II. In 1998, she was featured in the film Virus as the Russian research ship Akademik Vladislav Volkov. LAUNCHED: 1943, October → FATE: Sank May 27, 2009, six miles off the Florida Keys. |
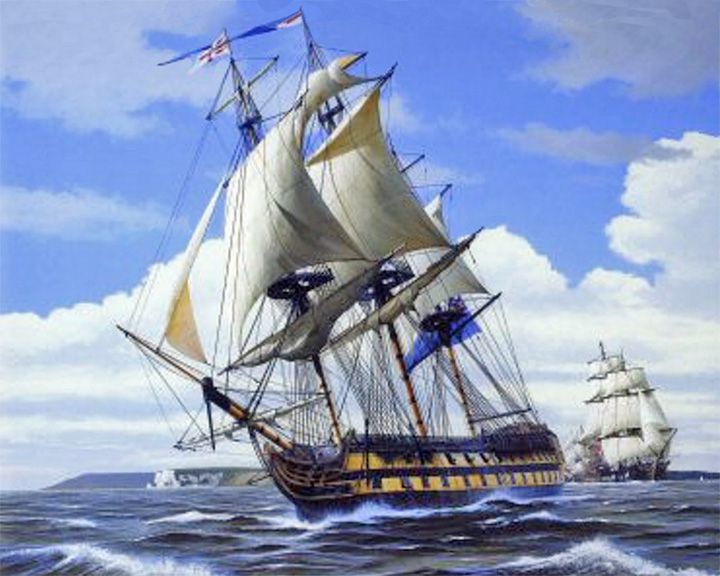 Vanguard, HMS — English ship of the line, 74-gun third-rate The flag ship of Horatio Nelson at the Battle of the Nile, 1798. Prince Alberto of Naples and Sicily, part of a royal entourage on board fleeing from Naples and the French, died on board. LAUNCHED: 1787, March 18 → FATE: Broken up in 1821. |
|
Page 5
|
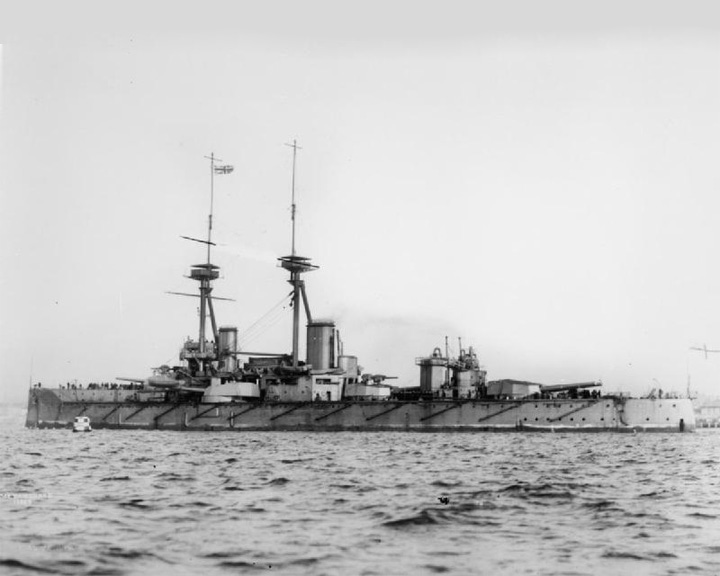 Vanguard, HMS (1909) — British St. Vincent class Dreadnaught She suffered a series of magazine explosions, sinking almost instantly, killing 843 of the 845 men aboard. Her captain coincidentally made a speech to the crew predicting the possible fate of the ship several hours before her sinking. Vanguard's wreck was heavily salvaged in search of non-ferrous metals before it was declared a war grave in 1984. Royal Navy divers placed a new Union Jack on the wreck. LAUNCHED: 1909, February 2 → FATE: Sunk by internal explosion at Scapa Flow, July 9, 1917. |
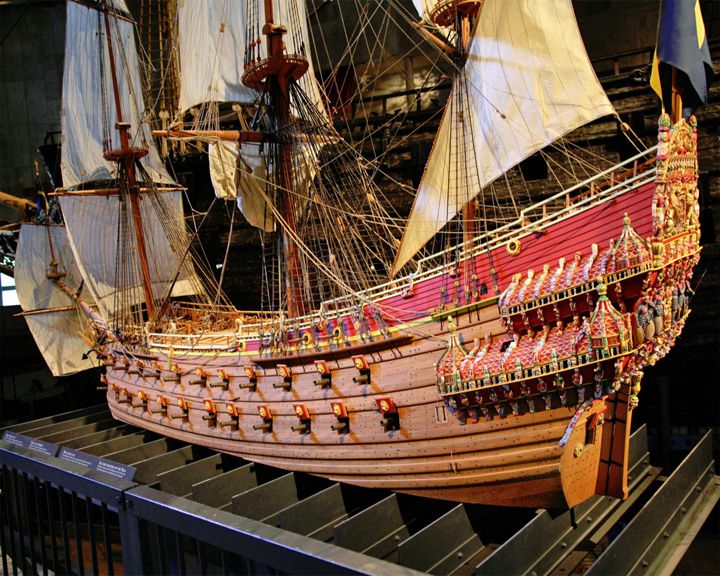 Vasa — Swedish wooden warship One of Sweden's most popular tourist attractions and a widely recognized symbol of the Swedish 'great power period'. During the 1961 recovery, thousands of artifacts and the remains of at least 15 people were found in and around the hull of the Vasa by marine archaeologists. LAUNCHED: 1627 → FATE: Sank on her maiden voyage in 1628 near Södermalm; salvaged in 1961 and now on display in the Vasa Museum in Stockholm. |
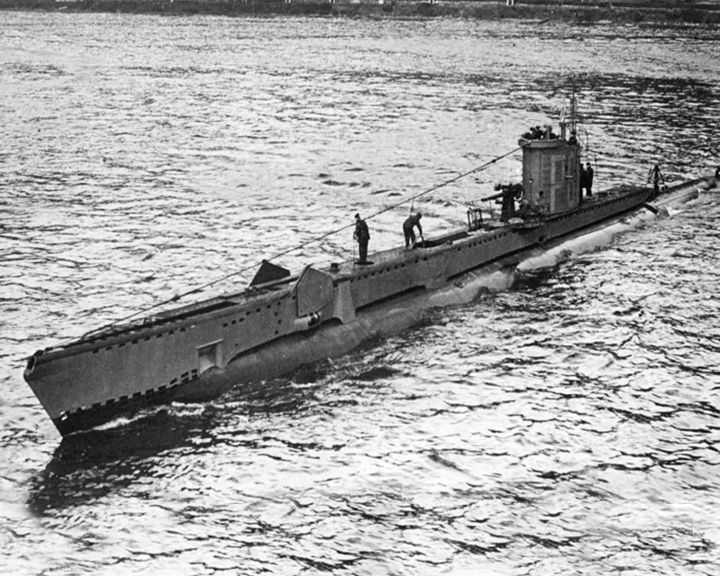 Venturer, HMS — British V-class submarine First time in naval warfare that one submarine stalked and sank another while both were submerged. Based on Enigma decrypts, she sought out and destroyed the German submarine U-864 in the Fedje area, February 9, 1945. LAUNCHED: 1943, May 4 → FATE: She was sold to Norway and renamed HNoMS Utstein. She was scrapped and broken up in 1964. |
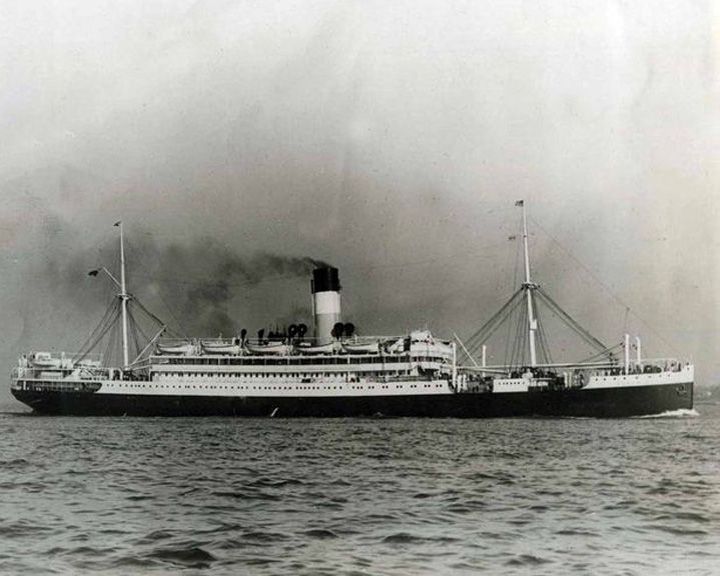 Vestris, SS — British passenger steamship The ship sank taking more passengers to their death than crew. 60 of 128 passengers survived, 155 of 198 crew survived. None of 13 children and only 8 of 33 women survived. LAUNCHED: 1912, May → FATE: Sank November 12, 1928. |
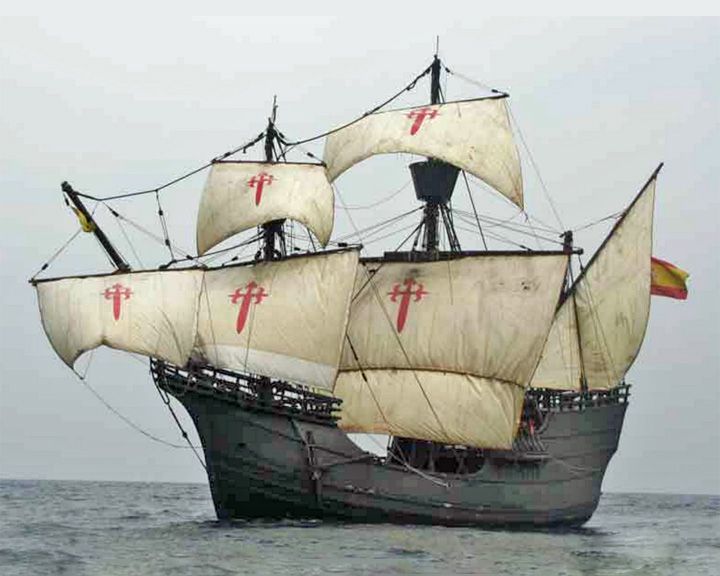 Victoria — Spanish carrack or nao First ship to circumnavigate the world — August, 1519 to September of 1522; a total of 42,000 miles. Captain Ferdinand Magellan was killed in the Phillipines; another four ships were lost along the way. LAUNCHED: 1518, about → FATE: 1522 or soon after. |
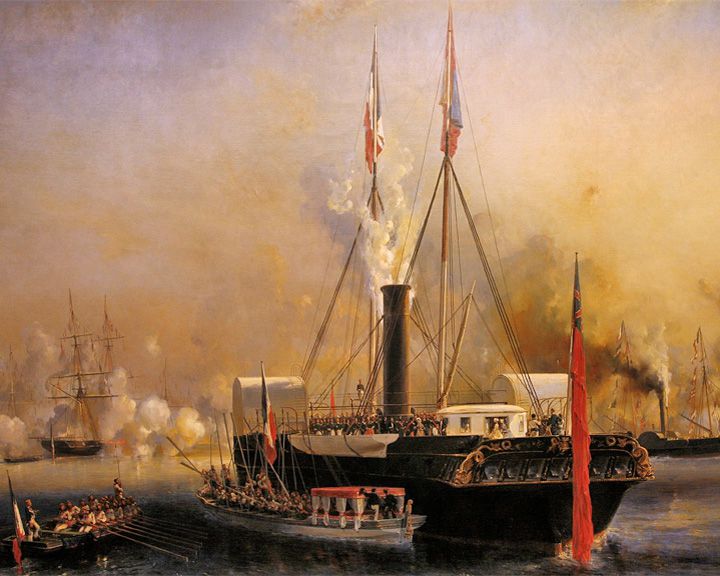 Victoria and Albert, HMY — British royal yacht; twin-paddle steamer First steam powered royal yacht built in Britain. The Queen and Prince Albert loved cruising around the coast of England. The yacht was renamed Osborne after the launch of HMY Victoria and Albert II January 16, 1855. LAUNCHED: 1843, April 25 → FATE: Scrapped, 1868. |
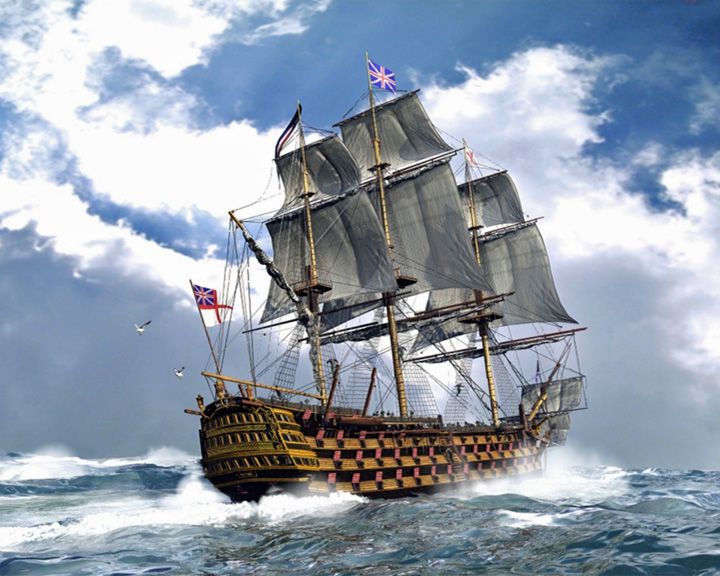 Victory, HMS — English first-rate ship of the line (Galleon) Lord Nelson's flagship at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805. She was refitted and repainted in 1800-1803, almost broken up in 1831, fitted up as a Naval School 1889, retired in 1904, and eventually restored. LAUNCHED: 1765, May 18 → FATE: Being restored at the HMNB, Portsmouth, England. |
 Ville de Nancy — American sloop of war Fictious ship in the movie Passageto Marseille, set during World War II and starring Humphrey Bogart. For the movie, Warner Bros. built a full-scale Merchant Marine ship modeled after the French ship Ville de Nancy. LAUNCHED: 1940 → FATE: Inconclusive. |
|
Page 6
|
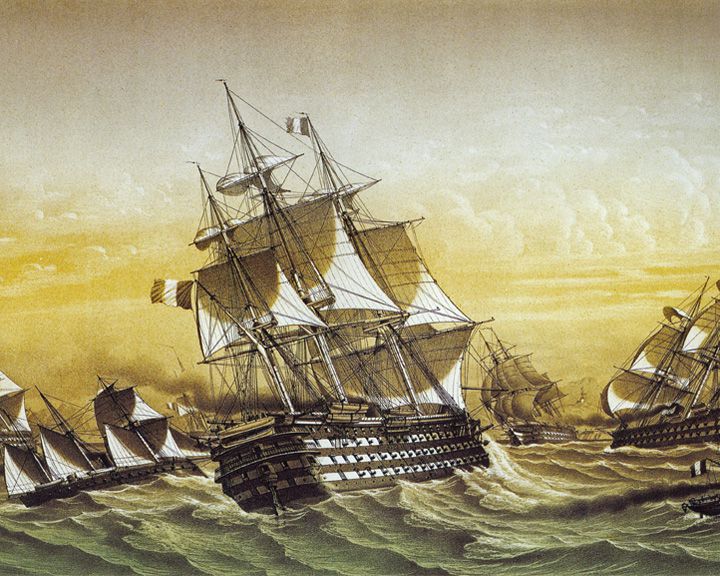 Ville de Paris — French ship of the line, large three-decker The flagship of the Comte de Grasse during the American Revolutionary War and the Siege of Yorktown. A ship of the line of the Royal Navy was named after her, HMS Ville de Paris, and launched in 1795. LAUNCHED: 1764 → FATE: Sank in September 1782 with other ships in a Central Atlantic hurricane. |
 Vincennes, USS — American sloop of war First U.S. ship to circumnavigate the globe. She was the flagship for the U.S. Exploring Expedition of 1838. LAUNCHED: 1826 → FATE: Sold in October of 1867 at Boston, Massachusetts; fate unknown. |
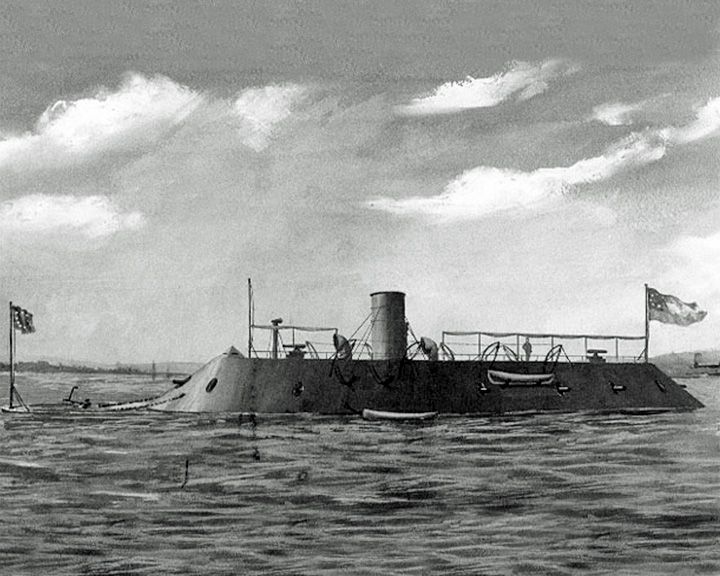 Virginia, CSS — Americant Confederat ironclad warship With USS Monitor, first naval battle between ironclad warships at the Battle of Hampton Roads. She was converted to an ironclad from a steam frigate. LAUNCHED: 1862, February → FATE: Destroyed by crew May 11, 1862. |
 (Another (Another Vital Spark — British Clyde puffer cargo ship Star of the book series and British TV comedy series, The Vital Spark about the adventures of the boat captain and his crew. The BBC Scotland TV program The Vital Spark (1959-1974 series) was set in the western isles of Scotland in the 1930s, based on the books by Neil Munro LAUNCHED: 1931, book published; 1959 for the start of TV series; boat built in 1943 → FATE: The boat is to be restored as a tourist attraction with the Inveraray Maritime Museum. |
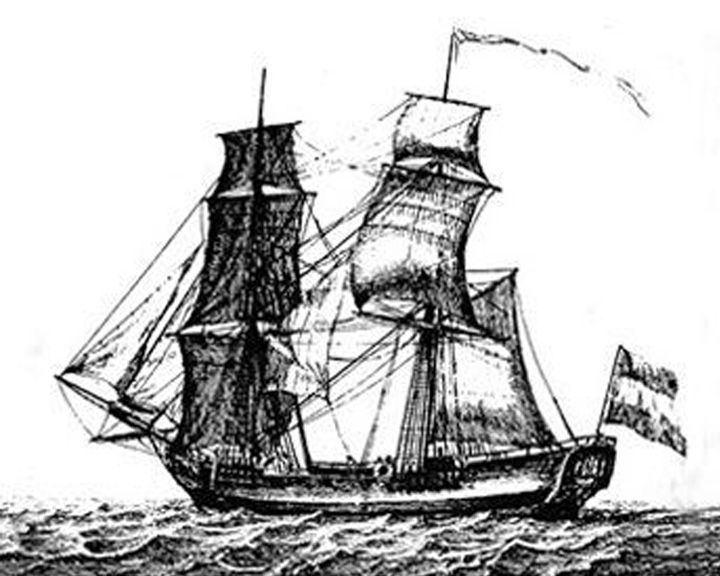 (Another (Another Vrouw Maria — Dutch merchant ship, wooden two-masted Treasure ship that went down with great artworks and jewelry for Catherine the Great. After its discovery in 1999, a Vrouw Maria Maritime Museum was established in Helsinki, Finland. LAUNCHED: 1770, circa → FATE: Sank October 3, 1771. |
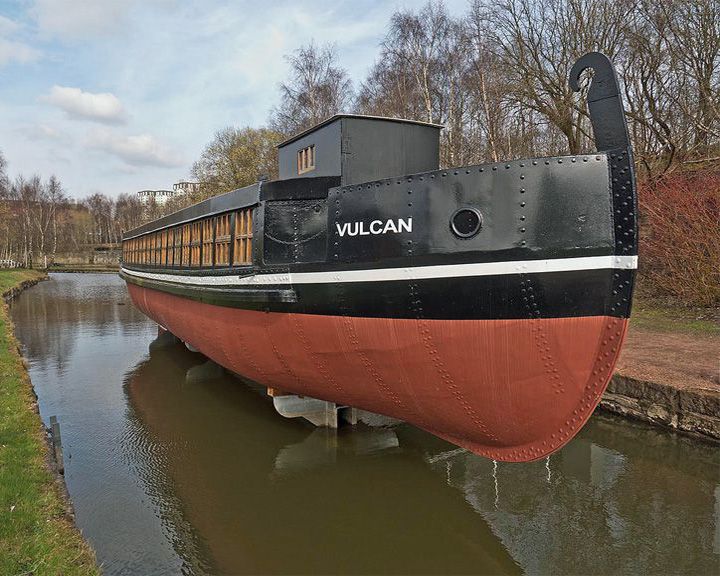 Vulcan — Scottish barge The original barge was the first all iron-hulled vessel to be built; the replica was the last Scottish vessel built using traditional riveting techniques. The iron canal boat named Trial, built by John Wilkinson in 1787, was not all iron. In 1988, a replica of the Vulcan was constructed. LAUNCHED: 1819, original ship; replica, 1985 → FATE: The original was sold for scrap 1873; the replica now sits decaying at Coatbridge, in North Lanarkshire, Scotland. |
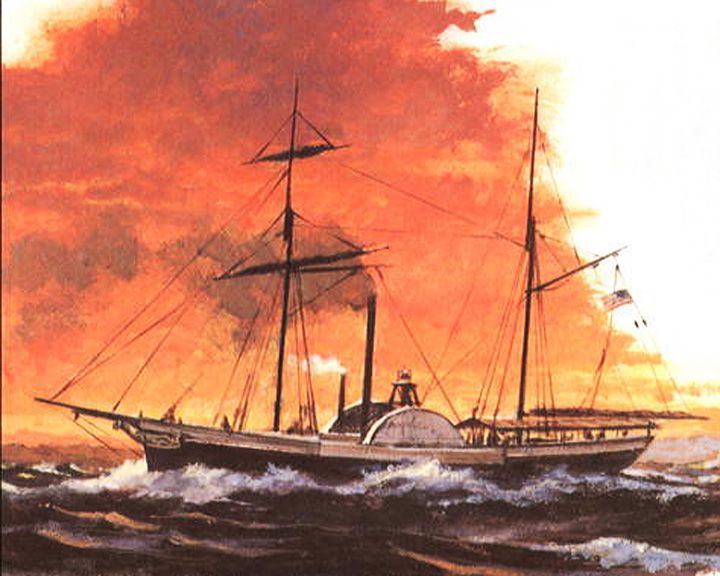 Walk-in-the-Water — American paddle steamboat, stern-wheeler with two masts First steamboat on Lake Erie and the eastern Great Lakes. Two large paddle boxes amidship housed her paddle wheels. LAUNCHED: 1818, August 23, first voyage → FATE: Grounded on the beach south of Buffalo, NY, October 31, 1821. |
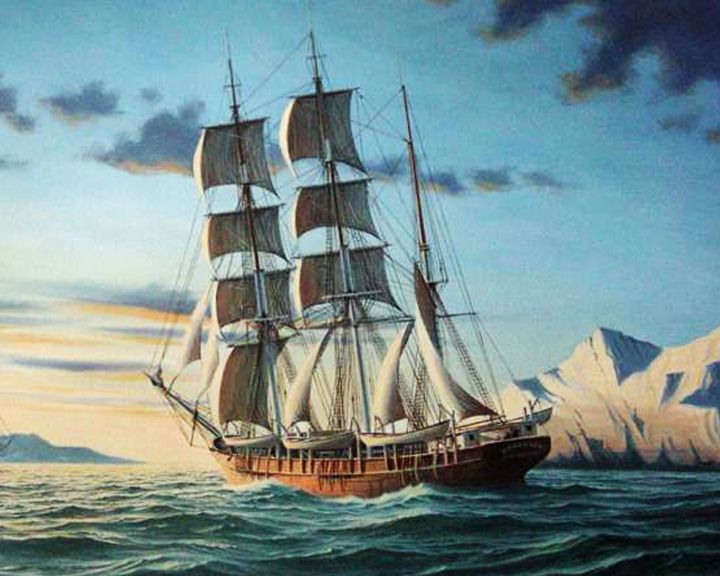 Wanderer — American whaling ship Last American whaling ship. The mast of the Wanderer stands as a flagpole in Boston Navy Yard, a few feet from where it was built. LAUNCHED: 1878 → FATE: Lost in a storm near Cuttyhunk Island, Massachusetts, on August 26, 1924. |
|
Page 7
|
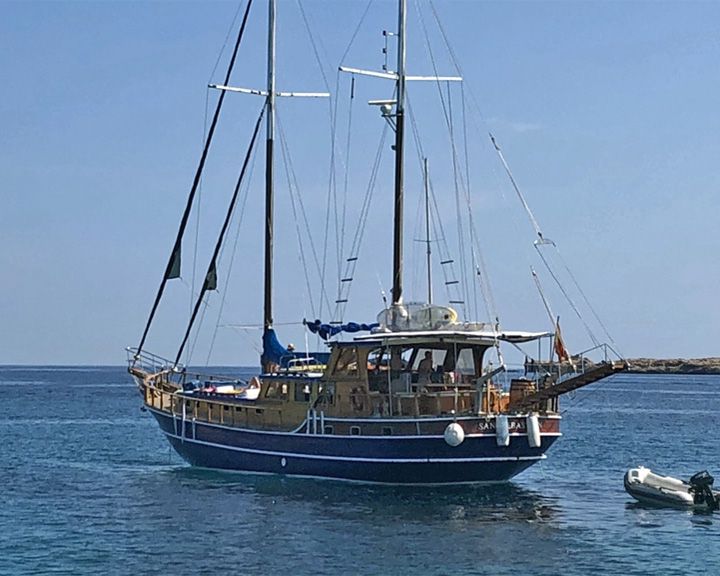 Wanderer — American yacht The boat in the 1992 comedy movie Captain Ron; starring Kurt Russell and Martin Short. The movie received mostly negative reviews. LAUNCHED: 1992 → FATE: Inconclusive. |
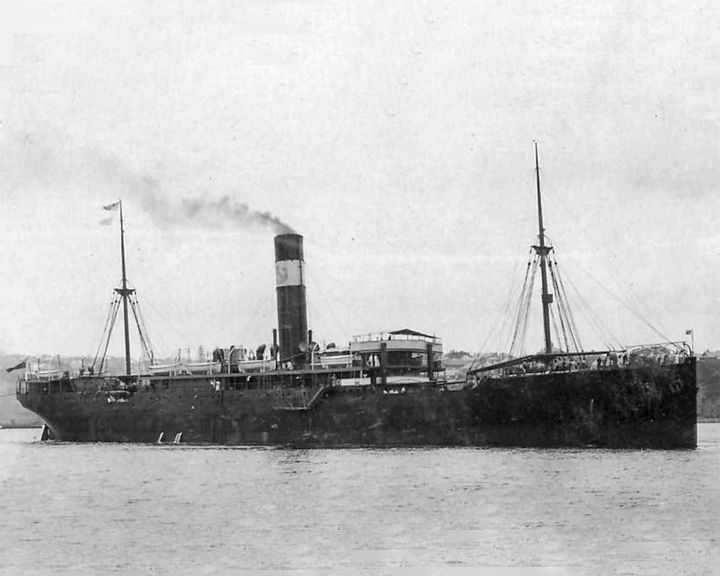 Waratah, SS — Australian steamship Known as the Australia's Titanic, she disappeared en route with 211 passengers and crew aboard. To this day, no trace of the ship has been found. LAUNCHED: 1908, October → FATE: Disappeared without trace south of Durban, July of 1909. |
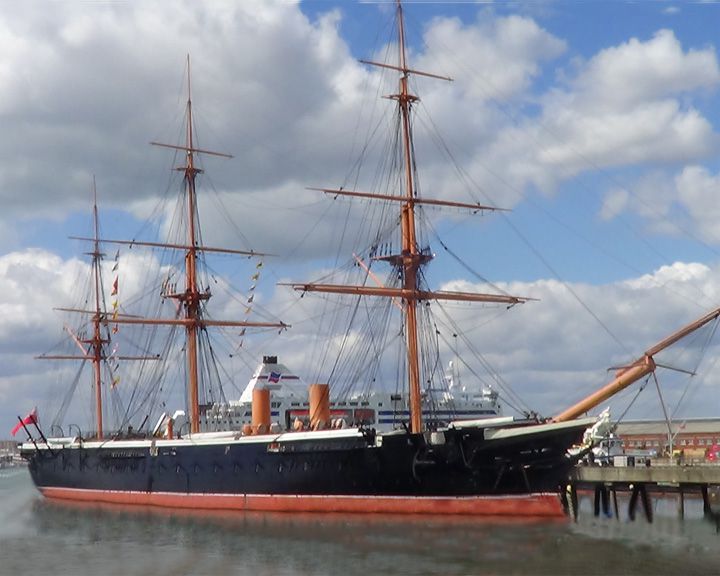 Warrior, HMS — British warship First British iron-hulled, armour-plated warship. She was the largest, fastest, most heavily armed and armored warship up to that time. LAUNCHED: 1860, December 18 → FATE: Currently berthed in Portsmouth, England as a museum. |
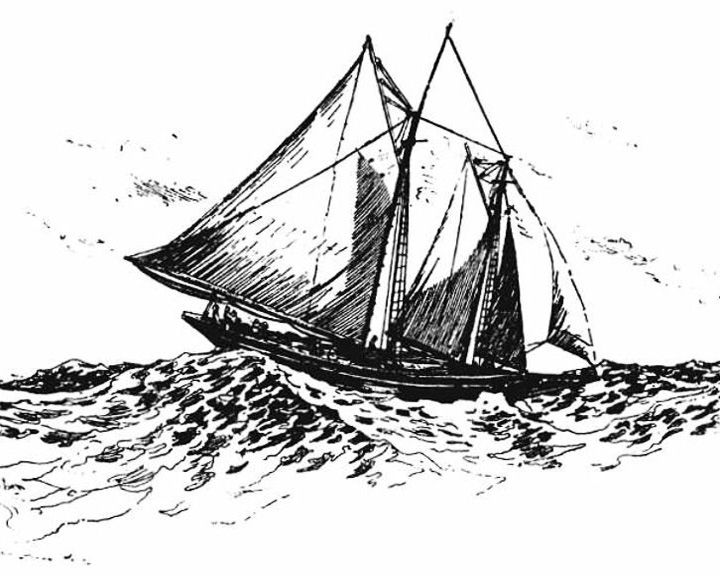 We're Here — American Schooner The fictional ship in the book and movie Captain Couraeous. Based on the 1897 book by Rudyard Kipling, it's a story of a boy and his adventures aboard a the ship. LAUNCHED: 1937 → FATE: Inconclusive. |
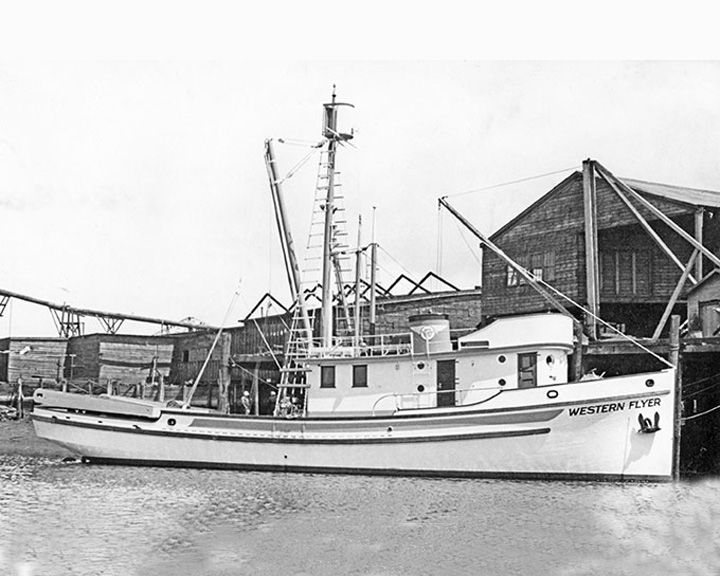 (Another (Another Western Flyer — American fishing boat Known for its use by John Steinbeck and Ed Ricketts in their 1940 expedition to the Gulf of California.. After Steinbeck's voyage, the ship was returned to commercial fishing, harvesting sardines, perch, and crab. Twice in 2012 the boat sprang leaks and sank and refloated each time. LAUNCHED: 1937, July 3 → FATE: Being restored to its historic glory by the Port Townsend Shipwrights Co-Op. |
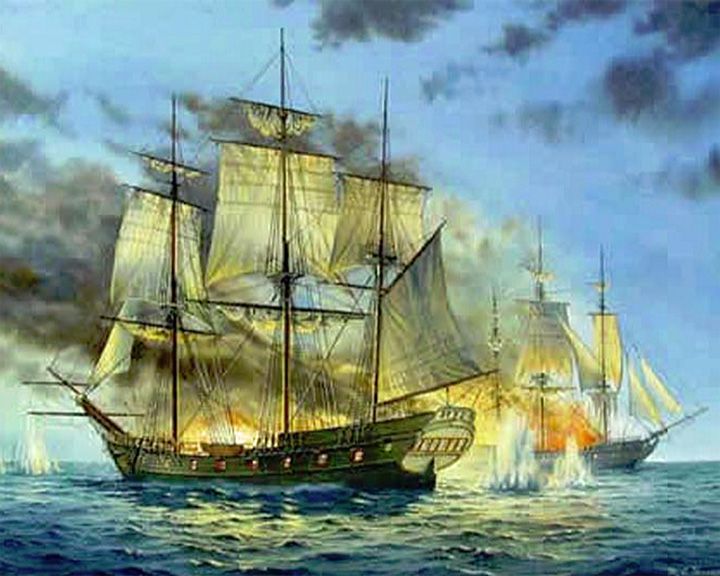 Whydah Gally — British sailing ship, square rigged three-masted Flagship of the pirate "Black Sam" Bellamy. The wreck was found in 1984. Artifacts from the wreck are on display at The Whydah Pirate Museum in Provincetown, Massachusetts. LAUNCHED: 1715 → FATE: Sank in a violent storm April 26, 1717. |
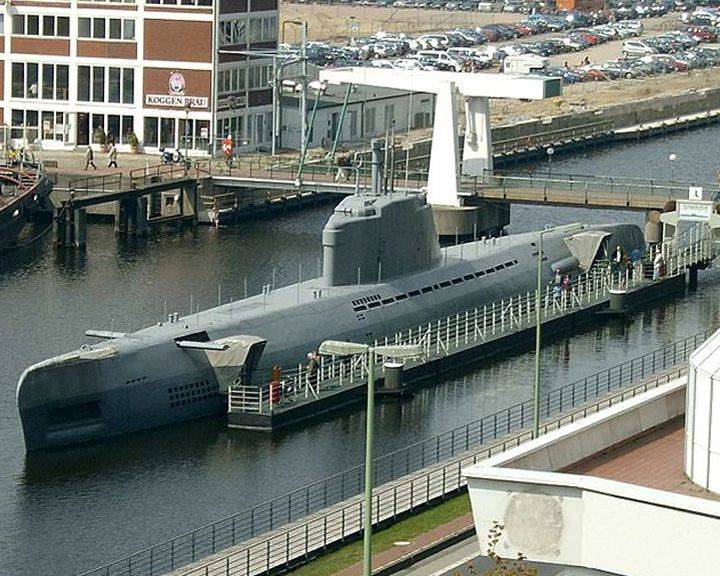 Wilhelm Bauer — German submarine, Type XXI One of several captured World War II Type XXI U-boats designed to operate primarily submerged. She is the only floating example of a this type of U-boat. LAUNCHED: 1945, January → FATE: Scuttled May 4, 1945; raised, June 1957; museum ship as of April 1984 at Bremerhaven, Germany. |
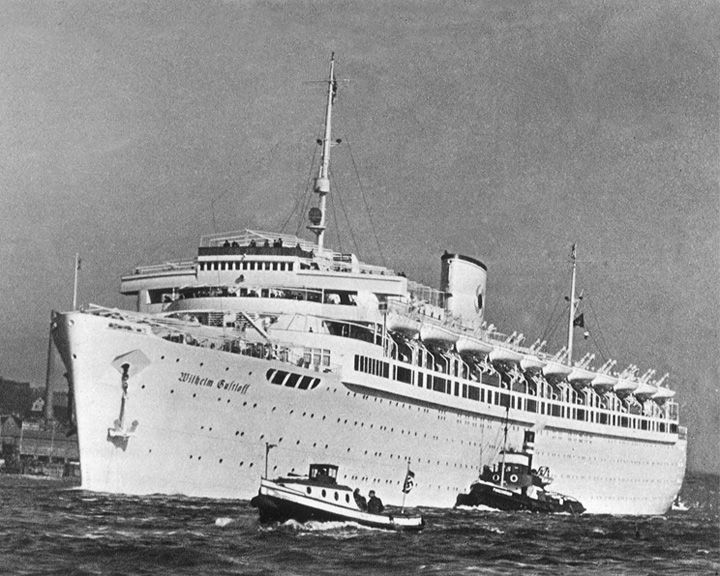 Wilhelm Gustloff, MV — German purpose-built cruise ship used as a hospital ship and troop ship in World War II Greatest ship disaster in recorded maritime history with an estimated 9,400 people were killed in the sinking. It was sunk by a Soviet submarine while participating in the evacuation of civilians, military personnel, and Nazi officials who were surrounded by the Red Army in East Prussia. LAUNCHED: 1937, May → FATE: Torpedoed in the Baltic Sea January 30, 1945. |
|
Page 8
|
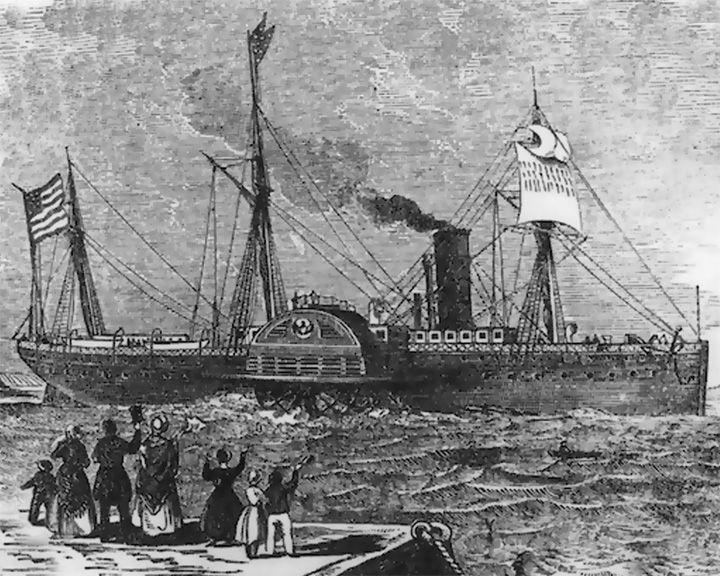 Winfield Scott, SS — American paddle steamer A sidewheel steamer that transported passengers and cargo between San Francisco and Panama in the early 1850s, during the California Gold Rush. She has been the object of numerous salvage operations since the crash and currently rests underwater as part of the Channel Islands National Park. LAUNCHED: 1850, October 5 → FATE: During a foggy night, crashed on Anacapa Island December 2, 1853. |
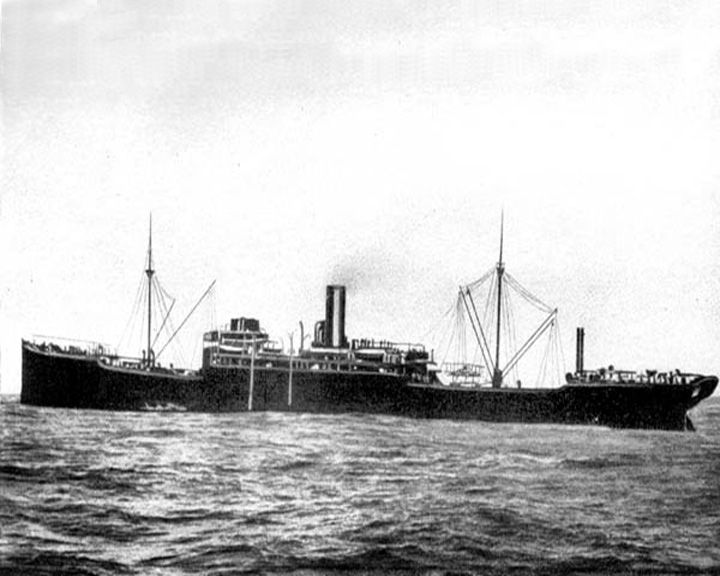 Wolf, SMS — German merchant raider Armed merchant raider of the German Navy in World War I and World War II. Not a fast ship, Wolf's advantage was deception, such as changing her appearance with fake funnels and masts, and false sides which kept her weapons hidden. LAUNCHED: 1913, March 18 → FATE: Out of service February, 1918; scrapped in 1931. |
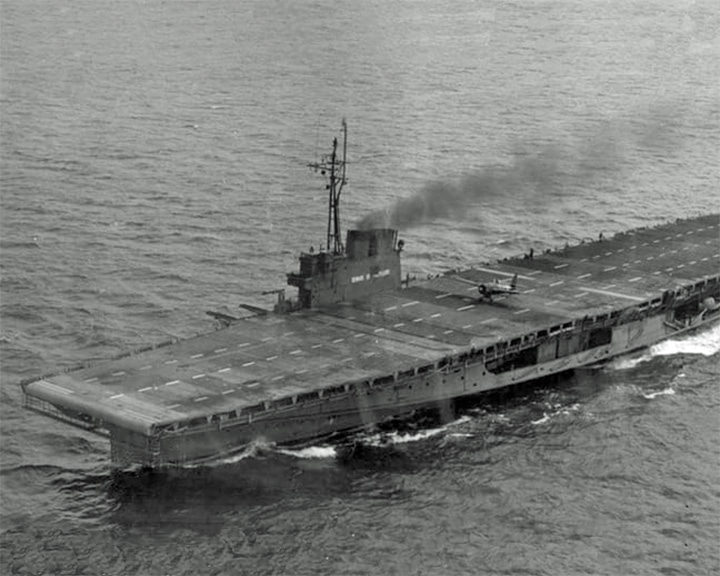 Wolverine, USS (originally Seeandbee) — American training ship Converted from a luxury side-wheel steamer cruise ship into a freshwater aircraft carrier serving in Lake Michigan for the advanced training of naval aviators in carrier take-offs and landings. As the Seeandbee, launched in 1912, she was the largest side-wheel steamer in the world at the time. LAUNCHED: 1942, August 12 → FATE: Sold for scrap December, 1947. |
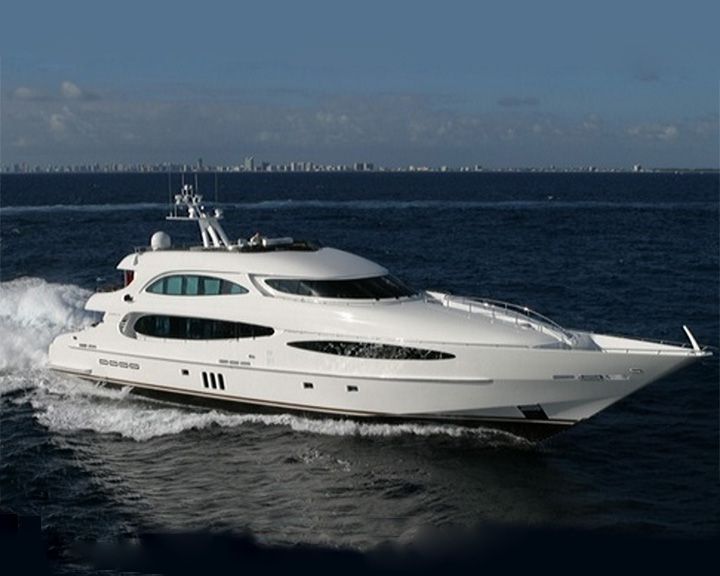 World is not Enough — American super yacht Fastest yacht in the world. She cruises at 50 knots and can reach speeds of up to 70 knots. LAUNCHED: 2005 → FATE: Still in use. |
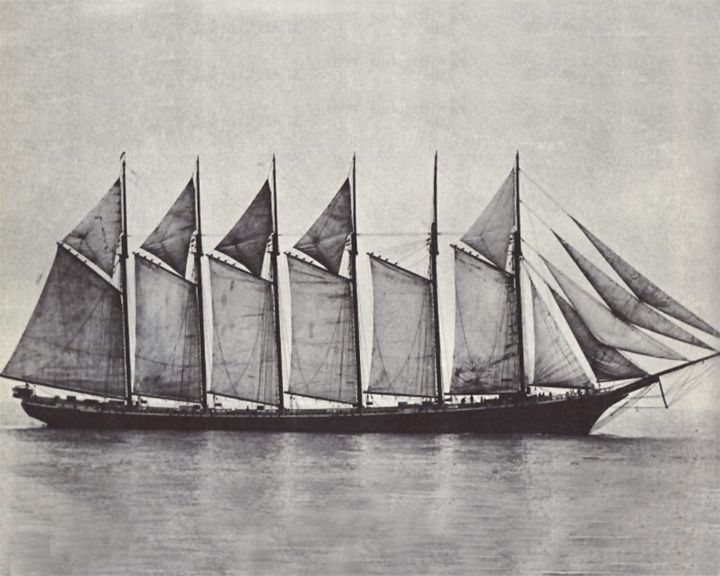 Wyoming — American six-masted schooner The largest known wooden ship ever built. Because of her length she tended to flex in heavy seas causing the long planks to twist and buckle, allowing water to seep into the hold. LAUNCHED: 1909, December 15 → FATE: Foundered in a storm in 1924 and sank off the coast of Cape Cod with the loss of all 14 crewmen. |
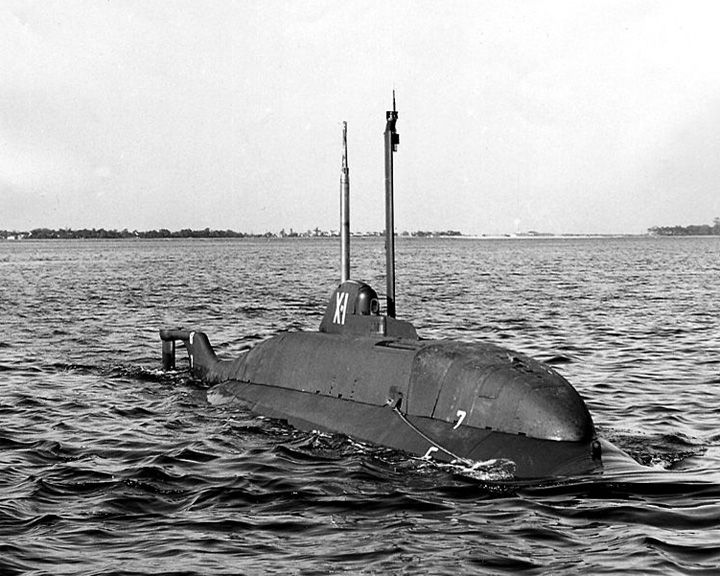 X-craft submarine — American miniature submarine Deployed September, 1943 against German warships based in Norway. These midget subs would be towed to their target area by a full-size submarine. Of the 20 built, seven were lost, 12 scuttled or scrapped. LAUNCHED: 1943 → FATE: Only one has survive and is on display at the Royal Navy Submarine Museum. |
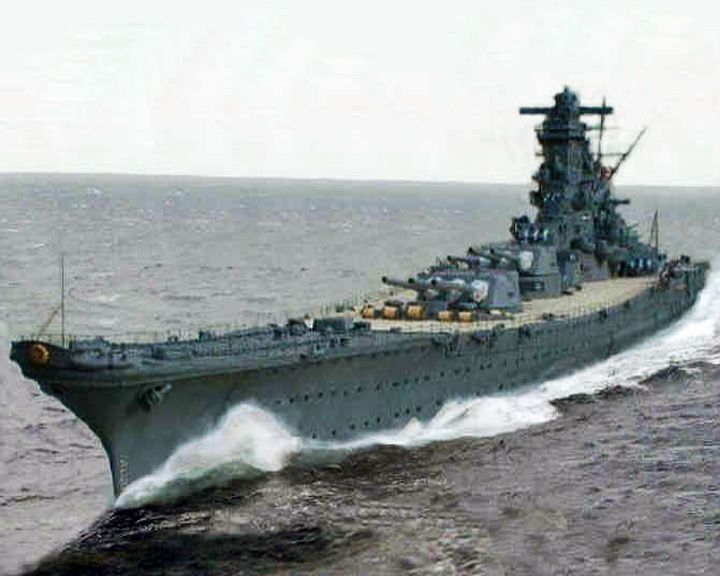 Yamato — Japanese battleship The largest, heaviest, and most powerful battleships ever constructed. She was the flagship of Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto during World War II. LAUNCHED: 1940, August 18 → FATE: Sunk north of Okinawa April 7, 1945. |
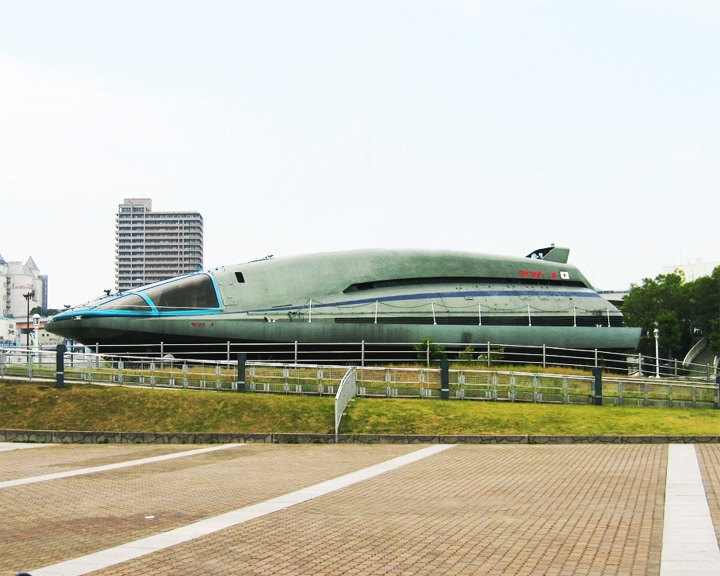 Yamato 1 — Japanese experimental ship She used magnetohydrodynamic drive s (MHDDs) driven by liquid helium-cooled superconductors . The ship, which had no moving parts, was successfully operated in Kobe harbor in June 1992. LAUNCHED: 1991 → FATE: She was on display at the Kobe Maritime Museum but was demolished in 2016. |
|
Page 9
|
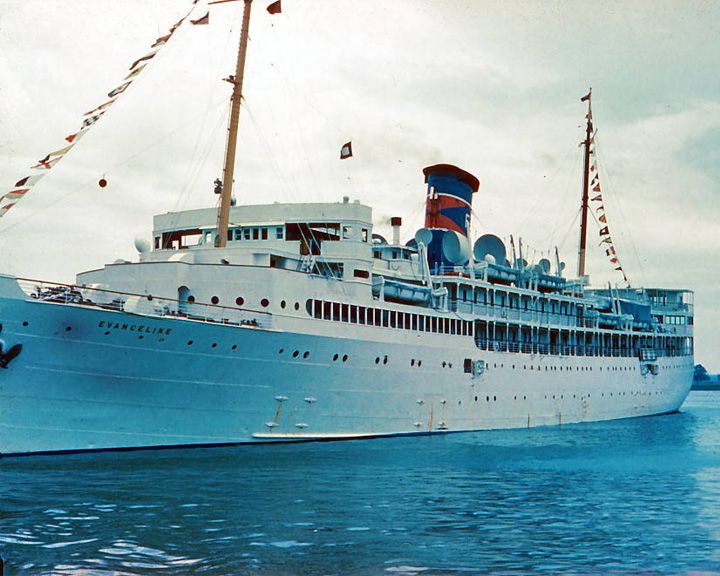 Yarmouth Castle, SS — American cruise ship Fire left 90 of 552 on board died. Her loss lead to the Safety of Life at Sea law. During World War II, she served as a troop ship and hospital ship in the Pacific. LAUNCHED: 1927 → FATE: Sunk in a blaze on the way to Nassau November 13, 1965. |
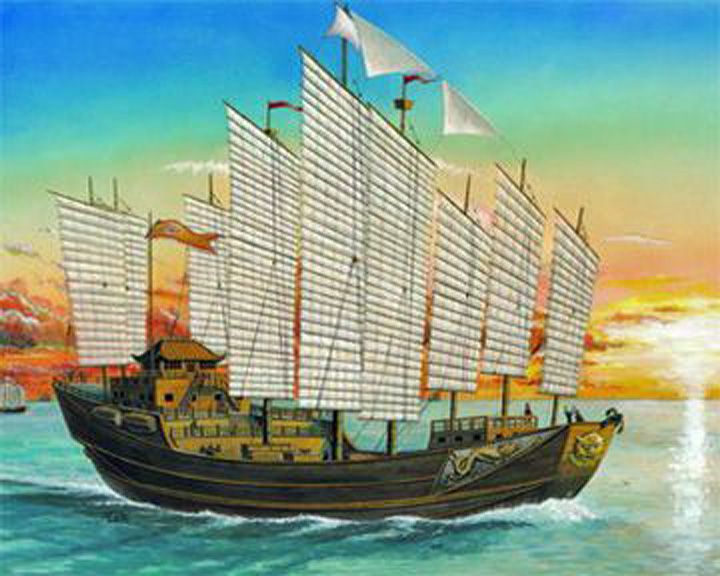 (Another (Another Zheng He's fleet — Chinese treasure ship The fleet's voyages came before most of the famous European voyages of discovery. Zheng He's seven expeditions were designed to establish a Chinese presence in the Indian Ocean and control trade. The ships dwarfed European ships of that century. LAUNCHED: 1405, first voyage → FATE: Last voyage, 1430. |
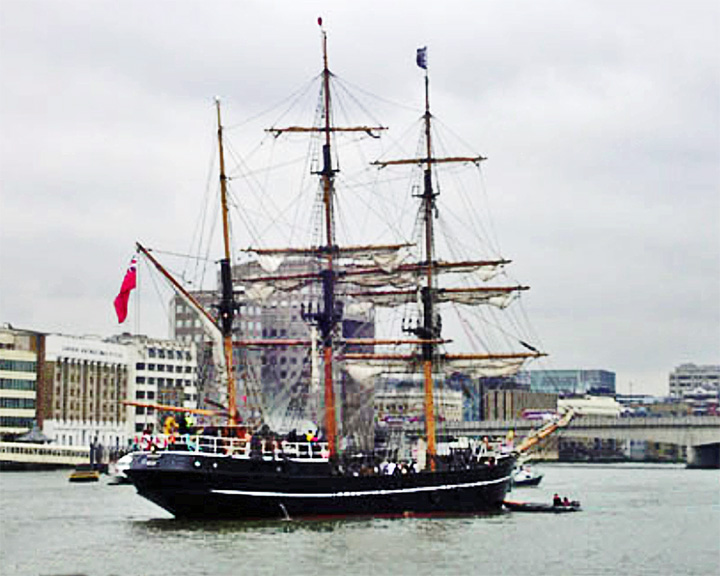 Zong — British square rigger slave ship Infamous for the 1781 massacre of 132 sick and dying slaves thrown overboard so the ship's owners could collect on their cargo insurance. The Zong had been a Dutch vessel the Zorgue seized by the British in 1781 off West Africa, along with 244 Africans on board. LAUNCHED: 1776, or ealier → FATE: Unknown. |
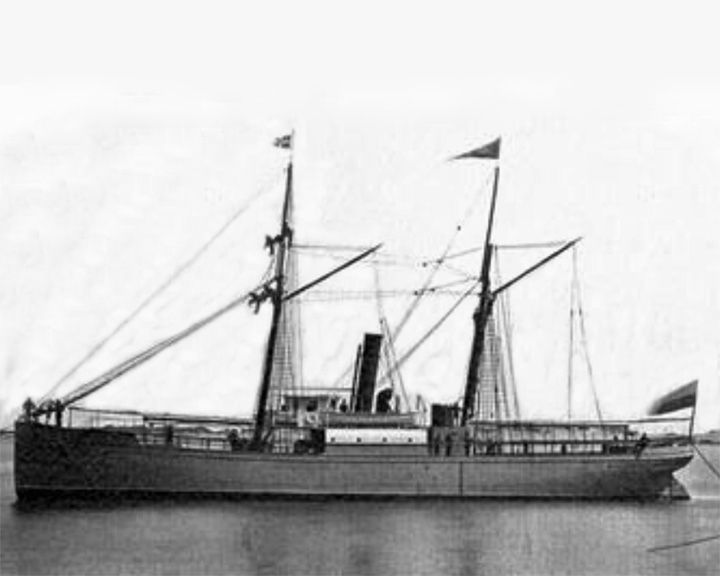 Zoroaster — Swedish oil tanker The first successful oil tanker, carrying the kerosene cargo in two iron tanks in her hull instead of many separate wooden casks. She was built by Ludwig Nobel, brother of Alfred who created The Nobel Prize. LAUNCHED: 1878 → FATE: Unknown. |
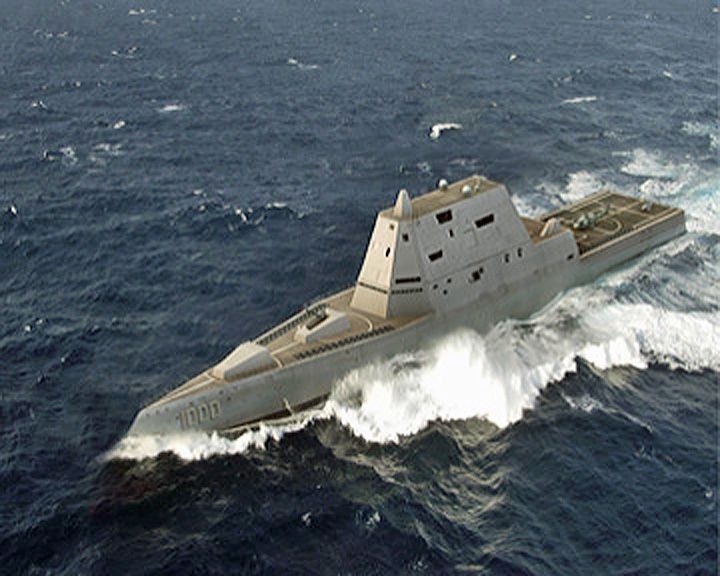 Zumwalt, USS — American guided missile destroyer Designed with stealth capabilities, having a radar cross-section akin to a fishing boat. Commanding officer is Captain James A. Kirk, coincidentially the same as the Star Trek captain. LAUNCHED: 2013, October → FATE: Currently at sea. |
The number of All Countries Ships and Boats T‑Z listed is 68 The contents of this page are available under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license and the GNU Free Documentation License (GFDL). |
|
|
First Ship on each page
| |
| Page | Ship Name (Country and Type) |
| 1. | Tang, USS (American Balao class submarine) |
| 2. | Thermopylae (English extreme clipper) |
| 3. | Trieste (Italian deep-diving research bathyscaphe) |
| 4. | Umbria, RMS (British ocean liner) |
| 5. | Vanguard, HMS (1909) (British St. Vincent class Dreadnaught) |
| 6. | Ville de Paris (French ship of the line) |
| 7. | Wanderer (American yacht) |
| 8. | Winfield Scott, SS (American paddle steamer) |
| 9. | Yarmouth Castle, SS (American cruise ship) |
All Countries | |
| 1. | Tang, USS American Balao class submarine |
| 2. | Tek Sin Chinese ocean-going junk |
| 3. | Terra Nova British wooden-hulled barque |
| 4. | Texas, USS American New York class battleship |
| 5. | The World, MS Swedish cruise ship |
| 6. | Theodore Too Canadian tug boat |
| 7. | Thermopylae English extreme clipper |
| 8. | Thomas W. Lawson American seven-masted schooner |
| 9. | Thresher, USS American nuclear submarine |
| 10. | Tigerfish, USS American attack submarine |
| 11. | Titanic, RMS British luxury ocean liner |
| 12. | Tonquin American merchant ship |
| 13. | Toya Maru Japanese train ferry |
| 14. | Trent, RMS British paddle steamer |
| 15. | Trieste Italian deep-diving research bathyscaphe |
| 16. | Trincomalee, HMS British Leda-class frigate |
| 17. | Turbinia British steamship |
| 18. | U-234 German submarine |
| 19. | U-480 German experimental Kriegsmarine Type VIIC submarine |
| 20. | U-505 German submarine |
| 21. | U-96 German German Type VIIC submarine |
| 22. | U-995 German submarine |
| 23. | Umbria, RMS British ocean liner |
| 24. | Unicorn British three-masted sailing ship |
| 25. | United States, SS American ocean liner |
| 26. | Upholder, HMS British U-class submarine |
| 27. | Valbanera, SS Scotish, then Spanish passenger steamship |
| 28. | Valencia, SS American passenger steamboat |
| 29. | Vandenberg, USAFS American transport ship |
| 30. | Vanguard, HMS English ship of the line |
| 31. | Vanguard, HMS (1909) British St. Vincent class Dreadnaught |
| 32. | Vasa Swedish wooden warship |
| 33. | Venturer, HMS British V-class submarine |
| 34. | Vestris, SS British passenger steamship |
| 35. | Victoria Spanish carrack or nao |
| 36. | Victoria and Albert, HMY British royal yacht |
| 37. | Victory, HMS English first-rate |
| 38. | Ville de Nancy American sloop of war |
| 39. | Ville de Paris French ship of the line |
| 40. | Vincennes, USS American sloop of war |
| 41. | Virginia, CSS Americant Confederat ironclad warship |
| 42. | Vital Spark British Clyde puffer |
| 43. | Vrouw Maria Dutch merchant ship |
| 44. | Vulcan Scottish barge |
| 45. | Walk-in-the-Water American paddle steamboat |
| 46. | Wanderer American whaling ship |
| 47. | Wanderer American yacht |
| 48. | Waratah, SS Australian steamship |
| 49. | Warrior, HMS British warship |
| 50. | We're Here American Schooner |
| 51. | Western Flyer American fishing boat |
| 52. | Whydah Gally British sailing ship |
| 53. | Wilhelm Bauer German submarine |
| 54. | Wilhelm Gustloff, MV German purpose-built cruise ship |
| 55. | Winfield Scott, SS American paddle steamer |
| 56. | Wolf, SMS German merchant raider |
| 57. | Wolverine, USS American training ship |
| 58. | World is not Enough American super yacht |
| 59. | Wyoming American six-masted schooner |
| 60. | X-craft submarine American miniature submarine |
| 61. | Yamato Japanese battleship |
| 62. | Yamato 1 Japanese experimental ship |
| 63. | Yarmouth Castle, SS American cruise ship |
| 64. | Zheng He's fleet Chinese treasure ship |
| 65. | Zong British square rigger |
| 66. | Zoroaster Swedish oil tanker |
| 67. | Zumwalt, USS American guided missile destroyer |
|
About the Data There are more than 400 ships in this database, but the initial list is only for famous ships names that begin with letters "A-B". For other listings, use the country and type tabs. Touching (or cursor over) a ship image produces an enlargement. Touch anywhere else (or move the cursor off the image) to close the larger image. Touching (or clicking on) any underlined name will link to a page with more information. Although submarines are usually called boats, they are grouped with ships here. Most of the information comes from Wikipedia. |
^
Other Pages in Names Galore: | |
Famous Cowboy Names Sports Team Names Other Name Lists | Name Generators Naming Fun Stories about Names |