|
|
All Countries Ships; Largest and Fastest
|
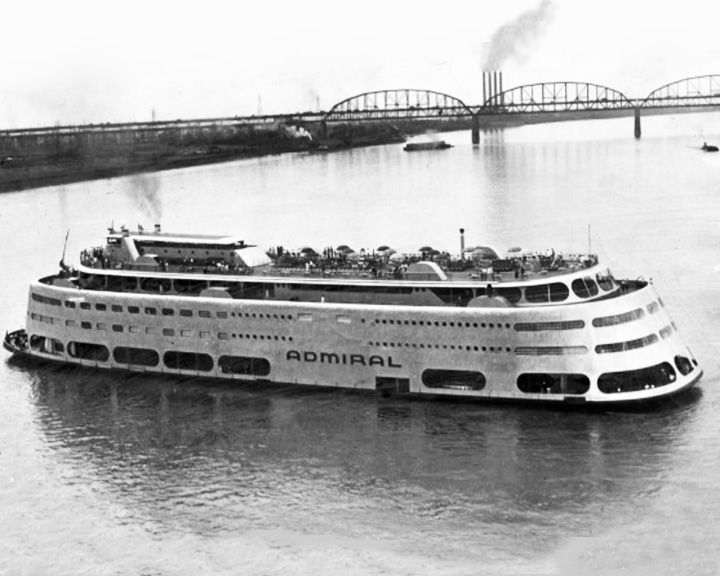 (Another (Another Admiral, SS — American river steamboat (cruise ship; converted to diesel in 1974) Was the largest river cruise ship in the world, sailing the Mississippi River from St. Louis. In 1979 she was converted to a land-based casino. She started out as the side-wheeled steel hulled steamboat, the Albatross, then became the Admiral in the 1940s. LAUNCHED: 1907 → FATE: Dismantled and sold for scrap in 2011. |
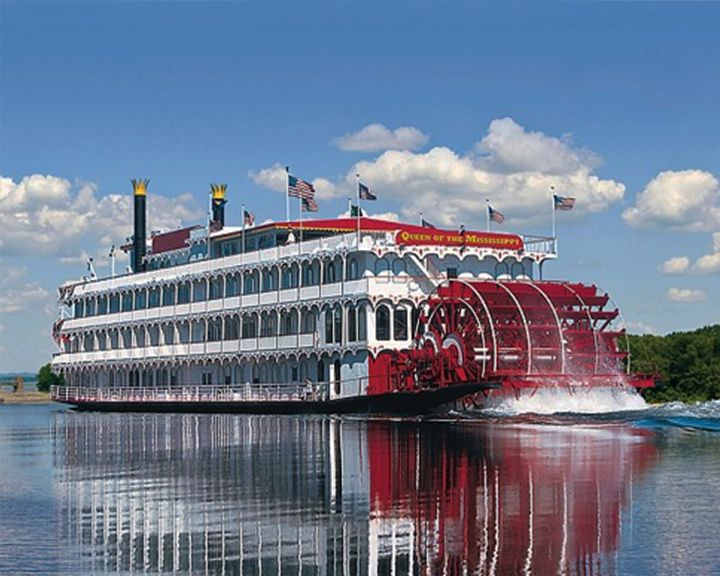 American Queen — American river paddle steamboat; stern-wheeler Largest steamboat ever built, as of 2012. In 2012 she participated for the first time in the Great Steamboat Race and came in second. LAUNCHED: 1995 → FATE: Still in operation on the Mississippi River. |
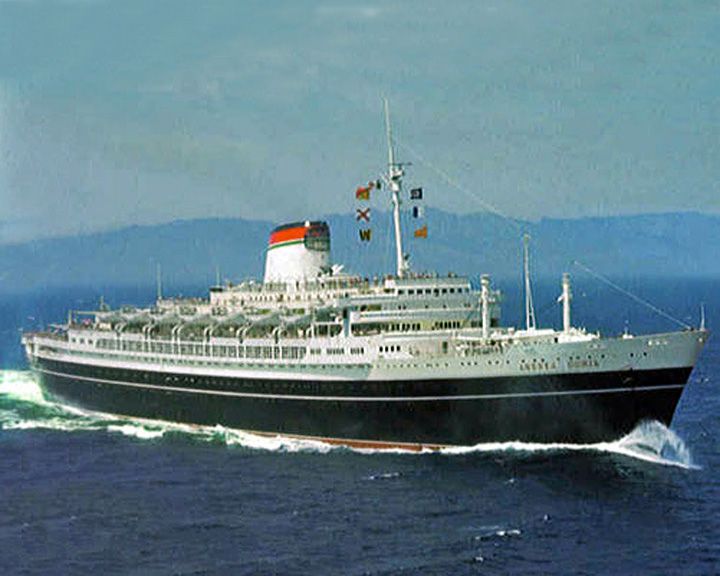 (Another (Another Andrea Doria, SS — Italian ocean liner Collided with the MS Stockholm in the Atlantic and sank; 52 people died. Of all Italy's ships at the time, she was the largest, fastest and supposedly safest. She was the last major transatlantic passenger ship to sink. LAUNCHED: 1953, January 18 → FATE: Sank July 26, 1956. |
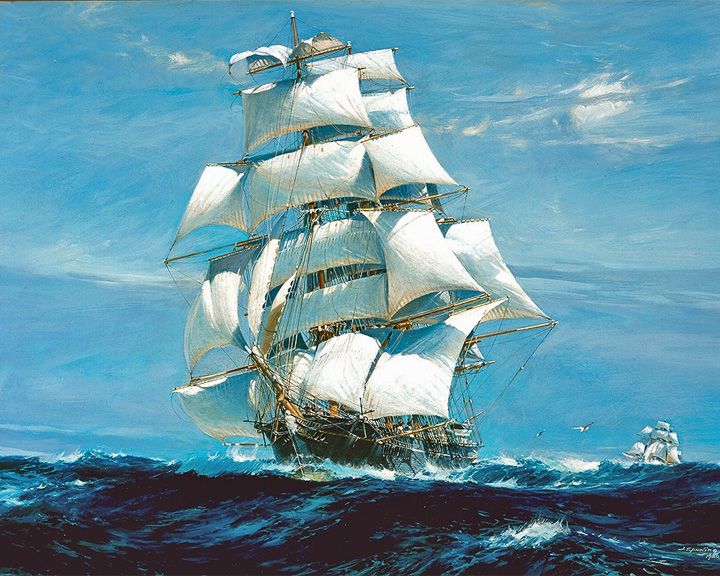 Ariel — English clipper ship Famous for almost winning The Great Tea Race of 1866, an unofficial race between Fuzhou, China and London. On September 6, 1866, the Taeping docked twenty minutes ahead of Ariel. LAUNCHED: 1865 → FATE: Went missing in early 1872. |
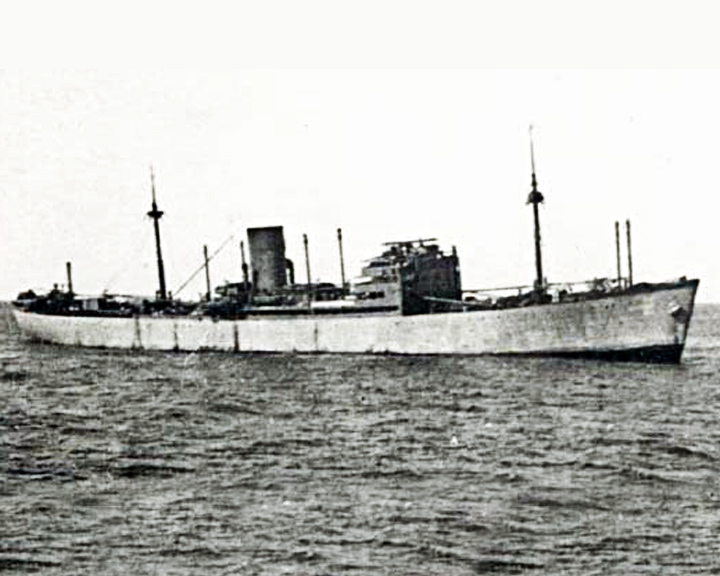 Atlantis — German auxillary cruiser or commerce raider She had the longest raiding career of any German commerce raider in either world war and was second only to Pinguin in tonnage destroyed. She began her career as the cargo ship Goldenfels. In late 1939 she was requisitioned by the Kriegsmarine and converted into a warship. LAUNCHED: 1937, Converted in 1939 → FATE: Sunk by a British ship November 22, 1941. |
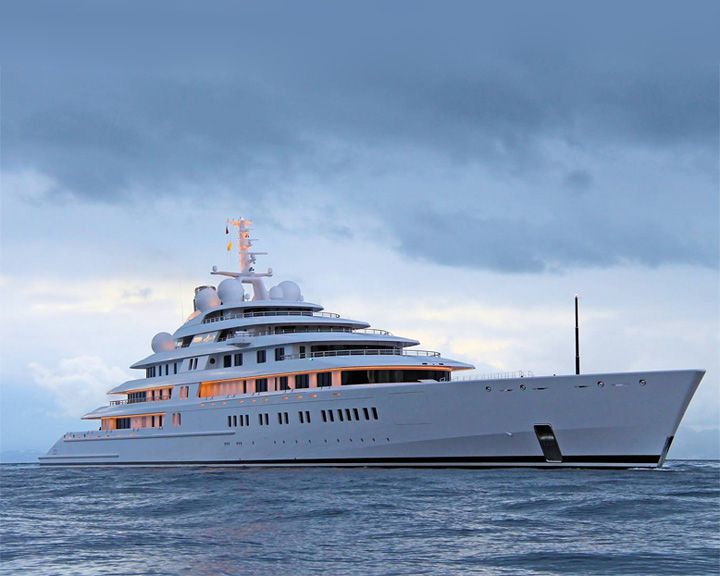 (Another (Another Azzam — Emirati luxury yacht, 180 meters (590 ft) in length; German built As of 2019, the world's largest private yacht with extravagant features and accommodations. At an estimated cost of US $605,000,000, she has a top speed of over 32 knots and carries a submarine and a missile defense system. LAUNCHED: 2013, April 18 → FATE: At sea, but not for charter. |
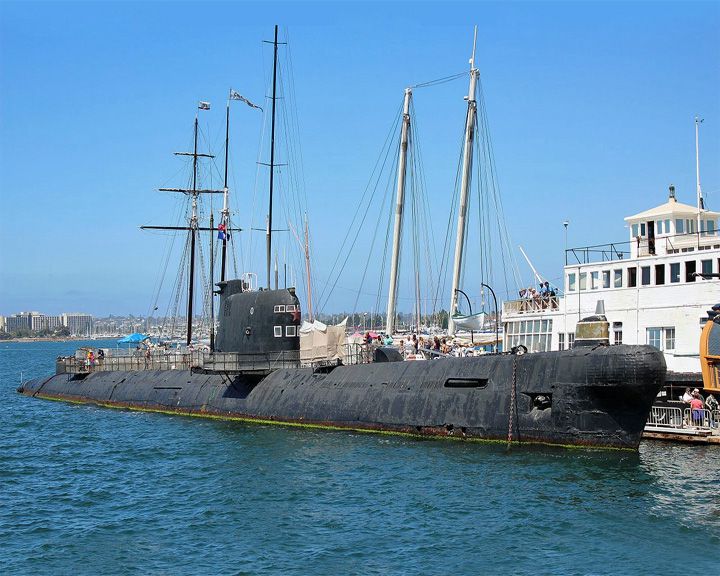 B-39 — Russian foxtrot-class submarine The Soviet Navy's largest non-nuclear submarines.. In 2012, she was used as a prop in the movie Phantom. Another B-39 is rusting in England (see Black Widow). LAUNCHED: 1967, April 18 → FATE: Decommissioned April 1994; now a museum ship at the Maritime Museum of San Diego, California. |


|
Page 2
|
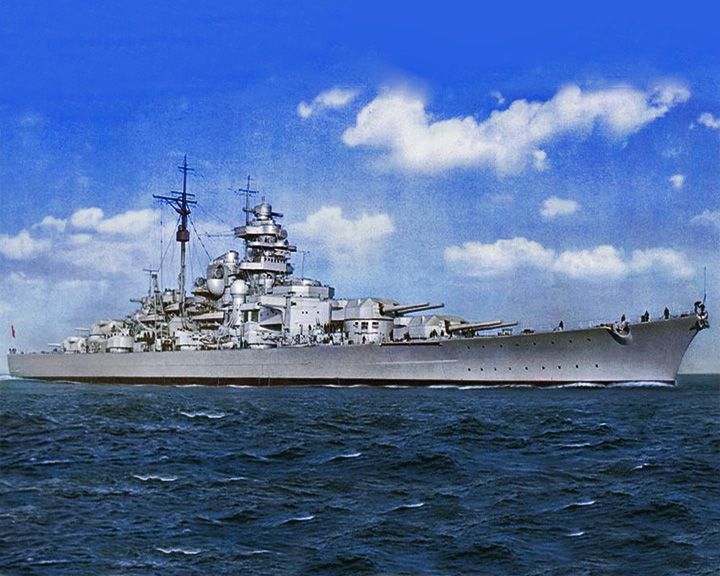 (Another (Another Bismarck — German battleship At the Battle of Denmark Straits, May, 1941, she sunk the British battlecruiser HMS Hood. Relentlessly pursued and sunk by the Royal Navy following Winston Churchill's order "Sink the Bismarck". She and her sister ship Tirpitz were the largest battleships ever built by any European country. LAUNCHED: 1939, February 18 → FATE: Sunk by British forces on May 27, 1941 in the North Atlantic. |
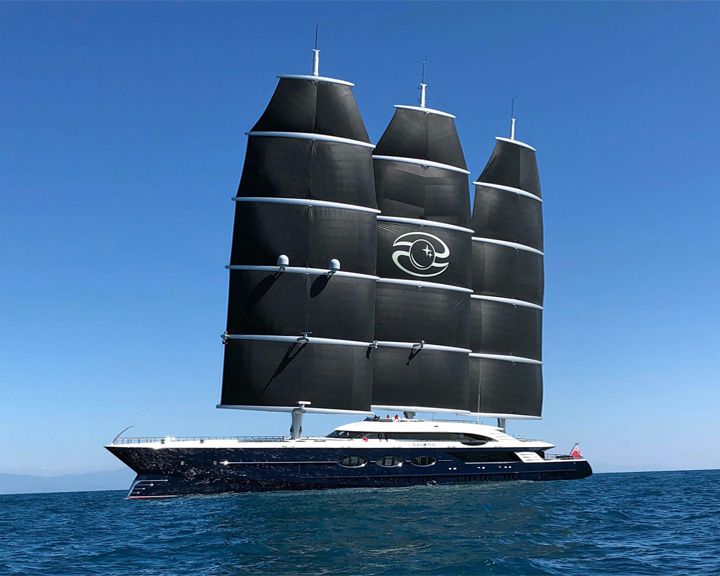 Black Pearl — American yacht The world's largest sailing yacht capable of running carbon free. Her sails consist of freestanding rotating masts with rigid yards that acts as square rigs. She can accommodate 12 passengers and features an on-deck Jacuzzi, swimming platform, and a tender garage. LAUNCHED: 2016 → FATE: In service. |
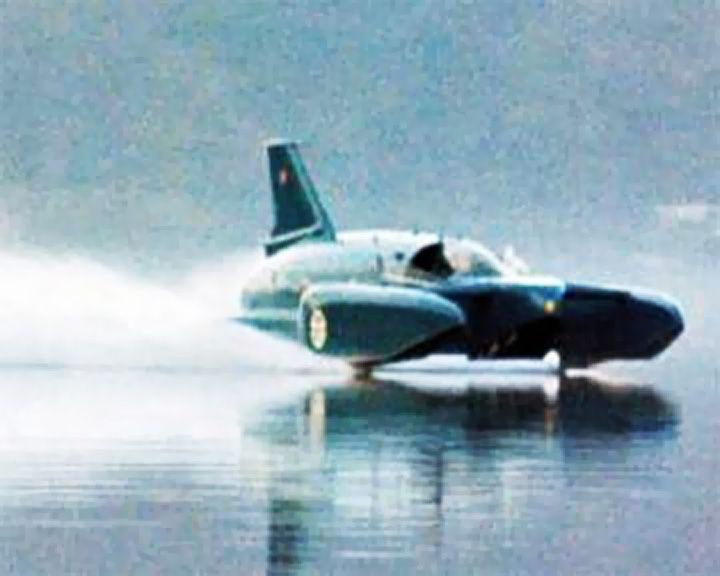 (Another (Another Bluebird K7 — British hydroplane, jet powered Set seven world water speed records between 1955-1964, reaching 276.3 mph or 444.7 km/h. She was developed and piloted by Donald Campbell. LAUNCHED: 1955 → FATE: Flipped and disintegrated at high speed on Coniston Water January 4, 1967, killing Donald Campbell. |
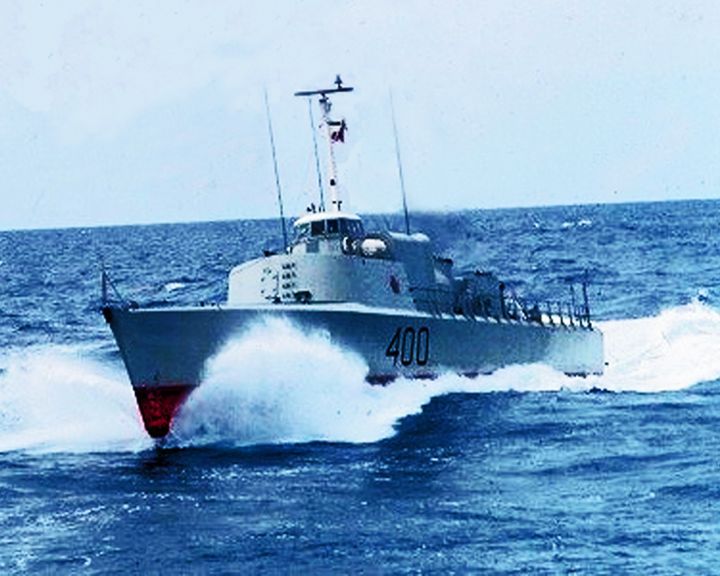 Bras d'Or, HMCS — Canadian hydrofoil The fastest unarmed warship in the world exceeding 63 knots (72 mph). As a project for the testing of anti-submarine warfare technology on an ocean-going hydrofoil, she was never fitted with equipment for warfare. LAUNCHED: 1968, July 12 → FATE: On display at the Musée Maritime du Québec. |
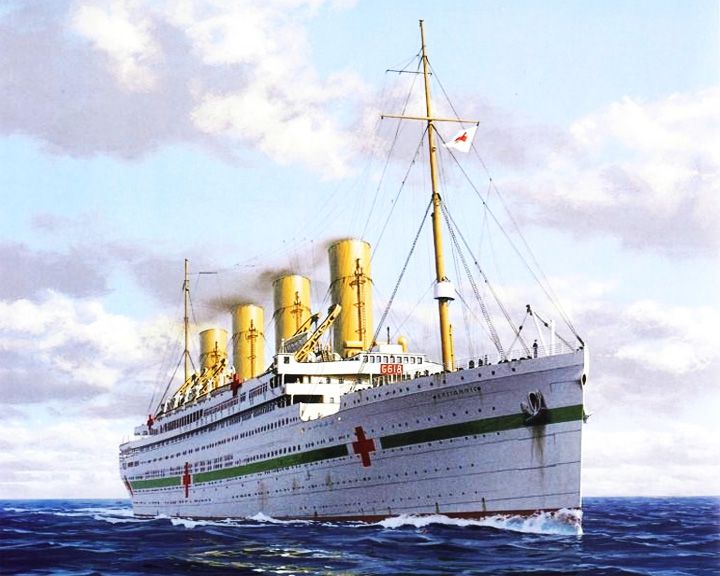 (Another (Another Britannic, HMHS — British ocean liner Largest ship lost during the World War I with the loss of 30 lives. Launched just before the start of the World War I, she was put to use as a hospital ship in 1915. With her loss, SS Bismarck was given to the White Star Line as part of post-war reparations. LAUNCHED: 1914, February 18 → FATE: Struck a mine and sank off the Greek island of Kea November 21, 1916. |
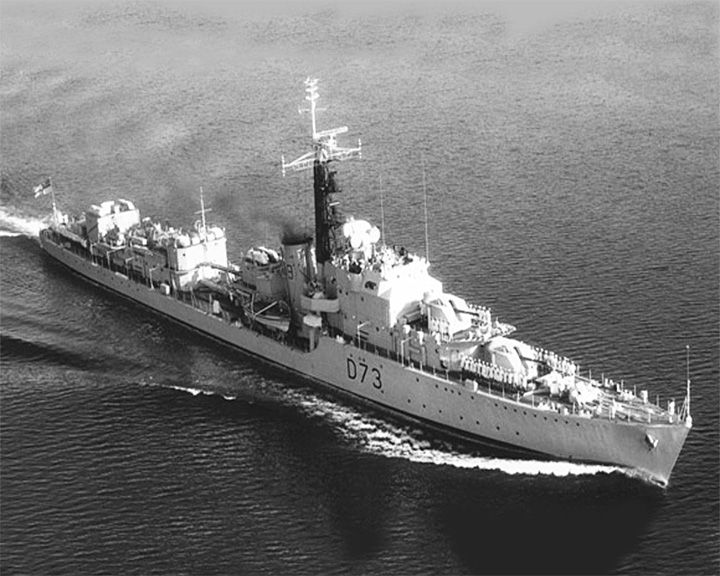 Cavalier, HMS — British C-class Destroyer Because of her high speed, she escorted the RMS Queen Mary and RMS Queen Elizabeth carrying troops across the Atlantic Ocean. In the summer of 2009 the Chatham Historic Dockyard Trust made available accommodation on board the ship for youth groups who wish to stay on board and experience life on board a Royal Naval Destroyer. LAUNCHED: 1944, April 18 → FATE: Preserved as a museum ship since 1998, now at the Chatham Historic Dockyard |
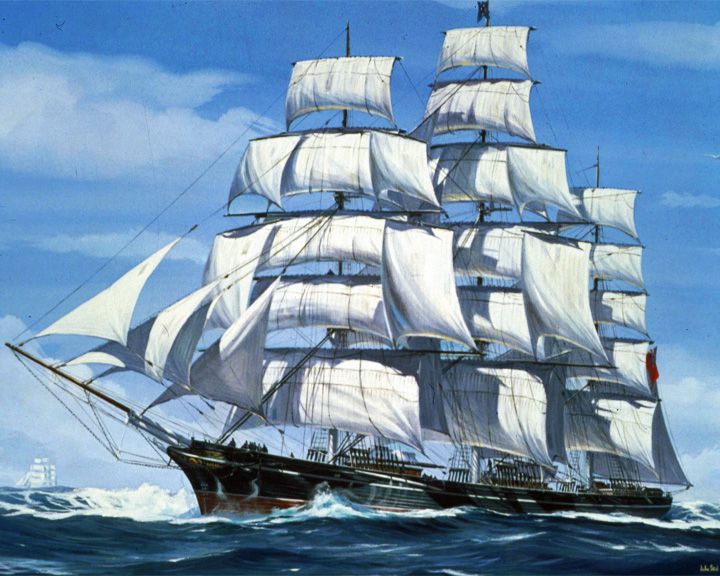 Champion of the Seas — English clipper ship On her maiden voyage, she set a record for the fastest run in 24 hours of 465 nautical miles or 861 km. She was the passenger ship built for the run from Liverpool, England to Melbourne, Australia. LAUNCHED: 1854, April 18 → FATE: Abandoned off Cape Horn in leaking condition in 1877. |
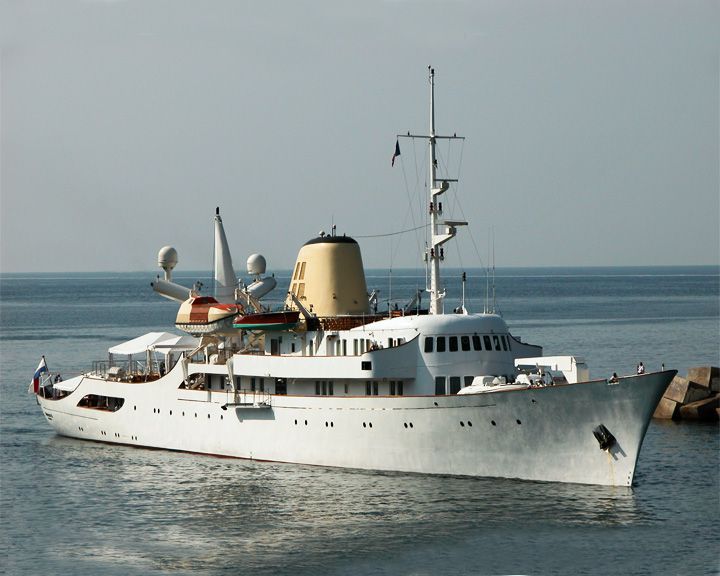 (Another (Another Christina O — Greek luxury yacht Famous yacht of Ari Onassis and his wife, former first lady, Jackie Kennedy. Originally a Canadian built anti-submarine River-class frigate, after WWII, she was purchased by Onassis, refitted as one the largest yachts in the world, and hosted many famous personalities. LAUNCHED: 1943, July 18 → FATE: Available for charter cruises from many ports. |
|
Page 3
|
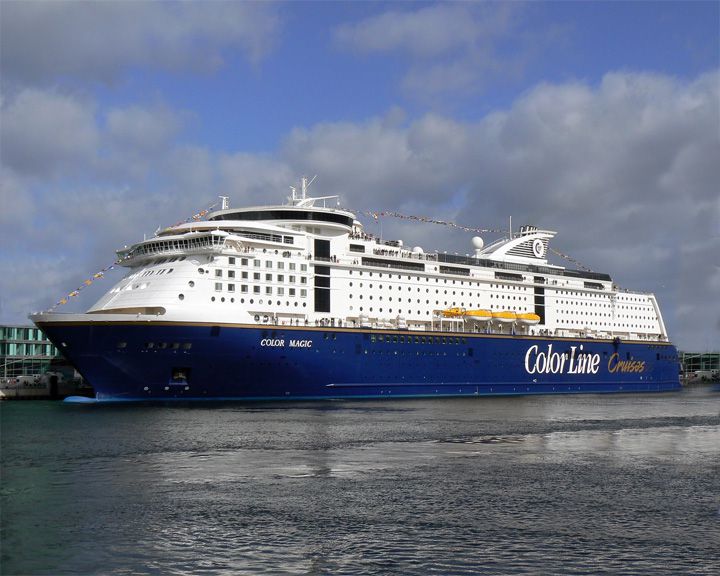 Color Magic — Norwegian cruise ferry The largest cruise ferry in the world. The ship operates between Oslo, Norway and Kiel, Germany. LAUNCHED: 2006, December 18 → FATE: Still in service. |
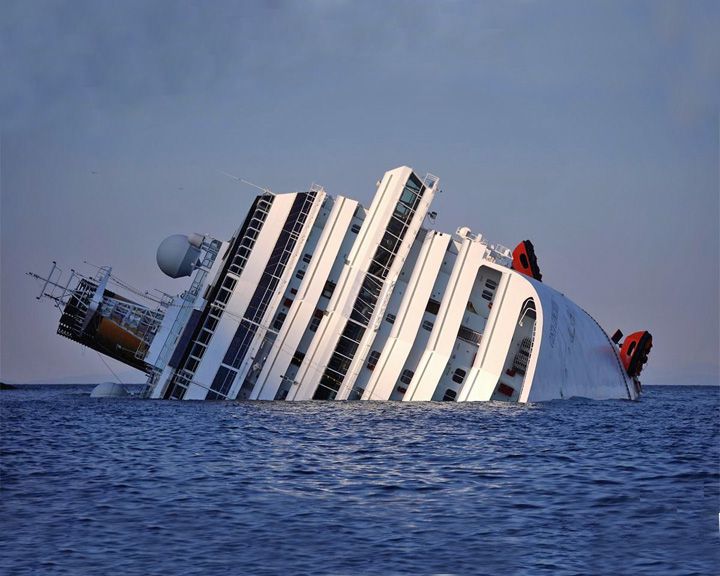 (Another (Another Costa Concordia — Italian cruise ship Largest cruise ship disaster; ran aground on a reef off Isola del Giglio and capsized; 32 people dead. In 2008, she suffered damage to her bow when high winds pushed the ship alongside its dock. LAUNCHED: 2005, September 18 → FATE: Capsized January 13, 2012. |
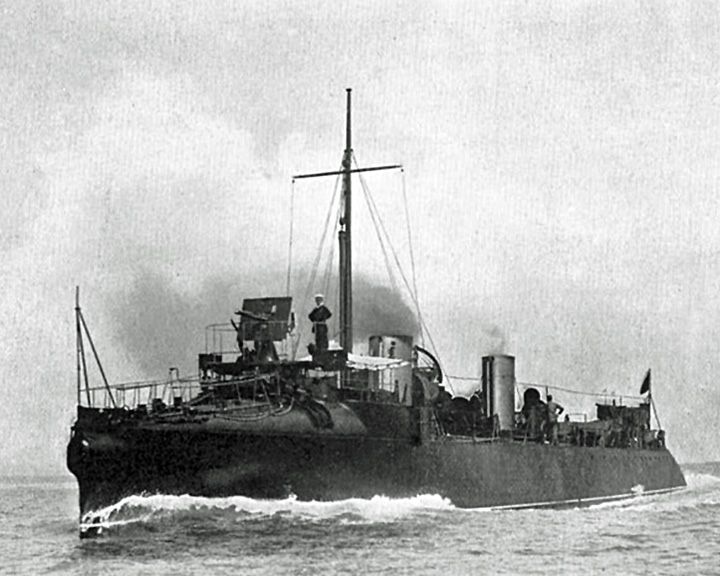 Darling, HMS — British torpedo boat destroyer First destroyer-type ship. Created to defend against torpedo boats. She was described at the time as the "fastest boat ever" having achieved a speed over 28 knots. LAUNCHED: 1893, November 18 → FATE: Scrapped in 1912. |
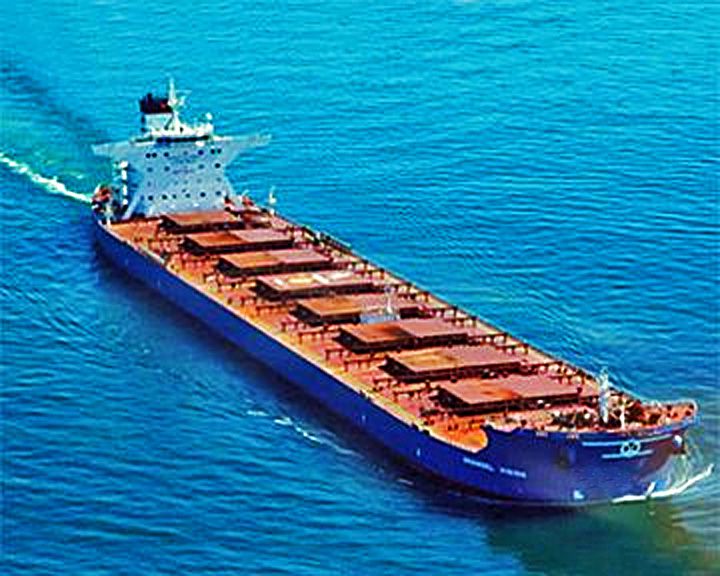 Derbyshire, MV — British cargo ship, oil-ore Largest British ship ever to have been lost at sea. All 42 crew members and two wives were lost with the ship during Typhoon Orchid in 1980. LAUNCHED: 1976, June → FATE: Sank south of Japan September 9, 1980. |
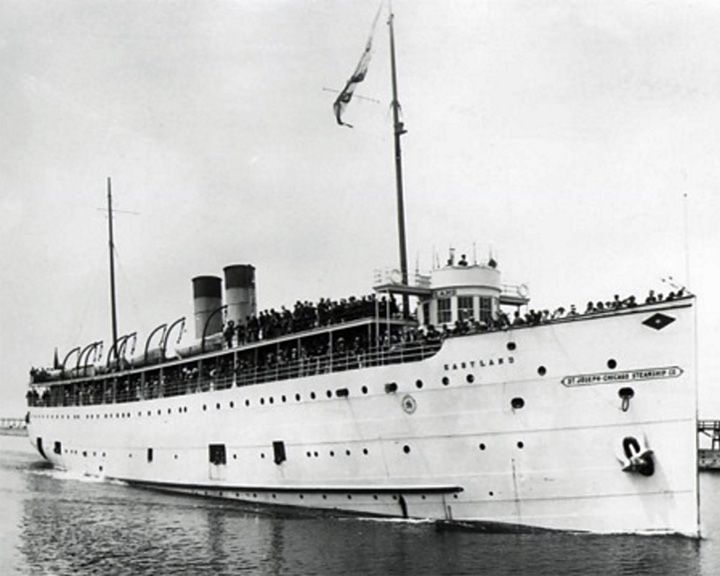 (Another (Another Eastland, SS — American steamship, passenger Largest loss of life from a single shipwreck on the Great Lakes. On the morning of July 24, 1915, the ship, being top-heavy, rolled over while docked in the Chicago River, killing 844 passengers and crew. LAUNCHED: 1903, May 18 → FATE: Sunk on July 24, 1915; raised, converted to a gunboat, renamed USS Wilmette February, 1918; sold for scrap in October of 1946. |
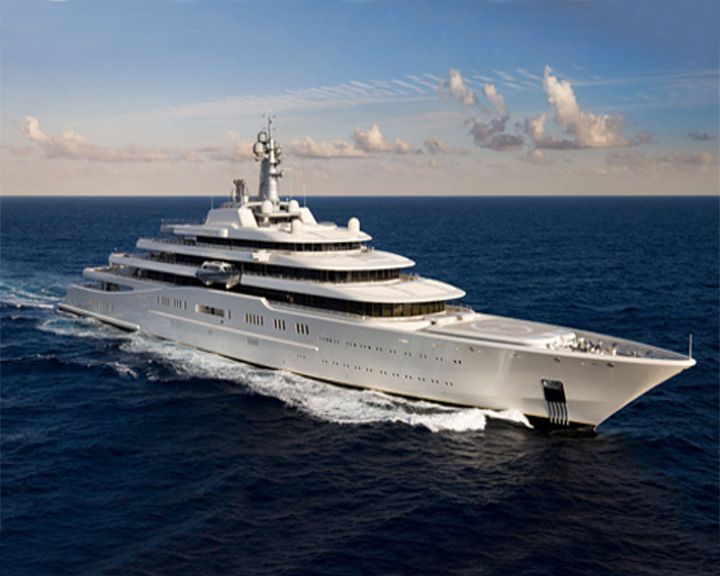 Eclipse — Russian luxury yacht, (German built) One of the largest private motor yacht at 162.5 meters (533 feet), costing over a billion dollars. She has two helicopter pads, 24 guest cabins, two swimming pools, and several hot tubs, and is also equipped with three launch boats and a mini-submarine. LAUNCHED: 2009, June 18 → FATE: Still in use. |
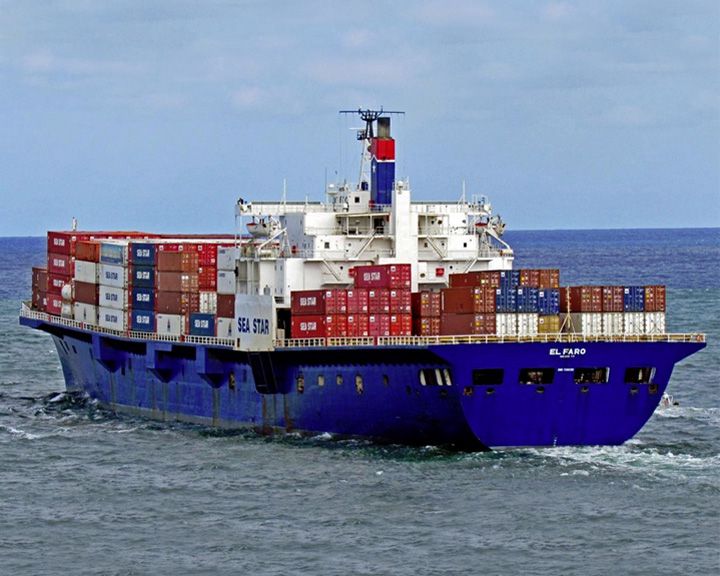 El Faro, SS — American container ship (cargo ship) The worst maritime disaster for a U.S.-flagged vessel in decades, resulting in the deaths of 33 crew. In 2003, prior to the invasion of Iraq in Operation Iraqi Freedom, the vessel, then named Northern Lights, ferried U.S. Marines and supplies from California to Kuwait. LAUNCHED: 1974, November 18 → FATE: Lost at sea with all hands on October 1, 2015 after losing propulsion near the eyewall of Hurricane Joaquin. |
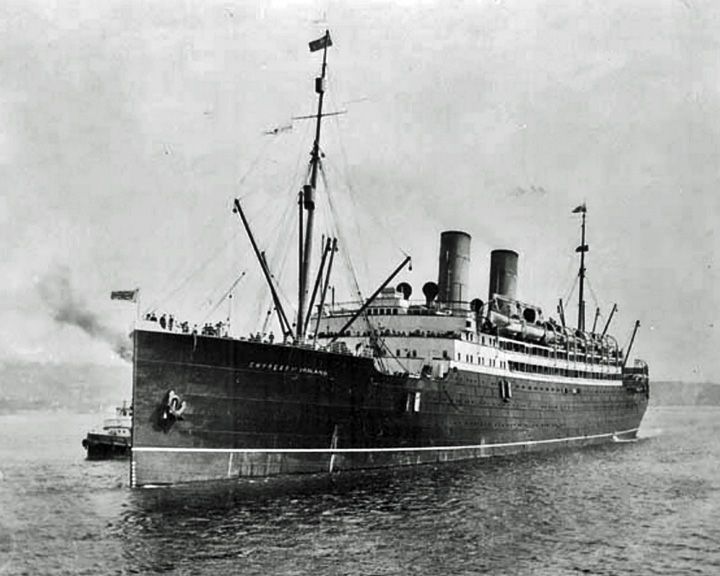 (Another (Another Empress of Ireland — Canadian ocean liner Collided with a Norwegian collier in 1914 claiming 1012 lives, the worst Canadian maritime accident in peacetime. The wreck lies in 40 meters (130 ft) of water, making it accessible to divers. Many artifacts from the wreckage are on display at the Site historique maritime de la Pointe-au-Père in Rimouski, Quebec. LAUNCHED: 1906, January 18 → FATE: Sank in the Saint Lawrence River following a collision May 29, 1914. |
|
Page 4
|
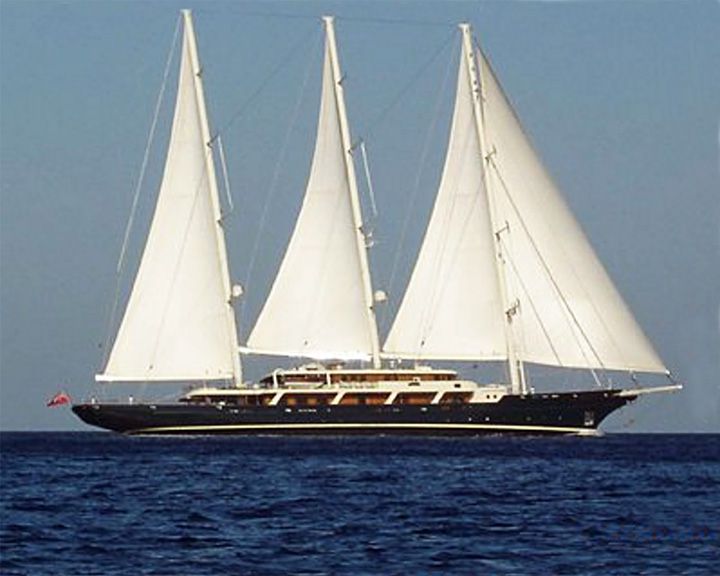 Eos — American three-masted Bermuda rigged schooner, built in Germany The largest sailing yacht in the world with an overall length of 305 feet or 92.92 meters. With much of its length in the bowsprit, the length at the waterline is less than the Maltese Falcon. LAUNCHED: 2006 → FATE: Still in service. |
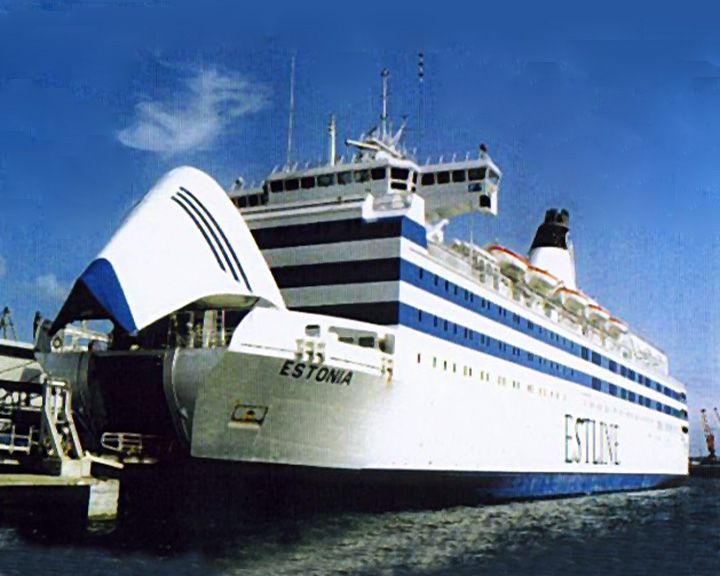 (Another (Another Estonia, MS — German cruise ferry with bow opening car ramp Worst maritime ship disaster in the European waters in peacetime after the Titanic, costing 852 lives. As the largest Estonian-owned ship of the time, she symbolized the independence Estonia regained after the collapse of the Soviet Union. LAUNCHED: 1980, April 18 → FATE: Capsized and sunk in the Baltic Sea on September 28, 1994. |
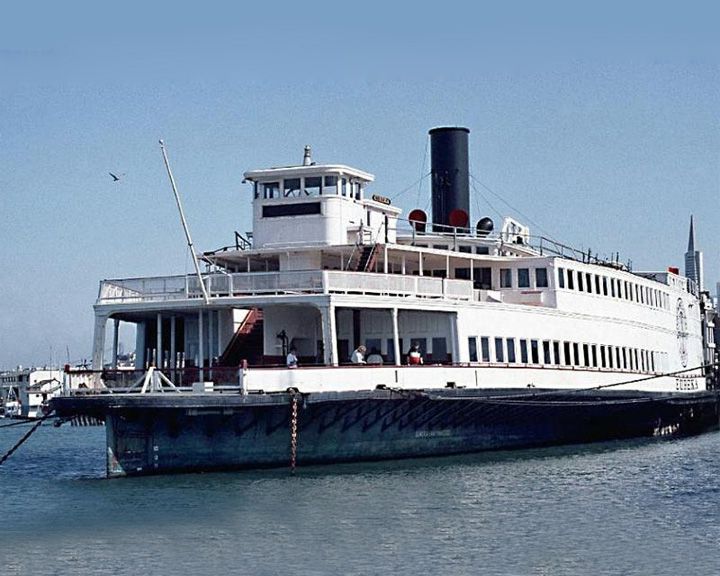 Eureka — American paddle steamboat, stern-wheeler, ferry The largest wooden passenger ferry ever built, certified to carry 3,500 people. She was the last example of the fleet of ferry boats carrying passengers and vehicles across the San Francisco Bay. LAUNCHED: 1890 → FATE: Preserved at the San Francisco Maritime National Historical Park. |
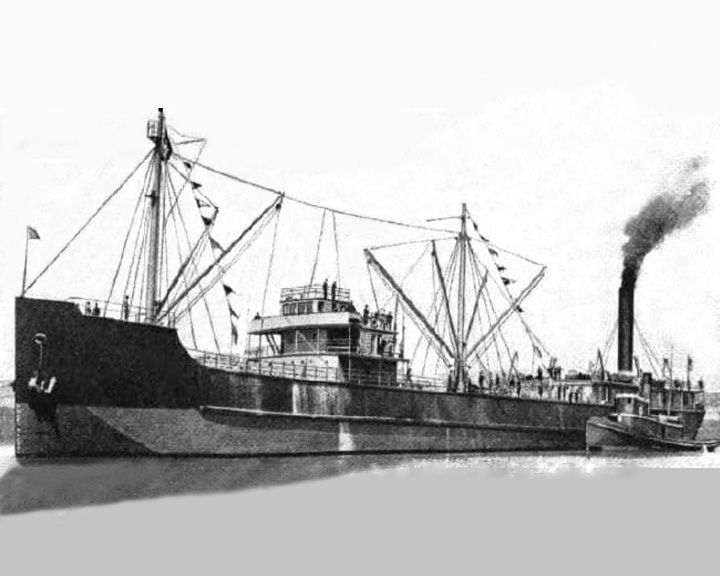 Faith, SS — American Concrete cargo steamer The first concrete ship built in the United States and the largest in the world at the time at 336.5 feet (102.6 meters) and 8000 tons. The first successfully launched cement ship was the 84 foot-400 ton Namsenfjord on August 2, 1917, N.K. Fougner of Norway. LAUNCHED: 1918, March 14 → FATE: After being cracked during a Gulf storm in 1921, she was towed to Cuba for use as a breakwater. |
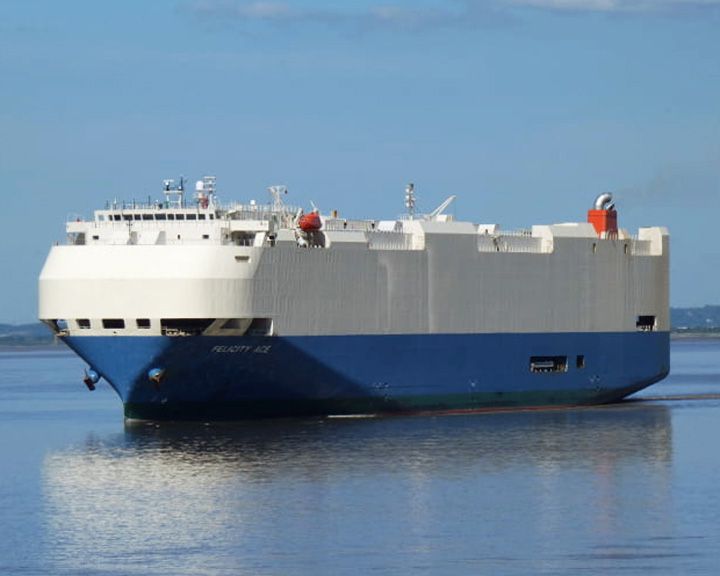 (Another (Another Felicity Ace — Japanese roll-on/roll-off cargo ship The greatest economic loss of cargo shipping in history, costing about $400 million dollars. She was carrying 3,965 Volkswagen Group cars, including Audi, Porsche, Lamborghini and Bentley models. All crew were safely evacuated. LAUNCHED: 2005, July 2 → FATE: She caught fire on February 16, 2022 south of the Azores, then on March 1, 2022, Felicity Ace capsized and sank. |
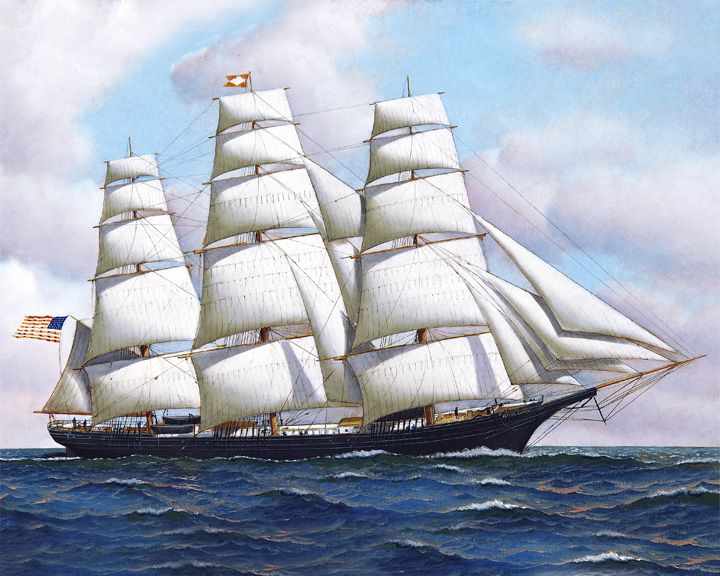 Flying Cloud — American clipper ship The most famous clipper ship, she set a world record (until 1989) for the fastest passage from New York to San Francisco in 89 days, more than 16,000 miles. The ship's navigator was a woman, Eleanor Creesy wife of Josiah Perkins Creesy who skippered Flying Cloud. LAUNCHED: 1851 → FATE: Went aground at Saint John, New Brunswick June 19, 1874. |
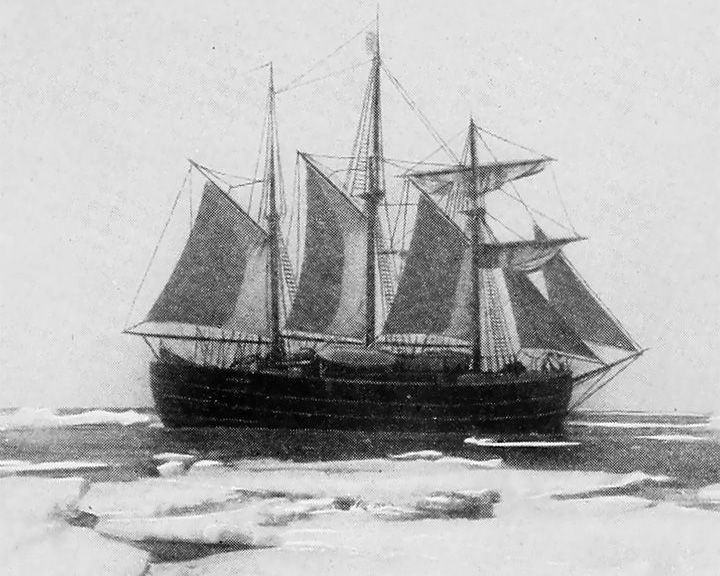 Fram — Norwegian schooner Used in expeditions in the Arctic and Antarctic regions by the Norwegian explorers. Most likely she was the strongest ship ever built, having sailed farthest north and south than any other wooden ship. LAUNCHED: 1892 → FATE: Currently on display at the Fram Museum, Oslo, Norway. |
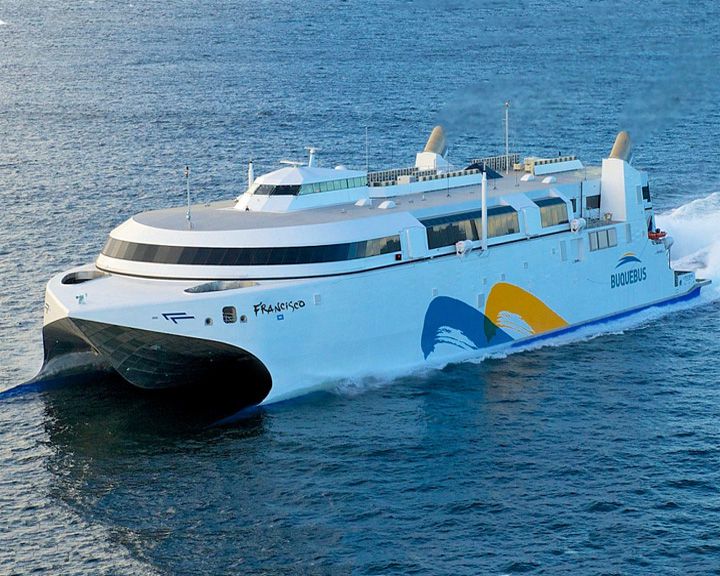 Francisco, HSC — Argentine high-speed catamaran The world's faster ferry sailing at a speed of 58 knots (67 mph). Named after Pope Francis, she is powered by liquefied natural gas. (More info) LAUNCHED: 2012, November 17 → FATE: Still operating. |
|
Page 5
|
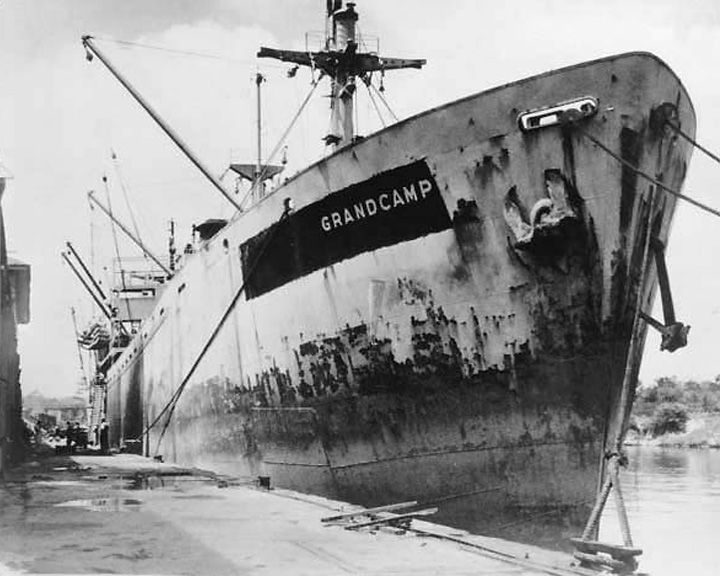 Grandcamp, SS — American liberty ship Origin of the deadliest industrial accident in U.S. history and one of the largest non-nuclear explosions. The initial blast and subsequent fires and explosions in other ships and nearby oil-storage facilities killed at least 581 people, wounding over 5,000. LAUNCHED: 1942, November → FATE: Exploded and destroyed April 16, 1947. |
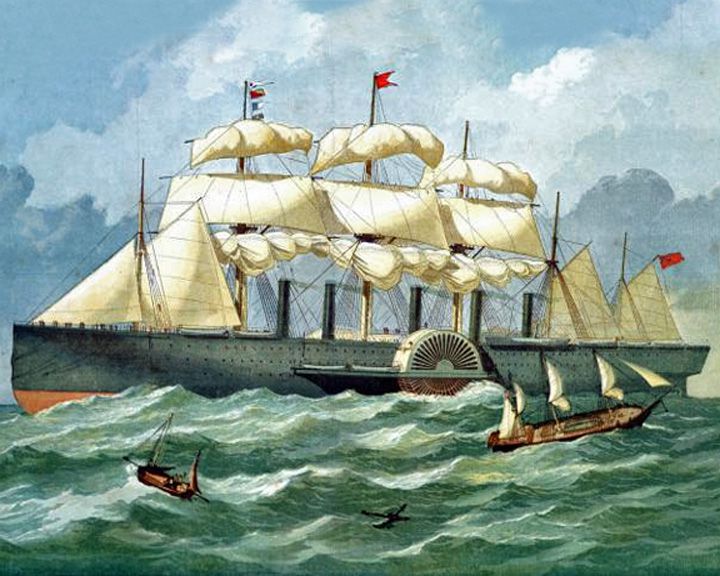 (Another (Another Great Eastern, SS — British iron paddle steamboat, side-wheeler with sails The world's largest steamship; successfully laid cable across the Atlantic Ocean. She completed 45 crossings in eight years; then she was used for carrying mail, then troops. LAUNCHED: 1858, January 18 → FATE: Broken up for scrap at Rock Ferry on the River Mersey in 1889. |
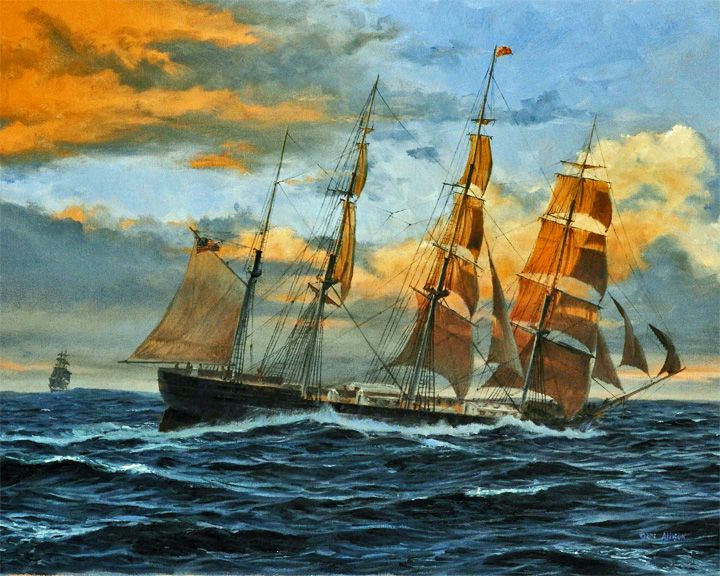 Great Republic — American clipper, four-masted The largest wooden clipper ship ever constructed, requiring 1,500,000 feet of pine, 336½ tons of iron, and 56 tons of copper. In 1853, fire sank her; but she was salvaged and rebuilt as a three deck vessel and went on to set transatlantic speed records. LAUNCHED: 1853, October 18 → FATE: Abandoned during a hurricane off Bermuda March 5, 1872. |
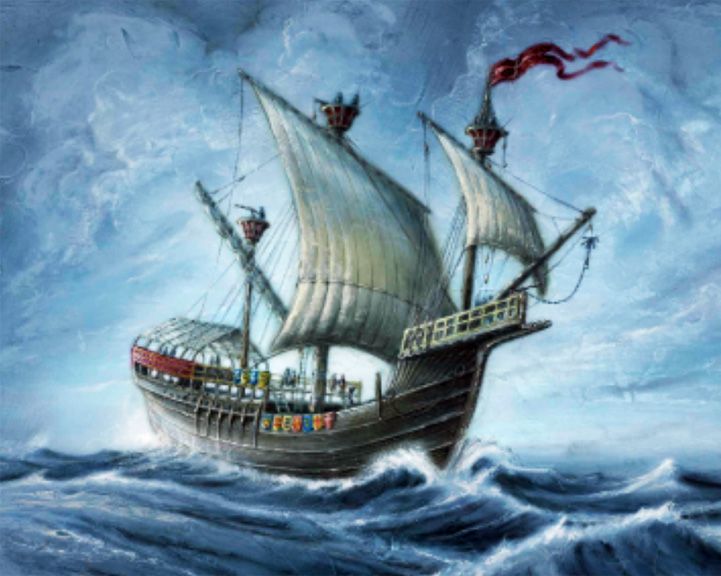 Gribshunden — Danish warship, one of the first carvel-built vessels and among the earliest armed with guns. She was the flagship of the King of Denmark, Hans, on her way to a political summit with the Swedish leader when she sank, killing a number of those aboard and the summit. In 2015, the wreckage attracted international attention when a near perfectly-preserved wooden figurehead of a mythical beast was brought to the surface. LAUNCHED: 1485 → FATE: In 1495, she sank after an accidental fire while in the Baltic Sea off the coast of Ronneby in southeastern Sweden. |
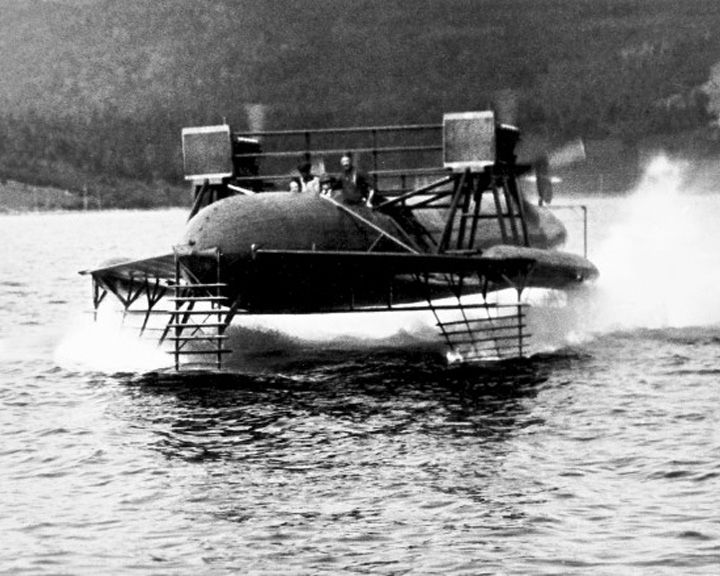 HD-4 — American hydrofoil An early research hydrofoil watercraft developed by the Alexander Graham Bell. She set a world marine speed record of 70.86 miles per hour (114.04 km/h), that stood for almost a year. LAUNCHED: 1919 → FATE: Dismantled in 1921, laying for decades on the shore at Beinn Bhreagh, Nova Scotia. |
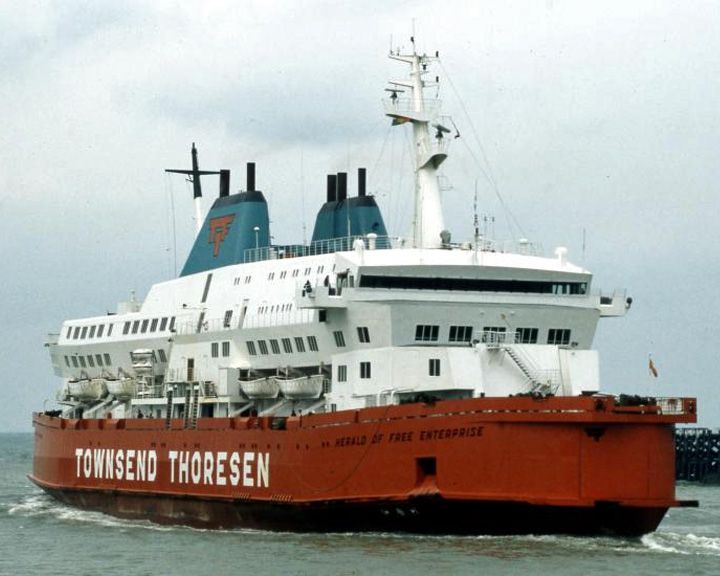 (Another (Another Herald of Free Enterprise, MS — British roll-on/rolll-off ferry Capsized moments after leaving the Belgian port, killing 193 passengers and crew, the highest death-count of any peacetime British maritime disaster since 1919. The ship owners, Townsend Thoresen, re-branded the company as P&O European Ferries, repaint the fleet's red hulls in navy blue and remove the TT logo from the funnels. LAUNCHED: 1980 → FATE: Because deck doors were left open, she filled with water and capsized March 6, 1987; was raised April 1987 and scrapped in 1988. |
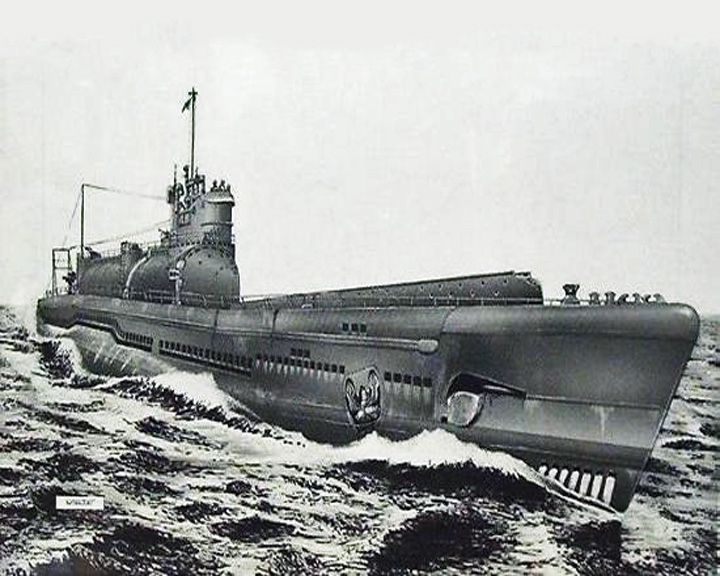 I-400 — Japanese submarine The largest non-nuclear submarines ever built. These submarine aircraft carriers were able to carry three aircraft underwater to their destinations, surface, launch their planes, then quickly dive again. LAUNCHED: 1943, January 1945 July → FATE: Scuttled near Kalaeloa, Hawaii on June 4, 1946. |
Icon of the Seas — American cruise ship Largest passenger ship ever constructed, accommodating 7600 guests and a gross tonnage of 250,800, surpassing Wonder of the Seas at 235,600.. At 1,198 feet (365 meters) in length, she is longer than the largest military ship ever built, the U.S. Gerald R. Ford-class aircraft carrier at 1,106 feet (337 meters). LAUNCHED: 2022, December 9 → FATE: Still in service. |
|
Page 6
|
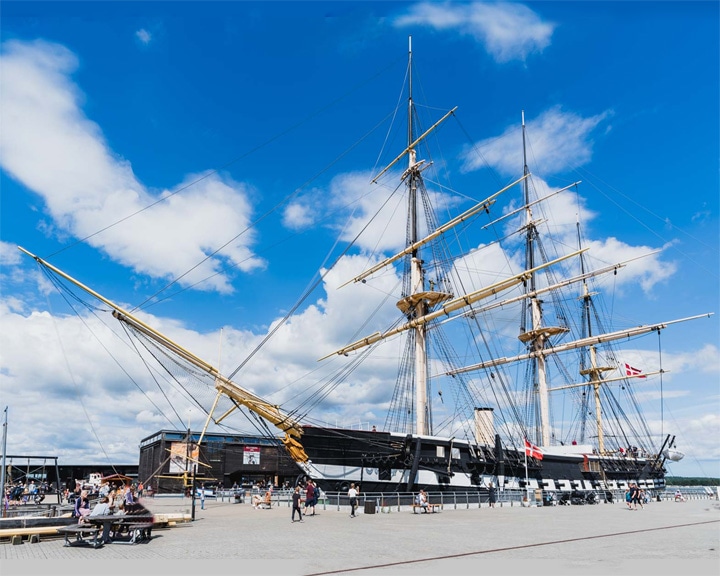 Jylland, HDMS — Danish screw-propelled steam frigate The world's largest wooden warship still in existence. She took part in the Battle of Heligoland May 9, 1864 LAUNCHED: 1860, November 20 → FATE: She is preserved as a museum ship in the small town of Eblet, Denmark. |
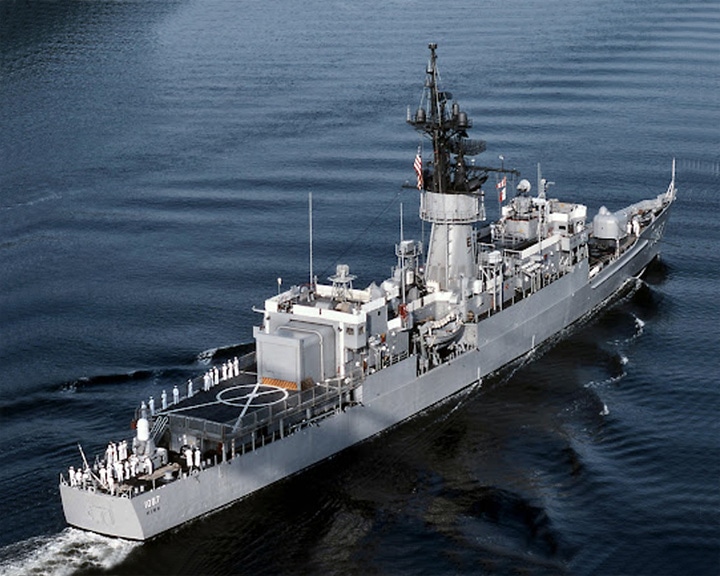 (Another (Another Kirk, USS — American destroyer escort, Knox-class She was sent to help evacuate Americans and fleeing refugees from South Vietnam, caring out one of the most significant humanitarian missions in U.S. military history.. During the evacuation, she was a makeshift landing pad for helicopters flown by South Vietnamese pilots fleeing with families and friends on board. LAUNCHED: 1971, September 25 → FATE: On 29 September 1999, the ship was purchased by Taiwan and renamed Fen Yang. |
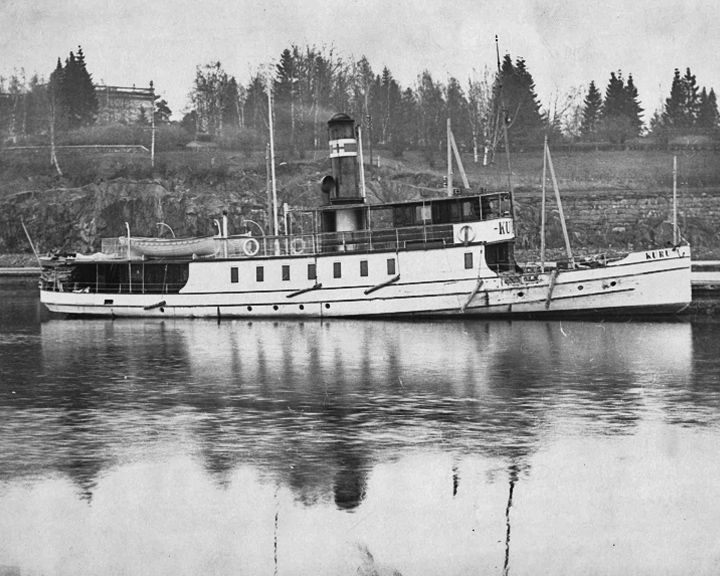 Kuru, SS — Finnish steamship On September 7, 1929, she capsized and sank on lake Näsijärvi, in Tampere making it the worst maritime disaster in Finnish waters with the loss of 136 lives. The capsizing was mainly due to a high center of gravity when a third deck level was added in 1927. LAUNCHED: 1915 → FATE: The wreck was raised and repaired shortly afterwards and served until 1936. |
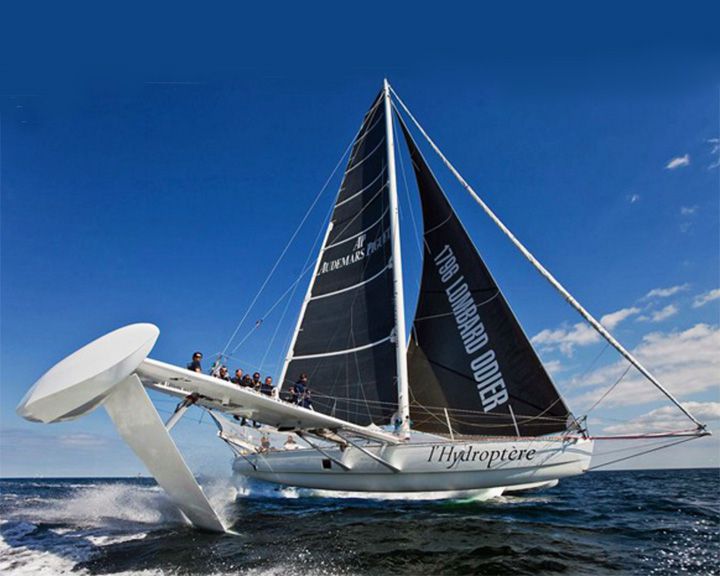 L'Hydroptère — French speed sailboat; experimental Currently the world's fastest sailboat. In 2008, it reached a sailing speed of 56.3 knots, the first sailboat to ever pass 100 km/h. LAUNCHED: 2008 → FATE: Still sailing. |
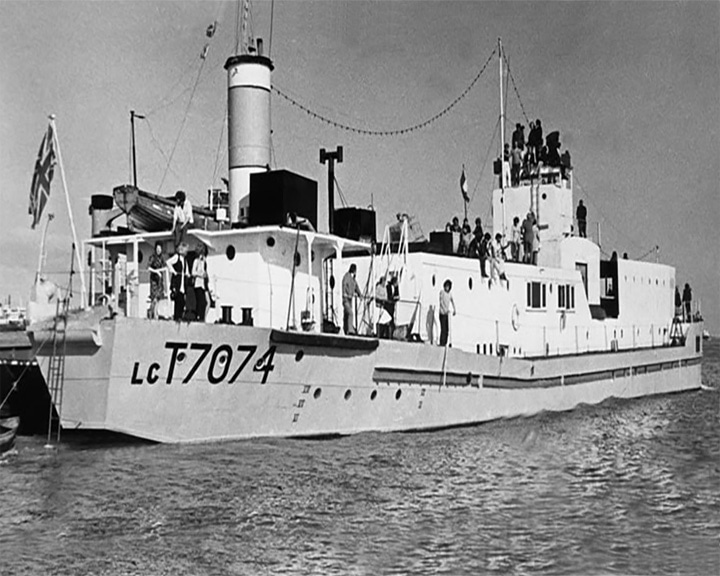 LCT7074, HM — British landing craft, tank (LCT) The last amphibious assault ship in the United Kingdom for landing tanks, other vehicles and troops on beachheads. De-commissioned in 1947 she was renamed Landfall and became the club ship for the Master Mariners’ Club of Liverpool. The craft was later converted into a riverfront nightclub. LAUNCHED: 1944, April 4 → FATE: Salvaged and restored by 2020, then moved to a permanent display at Portsmouth's The D-Day Story museum. |
 (Another (Another |
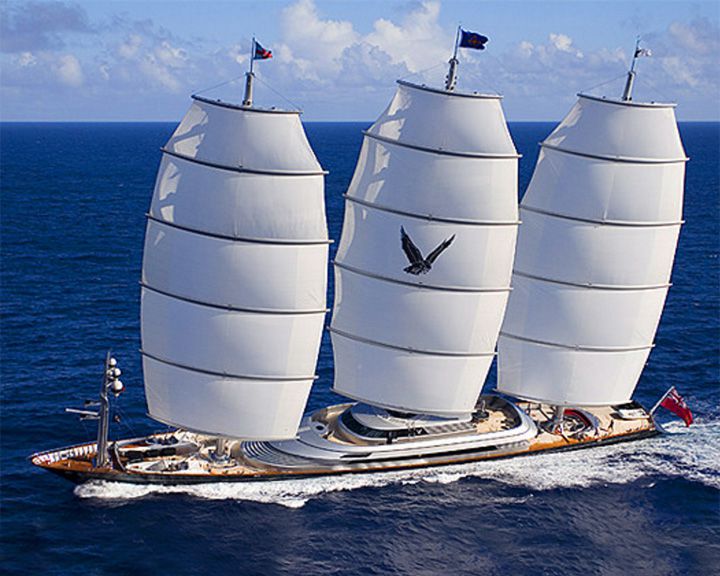 Maltese Falcon — American full-rigged luxury yacht; now owned by a Englishman The largest full-rigged luxury yacht in the world. She has 5 square sails on each of 3 masts that can be fully unfurled in 6 minutes. Some claim the Eos is larger. LAUNCHED: 2006 → FATE: Still in service. |
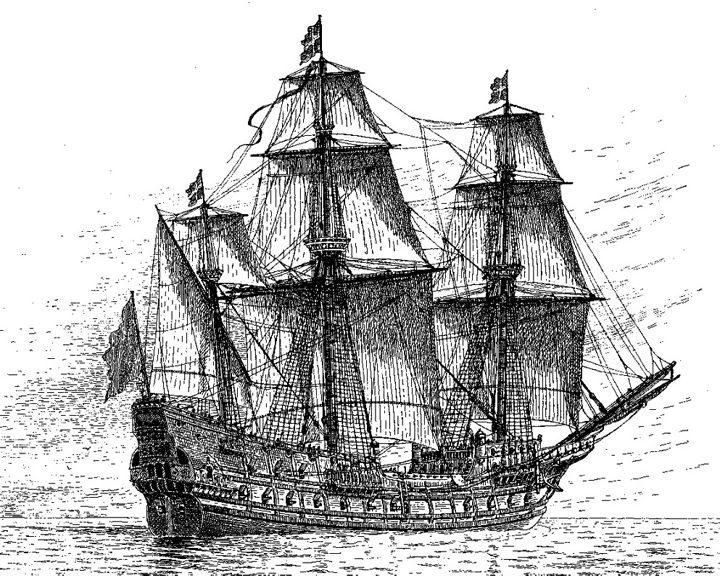 (Another (Another Mars — Swedish three masted warship One of the largest warships at the time and the first ship to sink another ship with gunfire. The shipwreck was found by a team of divers north of the island Oland August 19, 2011. LAUNCHED: 1564 → FATE: Caught fire and exploded during the First Battle of Oland, May 31, 1564. |
|
Page 7
|
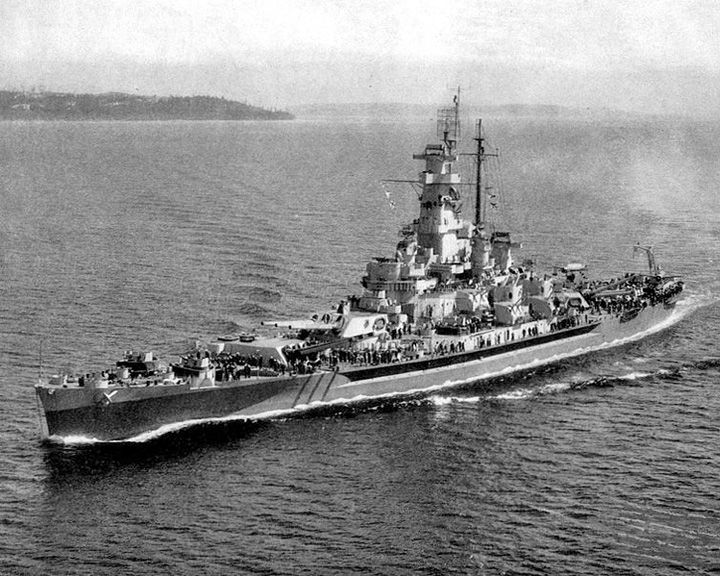 Massachusetts, USS — American South Dakota class battleship Has the distinction of having fired the US Navy's first and last 16-in shells of the World War II. Despite being used as a parts cache to get the Iowa-class battleships back in service, Massachusetts was designated a National Historical Landmark a 14 January 1986. LAUNCHED: 1941, June 18 → FATE: Became a in museum ship at Battleship Cove, Fall River, Massachusetts June, 1965. |
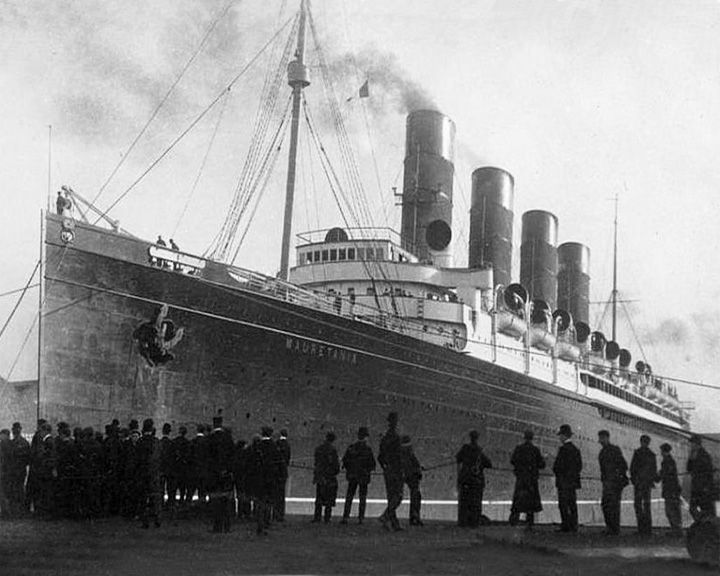 Mauretania, RMS — British ocean liner At the time, she was the largest and fastest ship in the world. She made an eastbound transatlantic crossing with a long-standing record average speed of 23.7 knots. She served as a hospital ship and troop ship in World War I. LAUNCHED: 1906, September 18 → FATE: Scrapped in 1934. |
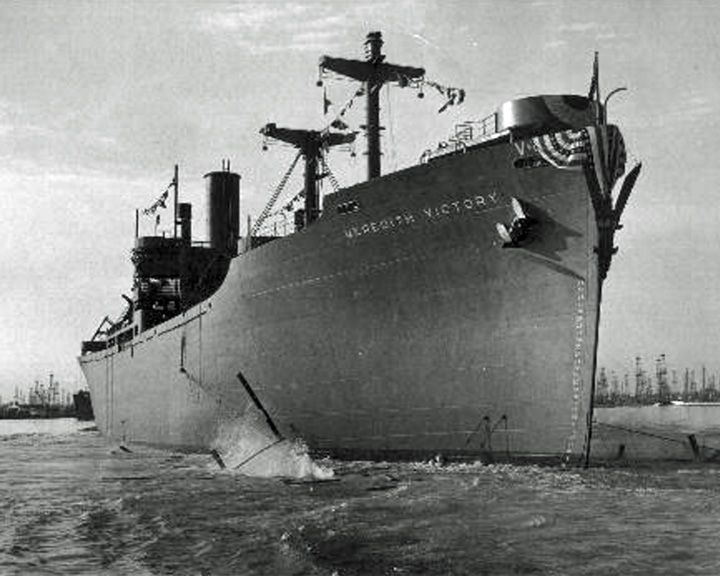 Meredith Victory, SS — American cargo ship, freighter The "Ship of Miracles" saved more than 14,000 refugees during the Korean War, the largest humanitarian rescue operation by a single ship. The ship was built to transport supplies and equipment overseas during World War II. LAUNCHED: 1945, June 18 → FATE: Broken up for scrap in China in 1993. |
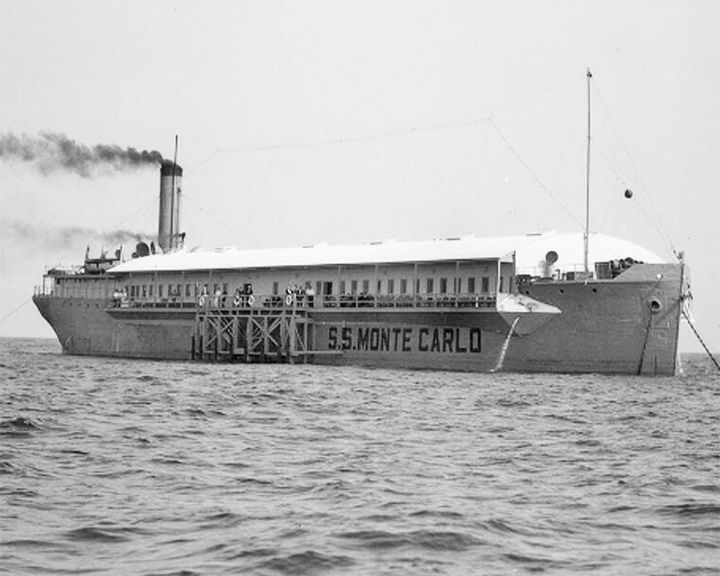 Monte Carlo, SS — American concrete ship She became a gambling and prostitution ship operating in international waters off the coast of Long Beach, California. In the 1930s, she was the largest of a fleet of ships making up Gambling Ship Row off the southern California. LAUNCHED: 1921, December → FATE: Wrecked during a storm in 1937, ending up on a San Diego beach where it remains. |
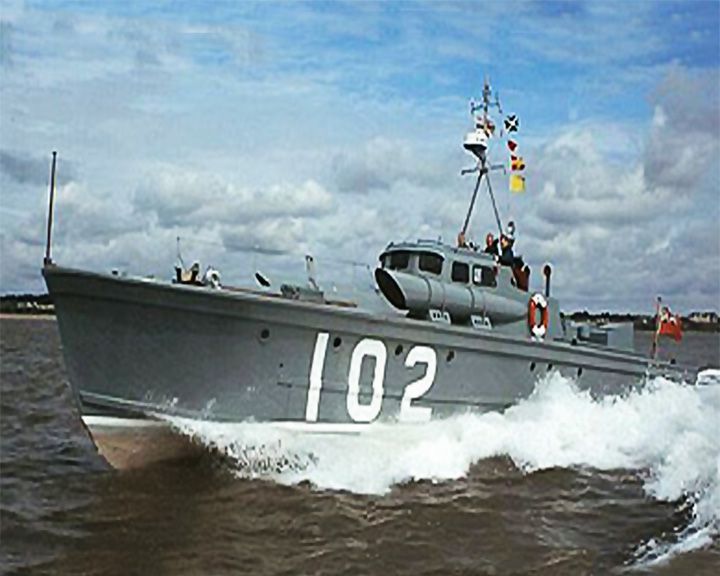 MTB 102 — British motor torpedo boat The the fastest wartime British naval vessel in service at 48 knots and the smallest vessel to ever serve as a flagship for the Royal Navy. In 1944 she carried Winston Churchill and General Eisenhower to review the fleet for Operation Overlord, the invasion of Normandy, World War II. She appeared as herself in the 2017 war film Dunkirk. LAUNCHED: 1937 → FATE: On exhibit at Lowestlft, on the North Sea. |
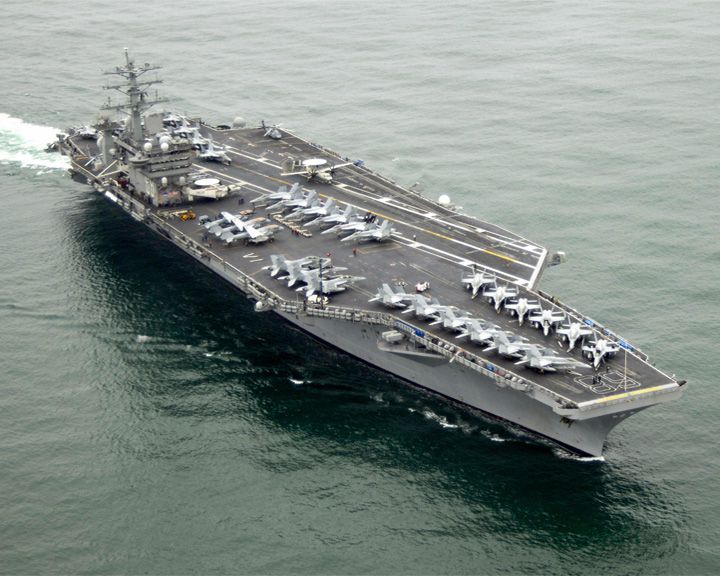 Nimitz, USS — American aircraft carrier; supercarrier Setting for the 1980 science fiction movie The Final Countdown. In May of 1981, one of her planes crashed on the flight deck, killing 14 crewmen. LAUNCHED: 1972, May → FATE: Still in service. |
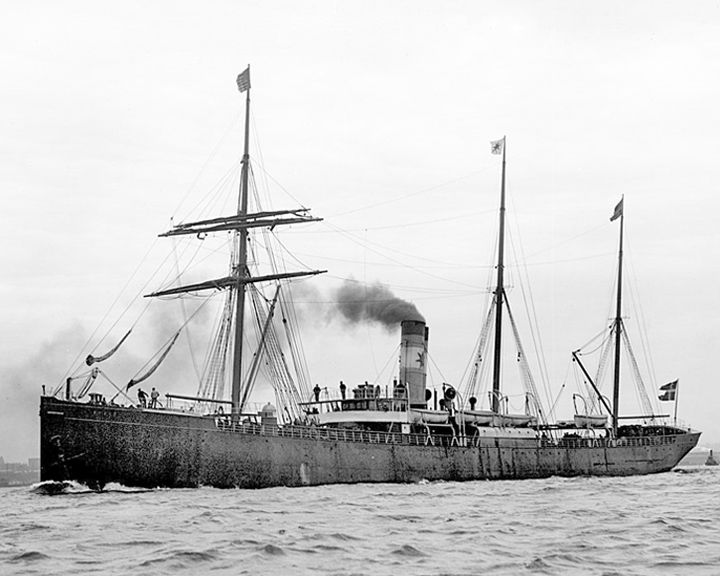 Norge, SS — Norwegian, then Danish ocean liner The biggest civilian maritime disaster in the Atlantic in the until the sinking of the Titanic. More than 635 people died during the sinking, among them 225 Norwegians. The disaster remains the worst in Danish maritime history. LAUNCHED: 1881, June 18 → FATE: Ran aground and sank June 28, 1904. |
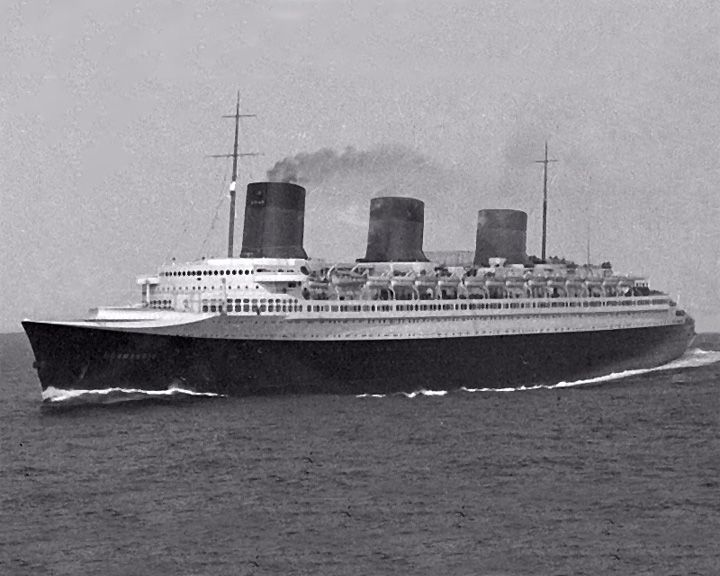 (Another (Another Normandie, SS — French ocean liner Largest, fastest and most powerful passenger ship ever built. Considered one of the greatest ocean liners in history, her Art Deco motif was so splendid she was known as the "Ship of Light" just as Paris was the "City of Light". LAUNCHED: 1935, October 29 → FATE: Caught fire and capsized in February 1942; scrapped October, 1946. |
|
Page 8
|
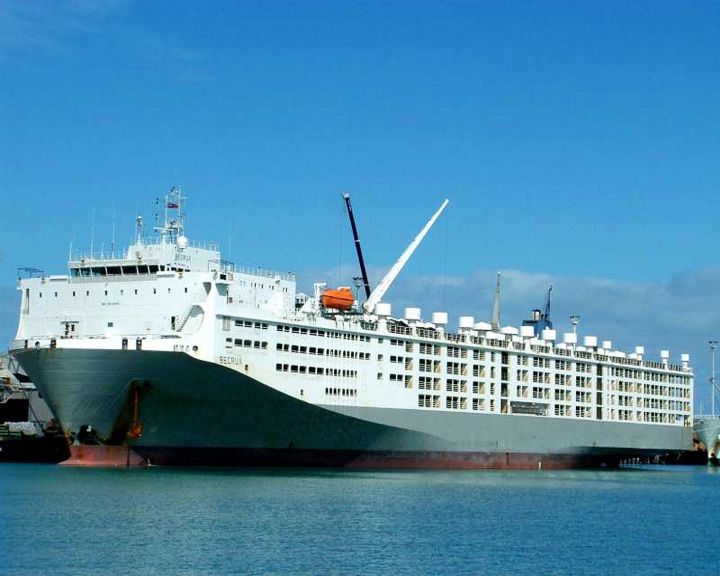 Ocean Dover, MV — Australian livestock carrier The largest livestock carrier in the world designed and built with special livestock support systems. She is capable of carrying 75,000 sheep or 18,000 cattle across oceans. In 2014, a fire broke out in the crew quarters, but was contained. LAUNCHED: 2002 → FATE: Still in service. |
 (Another (Another Oriskany, USS — American aircraft carrier, Essex class The world's largest, and the U.S.'s first, artificial reef. She had multiple reconfigurations and updates. In 1966, a flare accidentally ignited on the hangar bay causing a catastrophic fire killing 44 crewmen. LAUNCHED: 1945, October 18 → FATE: Sunk as an artifical reef May 17, 2006. |
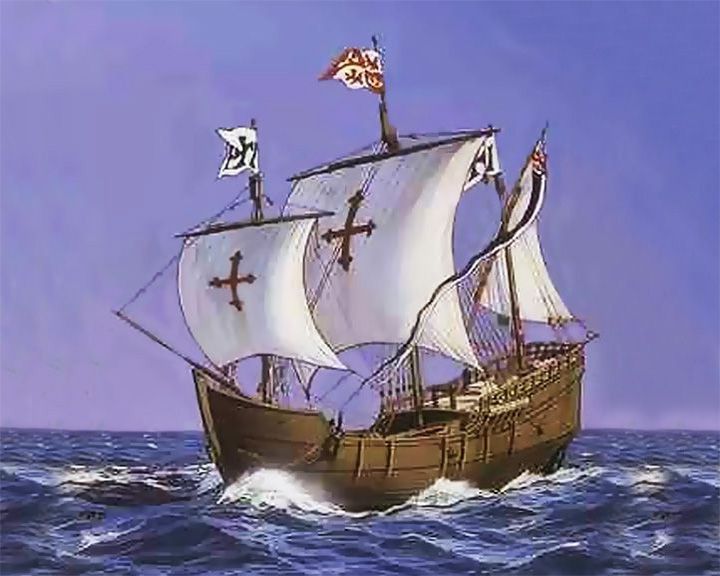 Pinta, (La) — Spanish three masted caravel One of Columbus' ships of discovery. The fastest of Columbus' three ships to America in 1492, and Columbus' flag ship on the return trip to Spain in 1943. She was among the fleet of 17 ships for Columbus' second voyage. LAUNCHED: 1441, circa → FATE: Around 1501. |
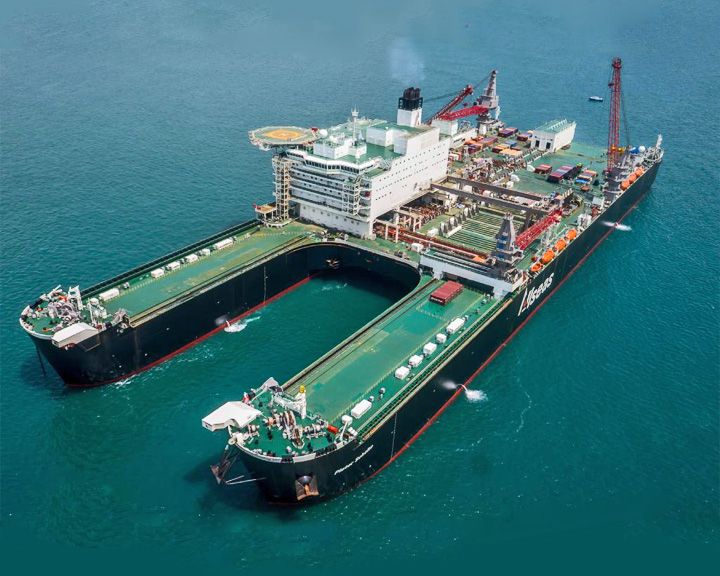 Pioneering Spirit — Swiss catamaran construction ship, Korean built The world's largest ocean vessel, designed for the single-lift installation and removal of large oil and gas platforms. Displacing 1 million tons, the vessel operates as a semi-submersible. Using ballasts, she is able to lower herself when installing payload or raise herself when removing payload. LAUNCHED: 2013, January 18 → FATE: Still in service. |
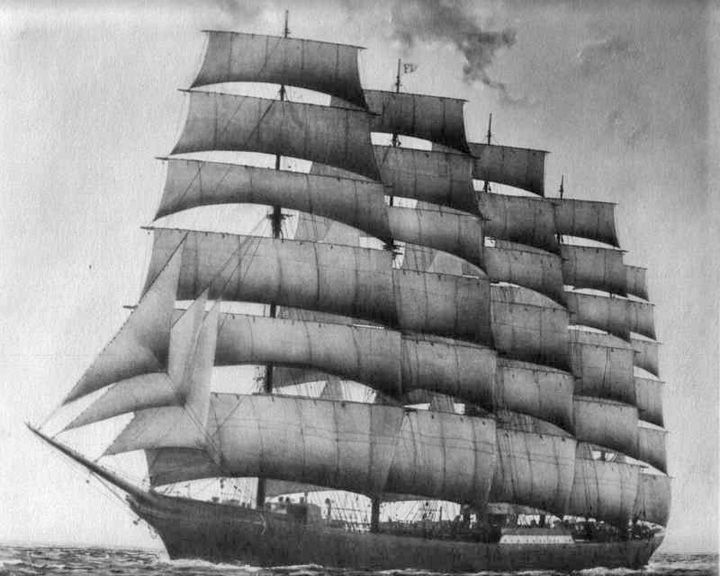 Preußen — German windjammer, five-masted The largest sailed ship ever built and the only five-masted, full-rigged, ship built until the 21st century. She was built entirely of steel. She was used in the saltpeter trade with Chile, setting speed records in the process. LAUNCHED: 1902, May 18 → FATE: Swept onto rocks and sank near the White Cliffs of Dover November 6, 1910. |
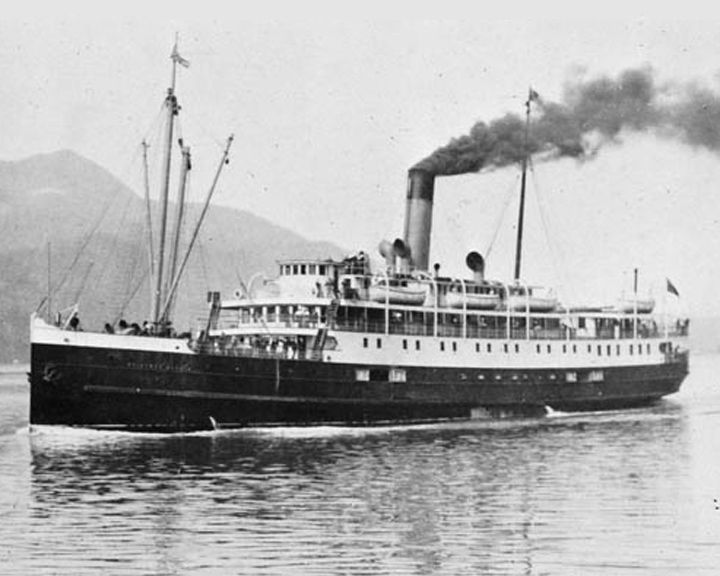 Princess Sophia, SS — Canadian passenger ship The worst maritime accident in the history of British Columbia and Alaska. The wreck and the loss of 343 people was controversial since some thought that all aboard could have been saved. LAUNCHED: 1911, November 18 → FATE: Grounded on October 24,1918 and sank following day during a storm near Juneau Alaska. |
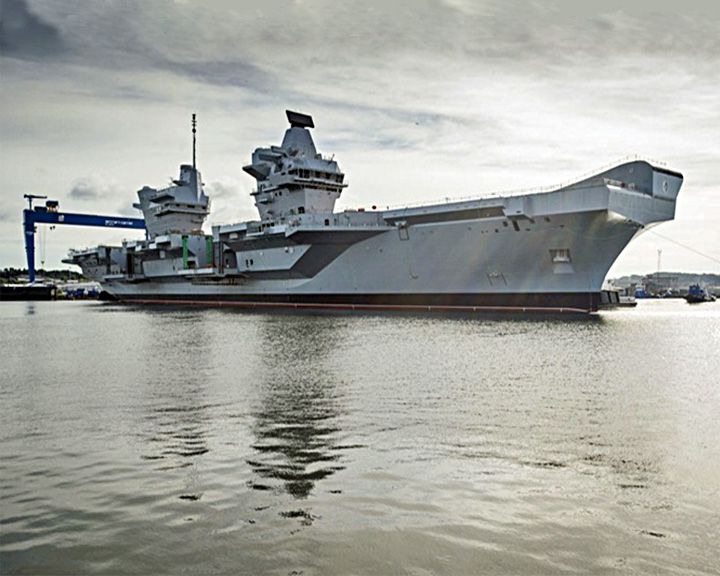 Queen Elizabeth, HMS — British aircraft carrier Largest warship ever built for the Royal Navy capable of carrying up to 40 aircraft. With no catapults and catch wires she carries only V/STOL aircraft, F-35B Lightning II fighters and Merlin helicopters. LAUNCHED: 2014, July 18 → FATE: In service 2017. |
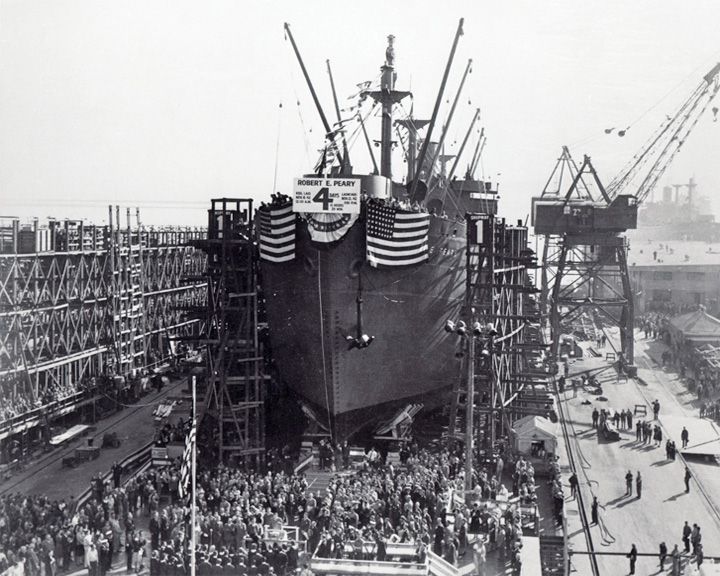 Robert E. Perry, SS — American liberty ship Gained fame during World War II for being built in the shortest time for such a large vessel. Typical completion of liberty ships took 50 days; she was completed in 4 days 15 hours and 29 minutes after the keel was laid down. LAUNCHED: 1942, November 12 → FATE: Scrapped at Baltimore, June 1963. |
|
Page 9
|
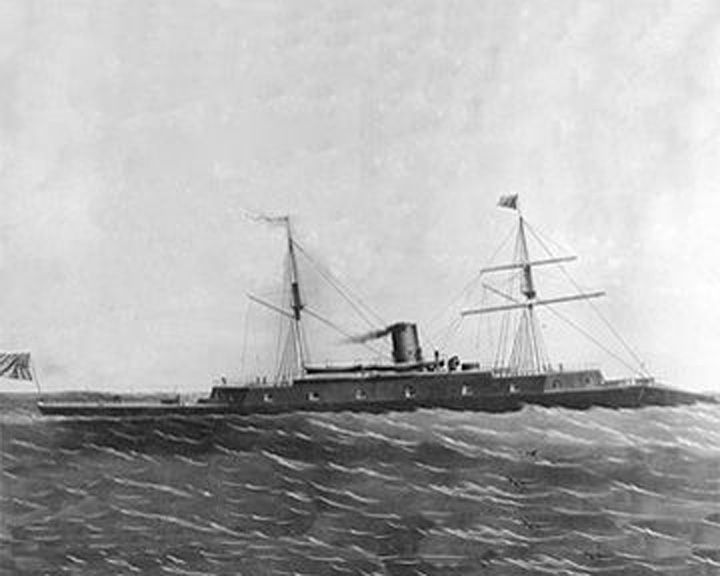 Rochambeau — American frigate, ironclad The longest wooden ship ever built. When the French thought Otto von Bismarck might be interested in the ship, they hurriedly bought her from the Americans and commission her in 1867. LAUNCHED: 1862, July 22 as Dunderberg → FATE: The French scrapped her in 1874. |
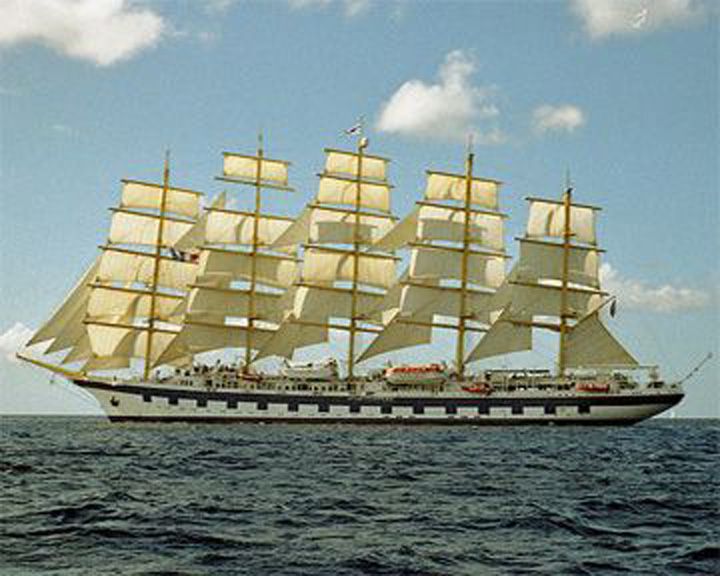 Royal Clipper — German tall ship; steel-hulled five masted fully rigged design The largest and only five-masted full-rigged sailing ship in service. Her design was based on the German ship Preussen, but was configured for passenger comfort rather than cargo carrying. LAUNCHED: 2001 → FATE: Still in service. |
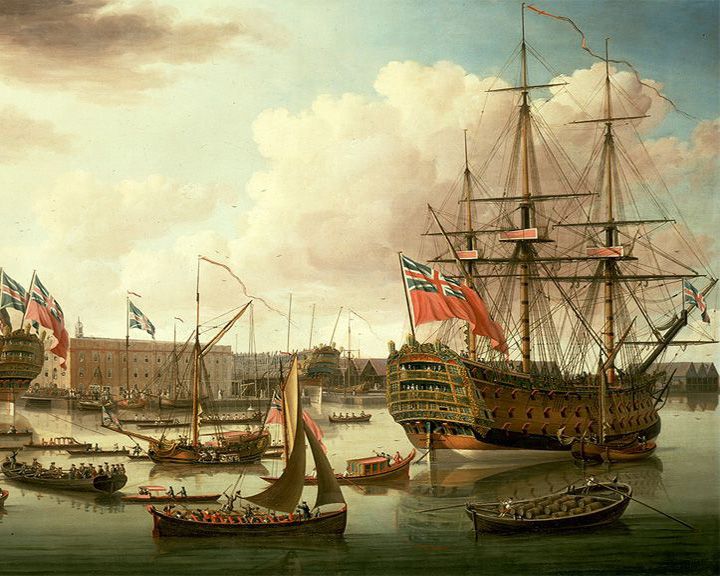 Royal George, HMS — English first-rate ship of the line One of the most serious maritime losses to occur in British water, sinking while undergoing routine maintenance taking more than 800 lives. She was the largest warship in the world at the time of launching. LAUNCHED: 1756, February 18 → FATE: Sank while anchored off Portsmouth August 29, 1782. |
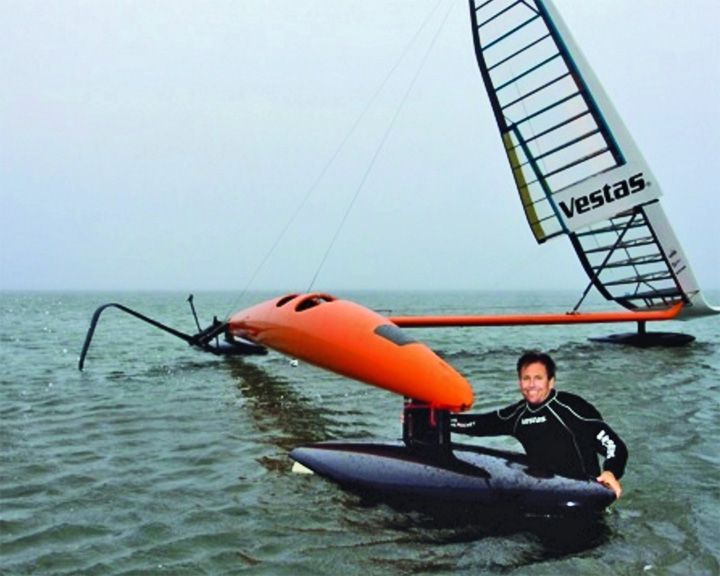 Sailrocket 2 — Australian speed sailboat Built to capture the class D sailing speed record, piloted by the project leader Paul Larsen at 65.45 knots in Walvis Bay, Namibia. In 2008, before crashing, the first Sailrocket reached a reported unofficial speed of 52.22 knots. LAUNCHED: 2011, March → FATE: Still racing. |
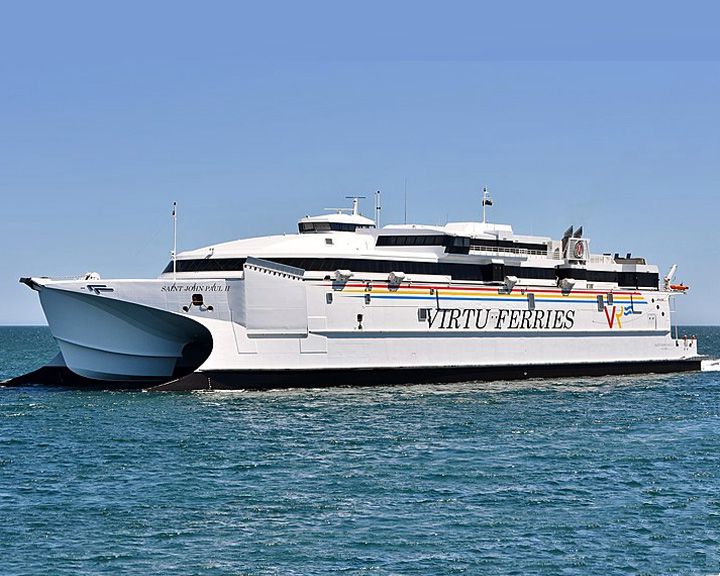 Saint John Paul II, MV — Maltese catamaran ferry The largest high-speed catamaran in the Mediterranean Sea and the second largest in the world as of 2020. Her service speed is approximately 37 knots, or 69 km/h (43 mph). She is operated by Virtu Ferries. LAUNCHED: 2018, December 22 → FATE: Still in operation. |
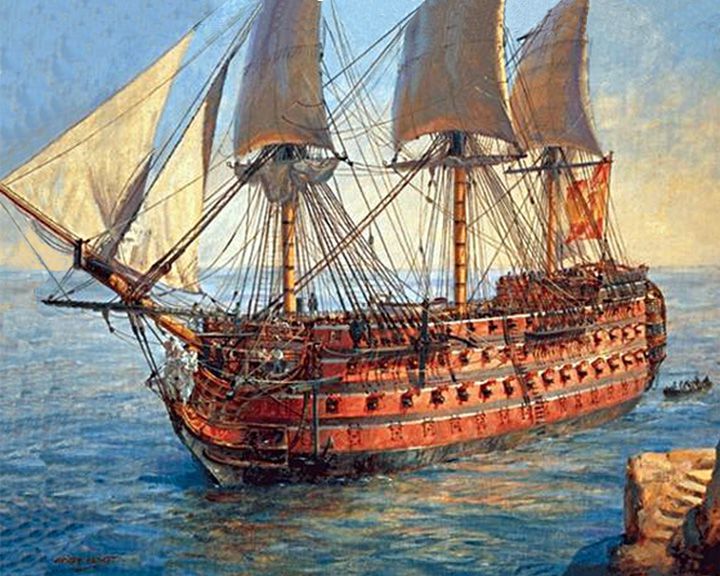 (Another (Another Santísima Trinidad — Spanish ship of the line, first-rate After refitting in 1804, the largest and heaviest-armed ship in the world with 140 guns on four decks. A full-size representation in on display in the harbour of Alicante, Spain as shown in "Another IMAGE". LAUNCHED: 1768 → FATE: Sank at the Battle of Trafalgar in October of 1805. |
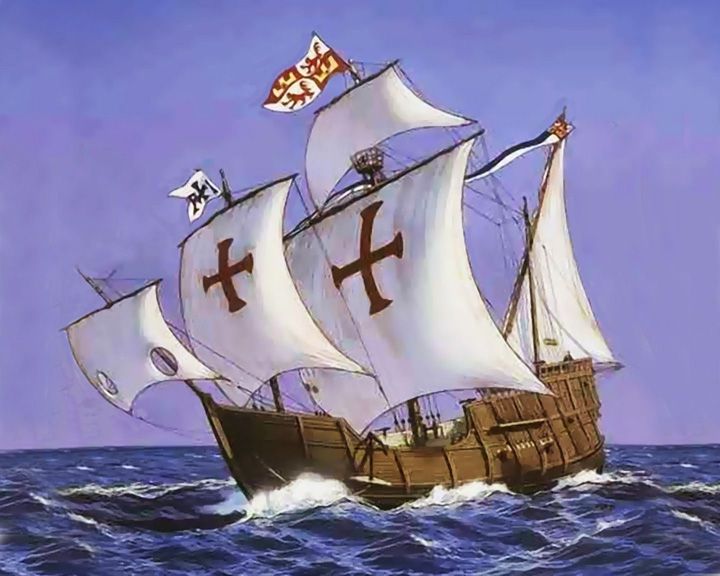 Santa Maria — Spanish carrack The largest of Columbus' ships of discovery. The anchor of the Santa María now resides in the Musée du Panthéon National Haitien, in Port-au-Prince, Haiti. LAUNCHED: 1460, circa → FATE: Ran aground and lost near Cap-Haitien, Haiti, December 25, 1492. |
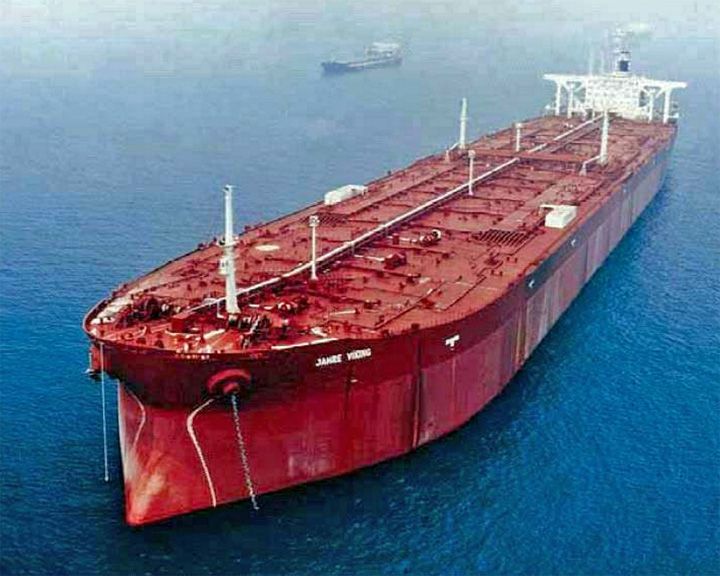 Seawise Giant — Japanese supertanker, variously owned Longest ship ever built at 458.46 meters or 1,504 feet. She was damaged during the Iran-Iraq War by an Iraqi Air Force in the Strait of Hormuz in May 1988. LAUNCHED: 1979 → FATE: Scrapped in January of 2010. |
|
Page 10
|
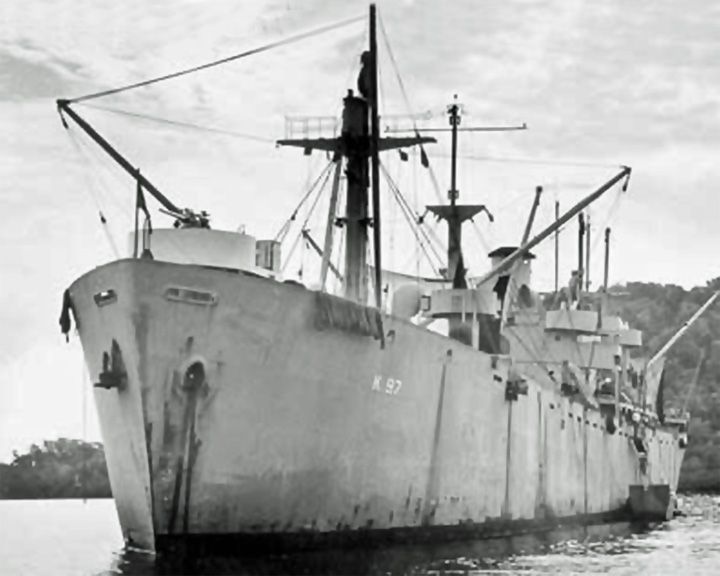 Serpens, USS — American Crater-class cargo ship The most catastrophic single-event loss of life in the history of the U.S. Coast Guard with 250 casualties. In the explosion, a 12-ton locomotive, the wooden pier it sat on, and 16 boxcars loaded with bombs and ammunition disappeared completely. LAUNCHED: 1943, April 5 → FATE: Exploded in complete destruction January 29, 1945, on the coast of Guadalcanal. |
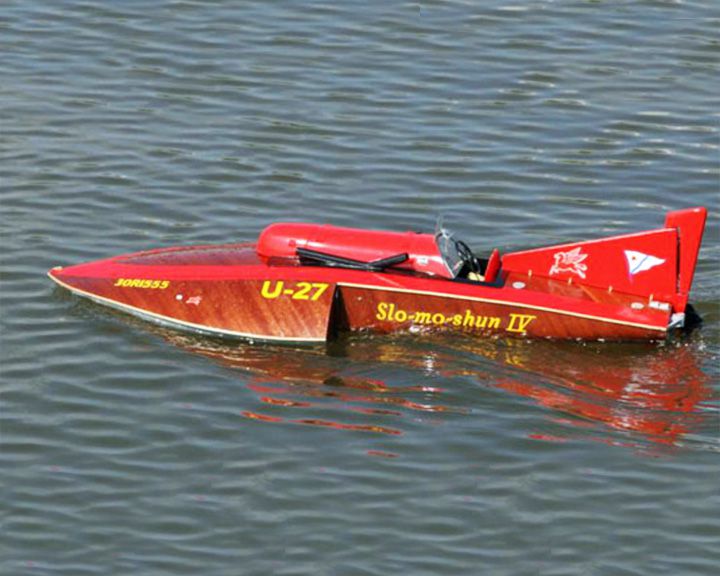 Slo-mo-shun IV — American racing hydroplane Winner of the 1950, 1952, and 1953 APBA Gold Cup Races; also set two straightaway speed records. Her hull was designed to lift the top of the propellers out of water at high speed, a technique called “prop riding,” which reduced drag. LAUNCHED: 1949, October → FATE: Wrecked in a pre-race test run in 1956; rebuilt and on exhibit at Seattle's Museum of History and Industry. |
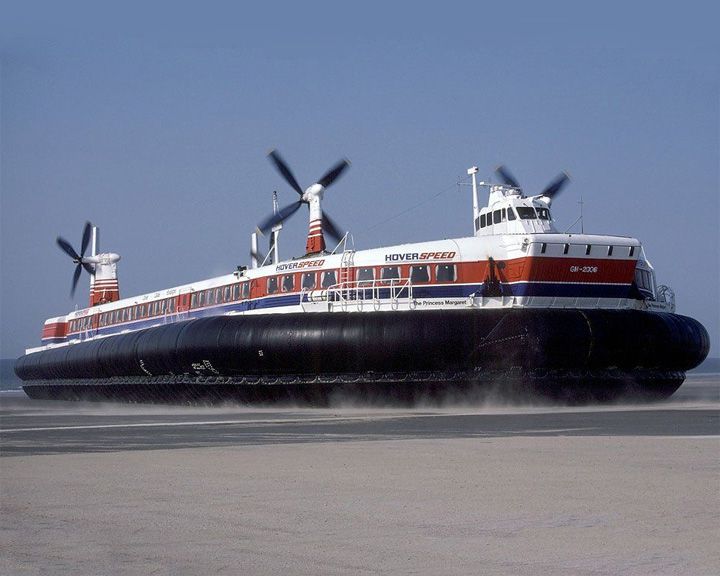 SN.R4 — British Mountbatten class hovercraft Was the largest civil hovercraft ever built, carrying 254 passengers and up to 30 cars. She is the only surviving hovercraft that served English Channel traffic from 1968 to 2000. The others, Sir Christopher, Sure, Swift, Princess Margaret, and The Prince of Wales, were all scrapped. LAUNCHED: 1968 → FATE: Preserved and on static display at the Hovercraft Museum at Lee-on-Solent, England. |
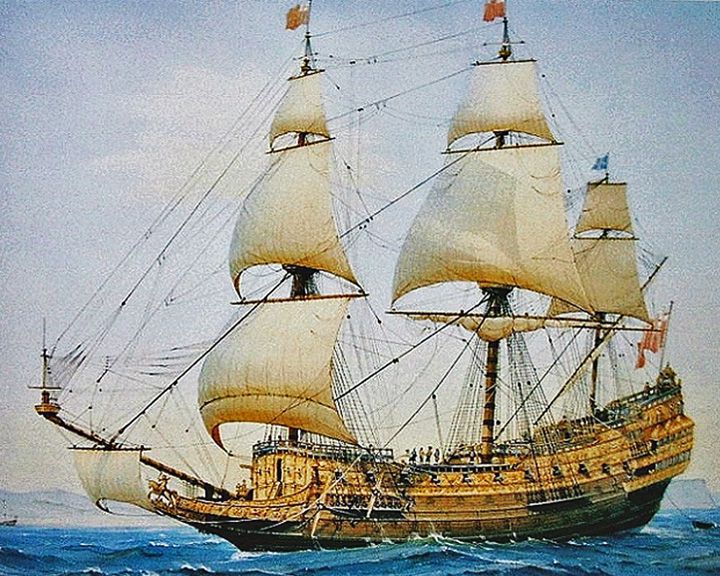 Sovereign of the Seas, HMS — English full-rigged warship The most extravagantly decorated warship in the early Royal Navy. She was armed with 102 bronze guns at the insistence of the king, Charles I of England. LAUNCHED: 1637, October 18 → FATE: Burnt to the water line January 27, 1697. |
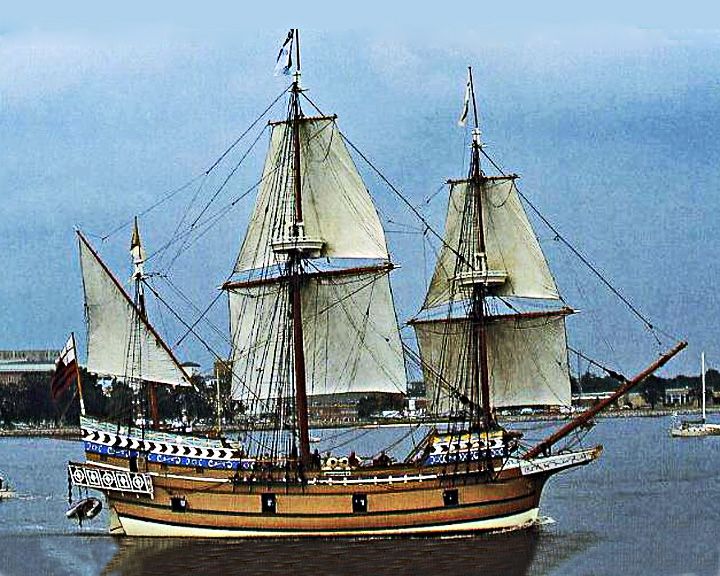 Susan Constant — British fully-rigged ship The largest of three ships of the English Virginia Company sailing to establish the new Colony of Virginia, Jamestown. Replicas of Susan Constant, shown in image, and her sister-ships are docked in the James River at Jamestown Settlement. LAUNCHED: 1607 → FATE: After 1615, fate unknown. |
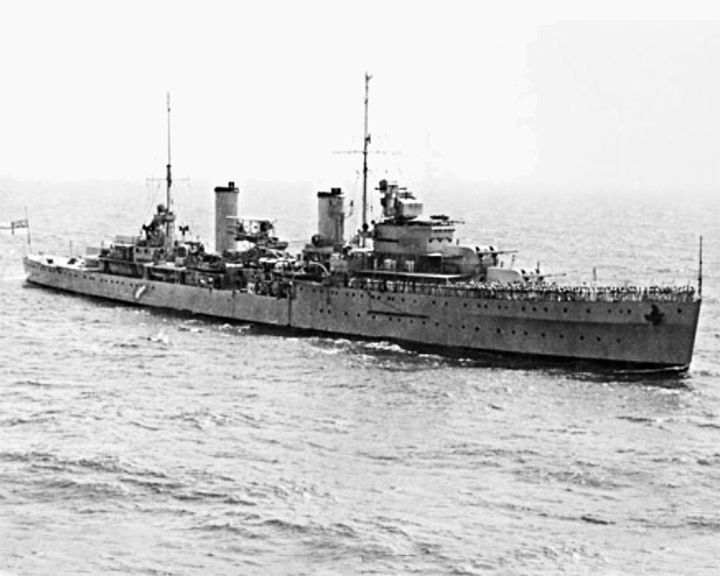 Sydney, HMAS — Australia Leander-class light cruiser The most devastating loss of life for the Royal Australian Navy when 645 personnel went down with the ship during the battle with the German auxiliary cruiser Kormoran. The wrecks of Sydney and the Kormoran were discovered off the coast of Shark Bay in 2008. The Australians who died are commemorated at the Australian War Memorial. LAUNCHED: 1934, September 22 → FATE: Sunk by the German auxiliary cruiser Kormoran, November 19, 1941 off the coast of Western Australia. |
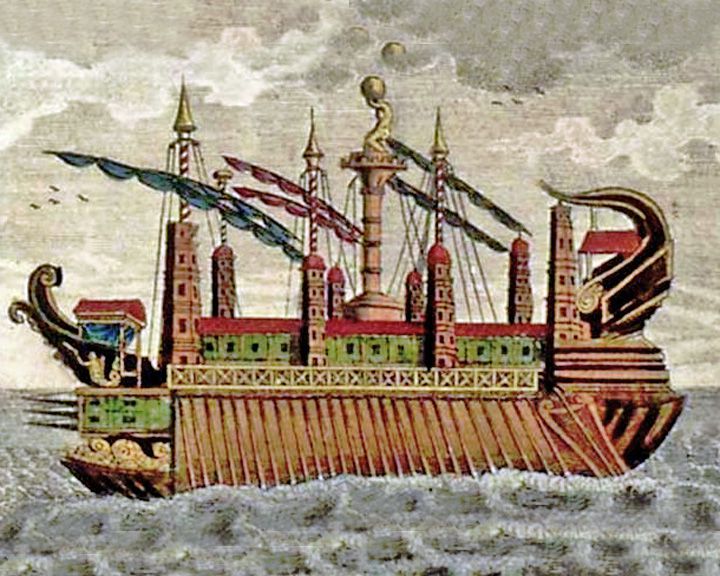 Syracusia — Greek cargo ship The largest transport ship of antiquity. It sailed only once to berth in Alexandria where it was later given to Ptolemy. LAUNCHED: 240, BC, circa → FATE: Unknown. |
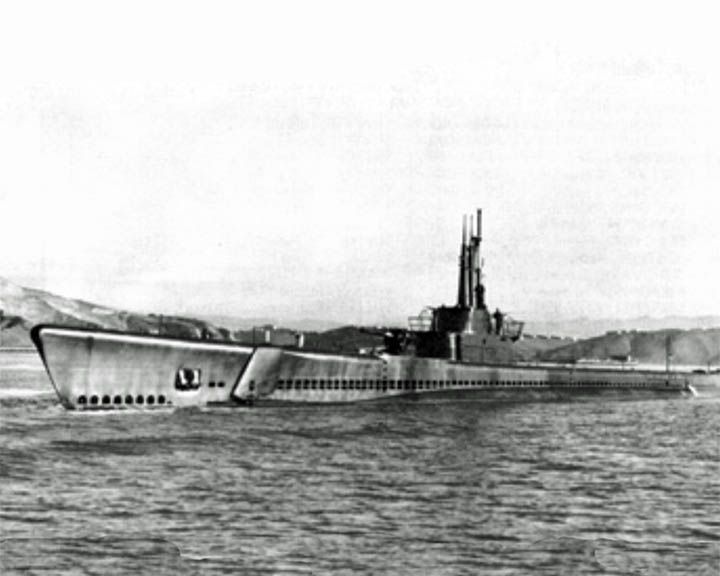 Tang, USS — American Balao class submarine Credited with sinking 31 enemy ships totaling 227,800 tons, unequaled among American submarines during World War II. When she was sunk by a circular run of her final torpedo, several crew escaped the sinking boat with a Momsen lung, the only known occasion of its use. 78 men were lost and the nine survived. LAUNCHED: 1943, August 18 → FATE: Sunk by her own torpedo in the Taiwan Strait October 24, 1944. |
|
Page 11
|
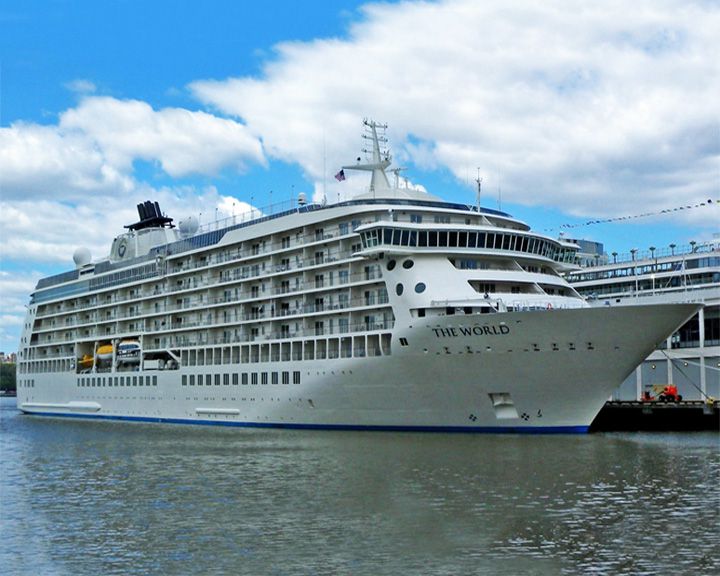 The World, MS — Swedish cruise ship A ship serving as a residential community owned by its residents. She became the largest passenger ship to transit the Northwest Passage by sailing from Nome, Alaska to Nuuk, Greenland in 25 days, August-September, 2012. LAUNCHED: 2002, March → FATE: Still in service. |
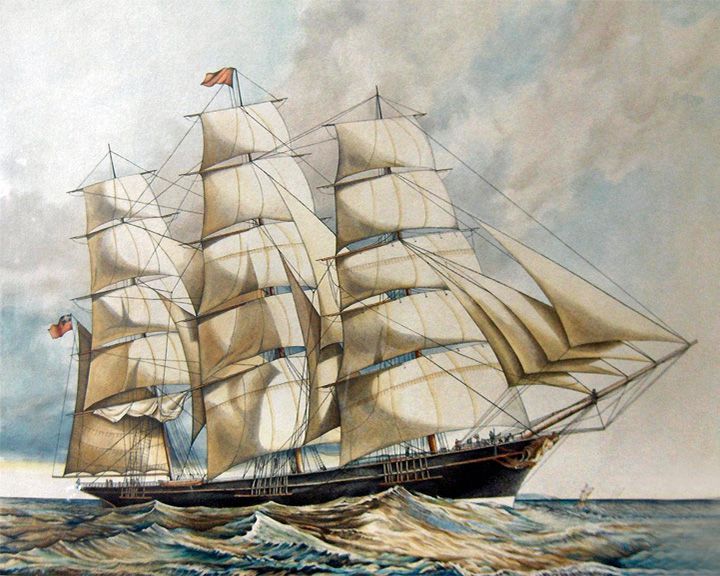 Thermopylae — English extreme clipper Raced the clipper Cutty Sark from Shanghai back to London and won by seven days. In 1897, she was sold to Portugal and renamed Pedro Nunes for used as a naval training ship. LAUNCHED: 1868, August → FATE: Sunk as target practice by the Portuguese Navy, October 13, 1907. |
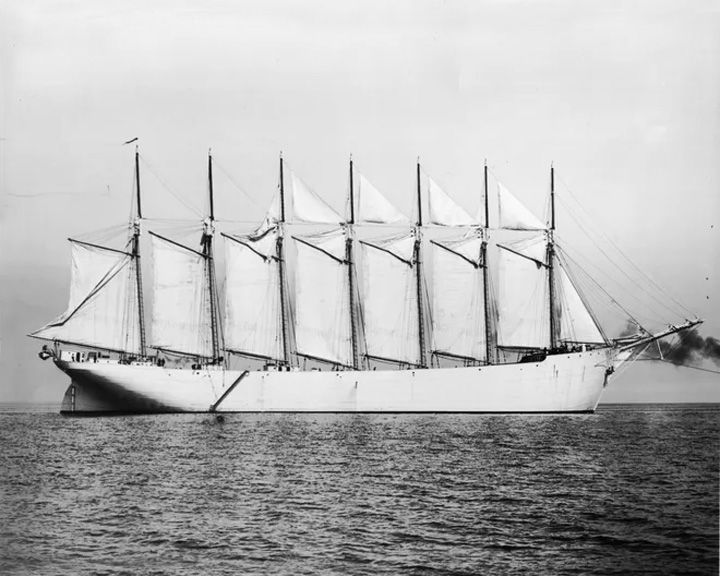 Thomas W. Lawson — American seven-masted schooner The largest schooner and largest sailing vessel without an auxiliary engine ever built. She proved problematic in the ports she was intended to operate in due to the amount of water she displaced. LAUNCHED: 1902, July, 10 → FATE: Sank in a storm while at anchor off Cornwall, England, in 1907 taking 16 of her crew with her. |
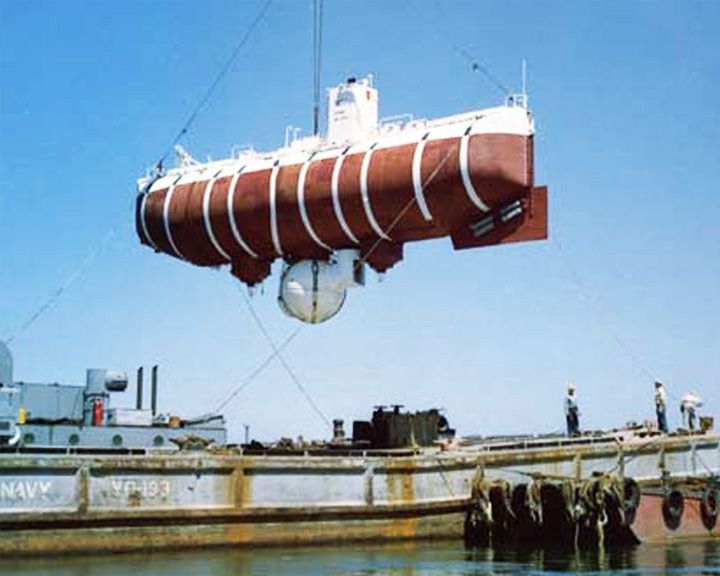 Trieste — Italian deep-diving research bathyscaphe; Swiss designed Dove to a record ocean depth of about 10,911 metres, or about 6.8 miles. She reached the ocean floor in the Mariana Trench on January 23, 1960. She found the missing submarine USS Thresher off the coast of New England in August of 1963. LAUNCHED: 1953, August 18 → FATE: On display at the U.S. Naval National Undersea Museum in Keyport, Washington. |
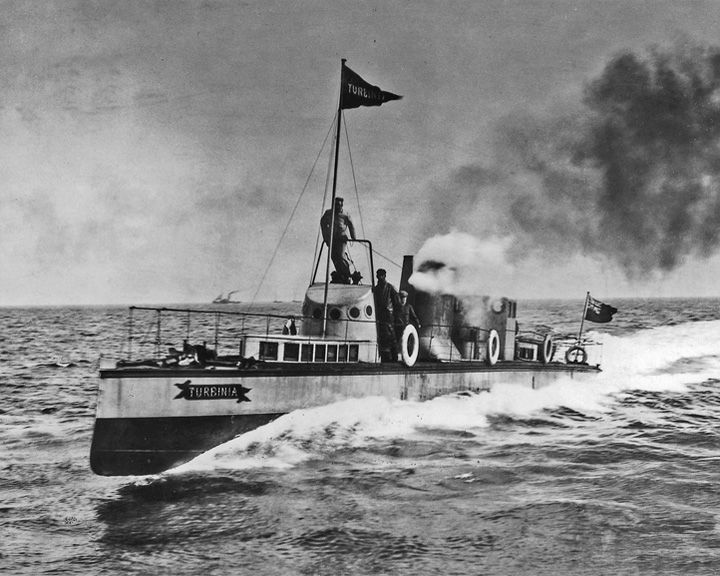 Turbinia — British steamship First steam turbine-powered steamship and the fastest ship in the world at that time at over 34 knots. She showed up unannounced at the Fleet Review for Queen Victoria's Diamond Jubilee at Spithead in 1897, racing up and down the ranks of other ships. LAUNCHED: 1894, August 18 → FATE: On display at the Discovery Museum at Newcastle upon Tyne, England. |
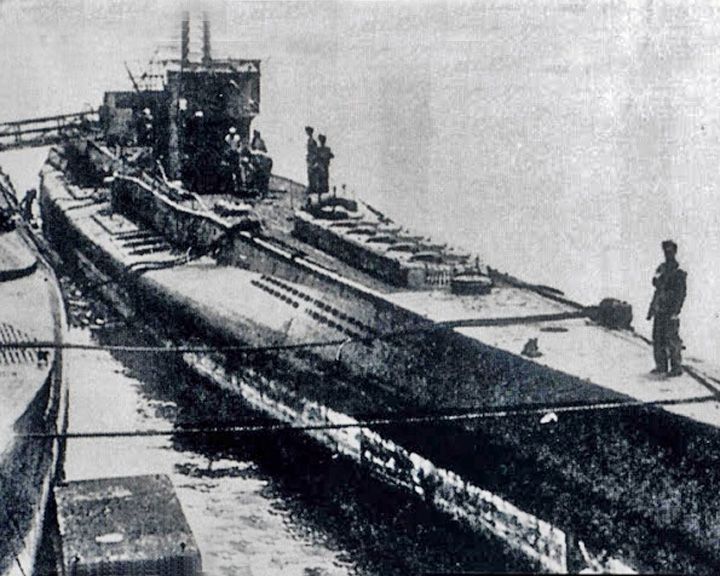 U-234 — German submarine Hitler's last submarine; ironically, there is an isotope of uranium designated U-234. While attempting to deliver uranium to Japan near the end of World War II, she surrendered to the United States on May 14, 1945. LAUNCHED: 1943, December → FATE: Sunk by torpedo November 20, 1947. |
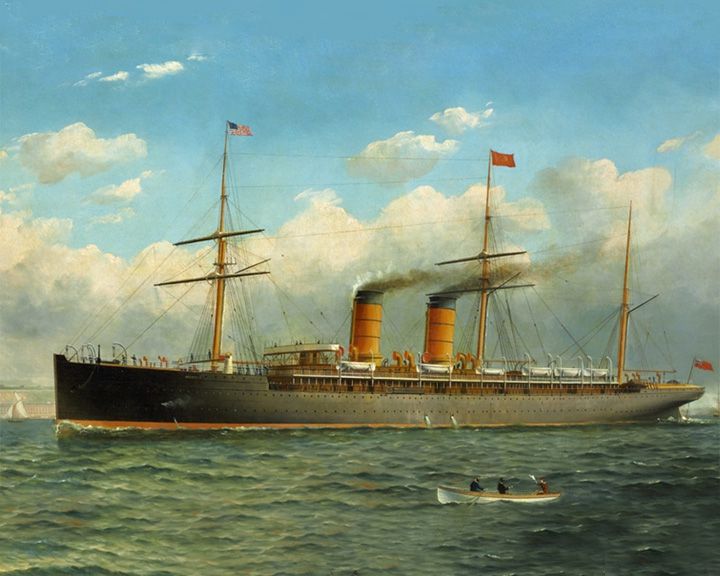 Umbria, RMS — British ocean liner With her sister ship, Etruria, the last two transatlantic ocean liners fitted with auxiliary sails. In May of 1903, the Mafia tried to blow her up but failed. LAUNCHED: 1884, June 18 → FATE: Scrapped in 1910. |
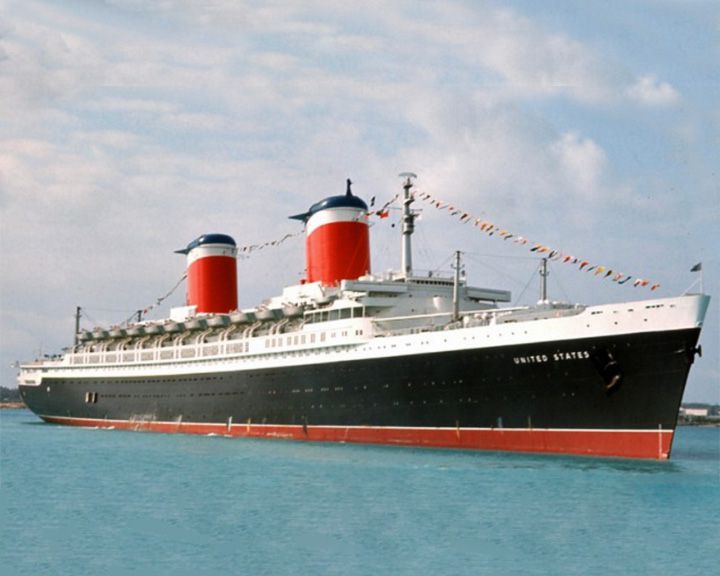 United States, SS — American ocean liner (steamship) The fastest liner ever built; virtually no wood used in her construction. On her maiden voyage she captured the Blue Riband with the fastest transatlantic crossing on record in 3 days, 10 hours, 40 minutes at an average speed of 35.59 knots. LAUNCHED: 1951, June 18 → FATE: As of February 7, 2012, work has begun on the restoration project to prepare the ship for her eventual rebuild. |
|
Page 12
|
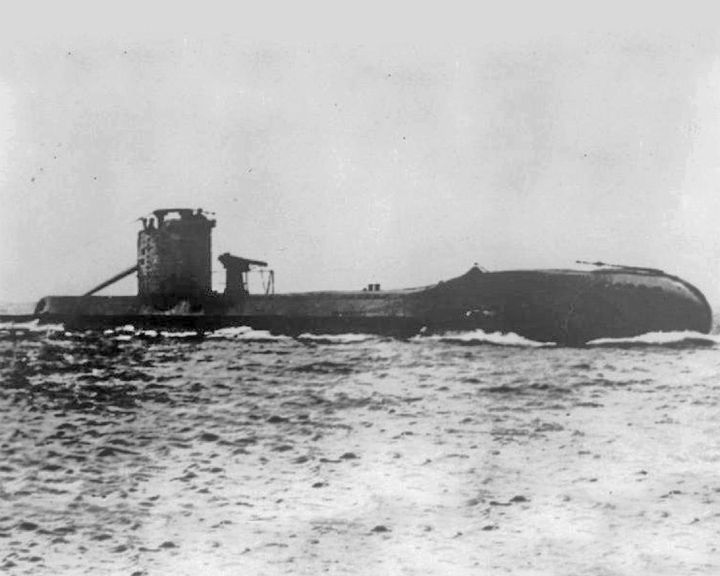 Upholder, HMS — British U-class submarine The most successful British submarine of the World War II sinking a gross tonnage of 93,031. She was one of four U-class submarines with 2 external torpedo tubes at the bows in addition to the 4 internal ones. LAUNCHED: 1940, July 8 → FATE: Lost northeast of Tripoli with all hands, probably sunk by enemy depth charges April 14, 1942. |
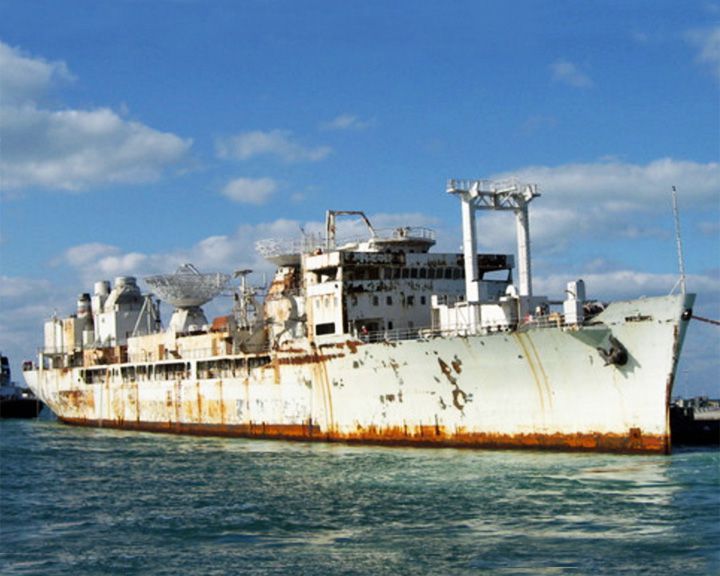 Vandenberg, USAFS — American transport ship Second-largest artificial reef in the world, after the aircraft carrier USS Oriskany. She transported troops in World War II. In 1998, she was featured in the film Virus as the Russian research ship Akademik Vladislav Volkov. LAUNCHED: 1943, October → FATE: Sank May 27, 2009, six miles off the Florida Keys. |
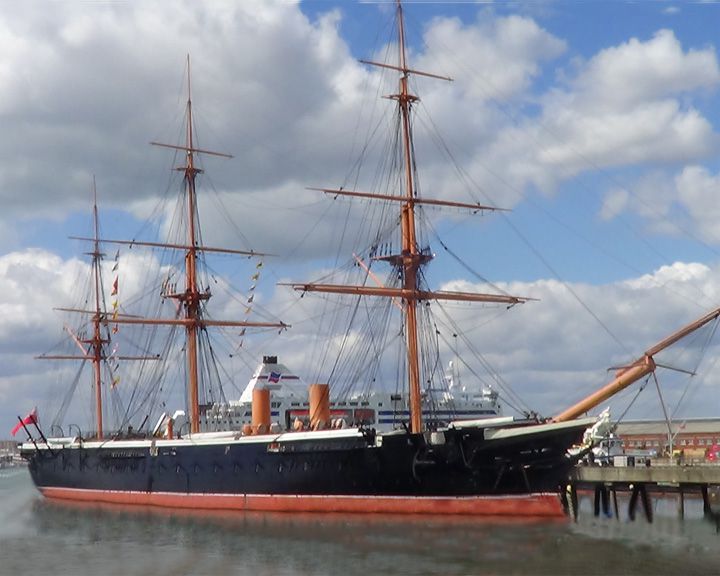 Warrior, HMS — British warship First British iron-hulled, armour-plated warship. She was the largest, fastest, most heavily armed and armored warship up to that time. LAUNCHED: 1860, December 18 → FATE: Currently berthed in Portsmouth, England as a museum. |
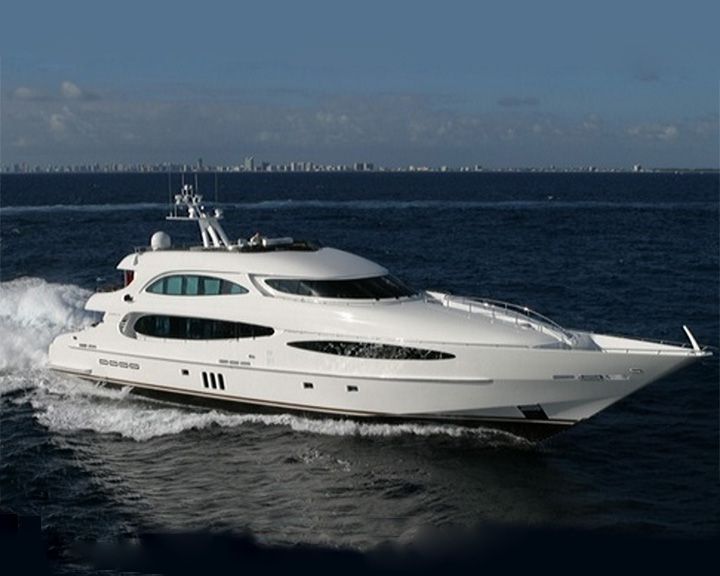 World is not Enough — American super yacht Fastest yacht in the world. She cruises at 50 knots and can reach speeds of up to 70 knots. LAUNCHED: 2005 → FATE: Still in use. |
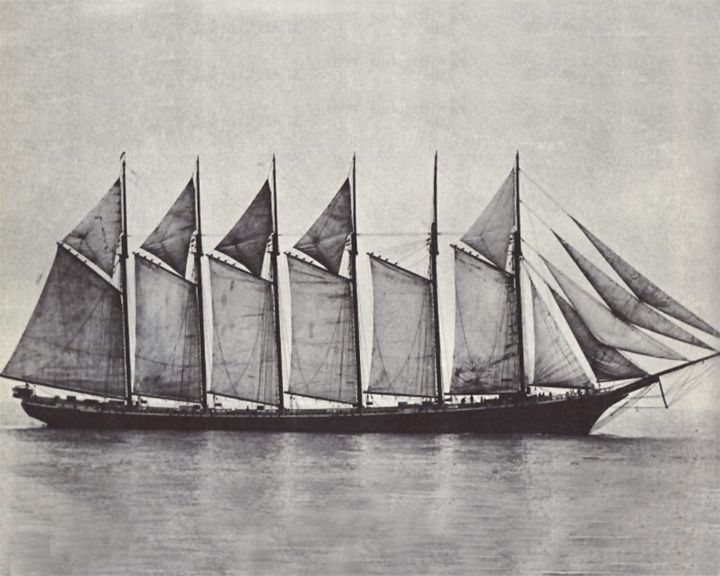 Wyoming — American six-masted schooner The largest known wooden ship ever built. Because of her length she tended to flex in heavy seas causing the long planks to twist and buckle, allowing water to seep into the hold. LAUNCHED: 1909, December 15 → FATE: Foundered in a storm in 1924 and sank off the coast of Cape Cod with the loss of all 14 crewmen. |
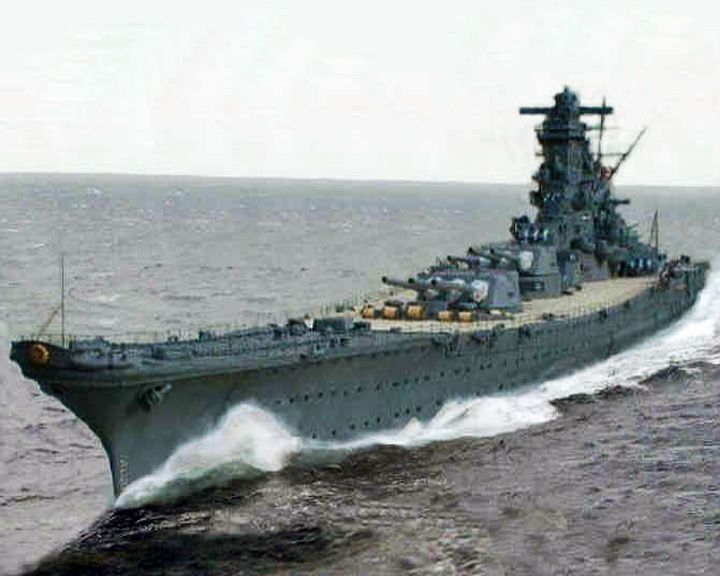 Yamato — Japanese battleship The largest, heaviest, and most powerful battleships ever constructed. She was the flagship of Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto during World War II. LAUNCHED: 1940, August 18 → FATE: Sunk north of Okinawa April 7, 1945. |
The number of All Countries Ships; Largest and Fastest listed is 93 The contents of this page are available under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license and the GNU Free Documentation License (GFDL). |
|
|
First Ship on each page
| |
| Page | Ship Name (Country and Type) |
| 1. | American Queen (American river paddle steamboat) |
| 2. | Bismarck (German battleship) |
| 3. | Color Magic (Norwegian cruise ferry) |
| 4. | Eos (American three-masted Bermuda rigged) |
| 5. | Grandcamp, SS (American liberty ship) |
| 6. | Jylland, HDMS (Danish screw-propelled steam frigate) |
| 7. | Massachusetts, USS (American South Dakota class battleship) |
| 8. | Ocean Dover, MV (Australian livestock carrier) |
| 9. | Rochambeau (American frigate) |
| 10. | Serpens, USS (American Crater-class cargo ship) |
| 11. | The World, MS (Swedish cruise ship) |
| 12. | Upholder, HMS (British U-class submarine) |
All Countries | |
| 1. | American Queen American river paddle steamboat |
| 2. | Andrea Doria, SS Italian ocean liner |
| 3. | Ariel English clipper ship |
| 4. | Atlantis German auxillary cruiser |
| 5. | Azzam Emirati luxury yacht |
| 6. | B-39 Russian foxtrot-class submarine |
| 7. | Bismarck German battleship |
| 8. | Black Pearl American yacht |
| 9. | Bluebird K7 British hydroplane |
| 10. | Bras d'Or, HMCS Canadian hydrofoil |
| 11. | Britannic, HMHS British ocean liner |
| 12. | Cavalier, HMS British C-class Destroyer |
| 13. | Champion of the Seas English clipper ship |
| 14. | Christina O Greek luxury yacht |
| 15. | Color Magic Norwegian cruise ferry |
| 16. | Costa Concordia Italian cruise ship |
| 17. | Darling, HMS British torpedo boat destroyer |
| 18. | Derbyshire, MV British cargo ship |
| 19. | Eastland, SS American steamship |
| 20. | Eclipse Russian luxury yacht |
| 21. | El Faro, SS American container ship |
| 22. | Empress of Ireland Canadian ocean liner |
| 23. | Eos American three-masted Bermuda rigged |
| 24. | Estonia, MS German cruise ferry |
| 25. | Eureka American paddle steamboat |
| 26. | Faith, SS American Concrete |
| 27. | Felicity Ace Japanese roll-on/roll-off cargo ship |
| 28. | Flying Cloud American clipper |
| 29. | Fram Norwegian schooner |
| 30. | Francisco, HSC Argentine high-speed catamaran |
| 31. | Grandcamp, SS American liberty ship |
| 32. | Great Eastern, SS British iron paddle steamboat |
| 33. | Great Republic American clipper |
| 34. | Gribshunden Danish warship |
| 35. | HD-4 American hydrofoil |
| 36. | Herald of Free Enterprise, MS British roll-on/rolll-off ferry |
| 37. | I-400 Japanese submarine |
| 38. | Icon of the Seas American cruise ship |
| 39. | Jylland, HDMS Danish screw-propelled steam frigate |
| 40. | Kirk, USS American destroyer escort, Knox-class |
| 41. | Kuru, SS Finnish steamship |
| 42. | L'Hydroptère French speed sailboat |
| 43. | LCT7074, HM British landing craft, tank (LCT) |
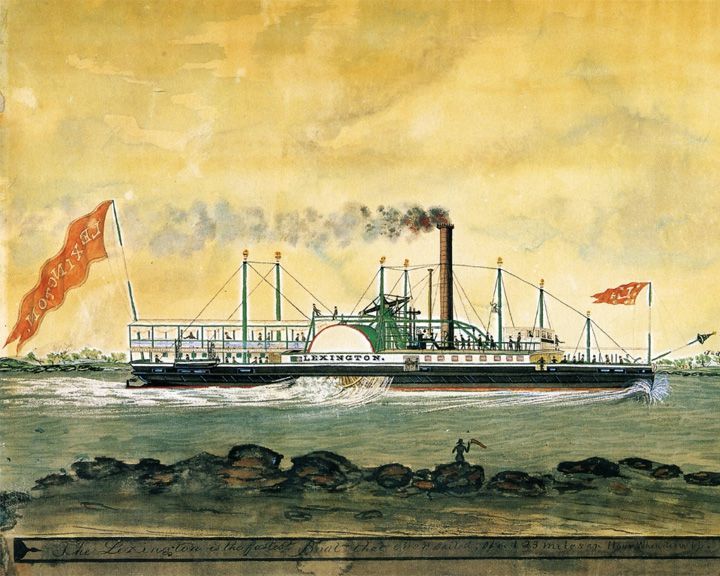
| 44. | Lexington American steamboat |
| 45. | Maltese Falcon American full-rigged |
| 46. | Mars Swedish three masted warship |
| 47. | Massachusetts, USS American South Dakota class battleship |
| 48. | Mauretania, RMS British ocean liner |
| 49. | Meredith Victory, SS American cargo ship |
| 50. | Monte Carlo, SS American concrete ship |
| 51. | MTB 102 British motor torpedo boat |
| 52. | Nimitz, USS American aircraft carrier |
| 53. | Norge, SS Norwegian, then Danish ocean liner |
| 54. | Normandie, SS French ocean liner |
| 55. | Ocean Dover, MV Australian livestock carrier |
| 56. | Oriskany, USS American aircraft carrier |
| 57. | Pinta, (La) Spanish three masted caravel |
| 58. | Pioneering Spirit Swiss catamaran |
| 59. | Preußen German windjammer |
| 60. | Princess Sophia, SS Canadian passenger ship |
| 61. | Queen Elizabeth, HMS British aircraft carrier |
| 62. | Robert E. Perry, SS American liberty ship |
| 63. | Rochambeau American frigate |
| 64. | Royal Clipper German tall ship |
| 65. | Royal George, HMS English first-rate ship of the line |
| 66. | Sailrocket 2 Australian speed sailboat |
| 67. | Saint John Paul II, MV Maltese catamaran |
| 68. | Santísima Trinidad Spanish ship of the line |
| 69. | Santa Maria Spanish carrack |
| 70. | Seawise Giant Japanese supertanker |
| 71. | Serpens, USS American Crater-class cargo ship |
| 72. | Slo-mo-shun IV American racing hydroplane |
| 73. | SN.R4 British Mountbatten class hovercraft |
| 74. | Sovereign of the Seas, HMS English full-rigged |
| 75. | Susan Constant British fully-rigged ship |
| 76. | Sydney, HMAS Australia Leander-class light cruiser |
| 77. | Syracusia Greek cargo ship |
| 78. | Tang, USS American Balao class submarine |
| 79. | The World, MS Swedish cruise ship |
| 80. | Thermopylae English extreme clipper |
| 81. | Thomas W. Lawson American seven-masted schooner |
| 82. | Trieste Italian deep-diving research bathyscaphe |
| 83. | Turbinia British steamship |
| 84. | U-234 German submarine |
| 85. | Umbria, RMS British ocean liner |
| 86. | United States, SS American ocean liner |
| 87. | Upholder, HMS British U-class submarine |
| 88. | Vandenberg, USAFS American transport ship |
| 89. | Warrior, HMS British warship |
| 90. | World is not Enough American super yacht |
| 91. | Wyoming American six-masted schooner |
| 92. | Yamato Japanese battleship |
|
About the Data There are more than 400 ships in this database, but the initial list is only for famous ships names that begin with letters "A-B". For other listings, use the country and type tabs. Touching (or cursor over) a ship image produces an enlargement. Touch anywhere else (or move the cursor off the image) to close the larger image. Touching (or clicking on) any underlined name will link to a page with more information. Although submarines are usually called boats, they are grouped with ships here. Most of the information comes from Wikipedia. |
^
Other Pages in Names Galore: | |
Famous Cowboy Names Sports Team Names Other Name Lists | Name Generators Naming Fun Stories about Names |