|
|
All Countries Warships, not in World Wars
|
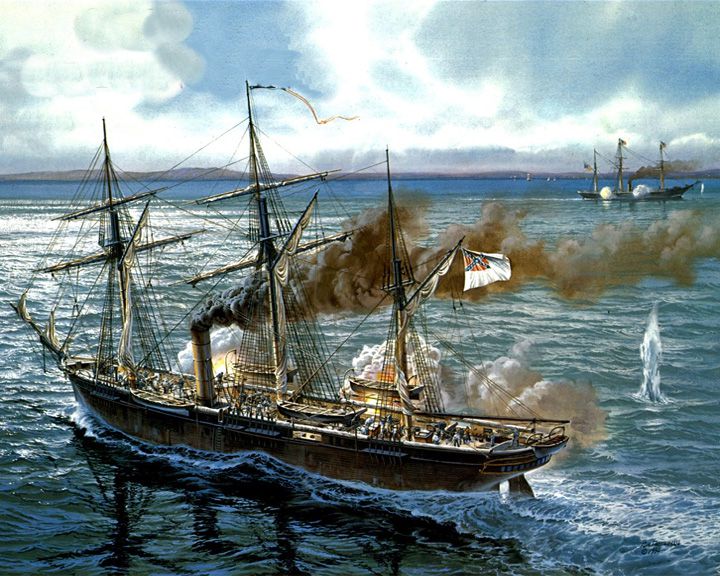 Alabama, CSS — American Confederate screw sloop-of-war A successful commerce raider that attacked Union merchant and naval ships during the American Civil War. She boarded nearly 450 vessels and captured or burned 65 Union merchant ships. LAUNCHED: 1862, July 18 → FATE: Sunk in June 1864 by USS Kearsarge at the Battle of Cherbourg. |
 (Another (Another Albert M. Boe — American liberty ship Last Liberty ship built. Though currently landlocked, she is still in use as the home of Trident Seafoods. The ship was withdrawn from the reserve fleet on 19 August 1964 and converted for use as the fish cannery ship Star of Kodiak. LAUNCHED: 1945, September 18 → FATE: Converted to a fish cannery ship in 1964. |
 Alligator — American submarine First U.S. Navy submarine. The first American submarine, called Turtle (1776), never served in the U.S. Navy. The first commissioned U.S. submarine was the USS Holland in 1862. LAUNCHED: 1862, May 18 → FATE: Sank in bad weather off Cape Hatteras April 2, 1863. |
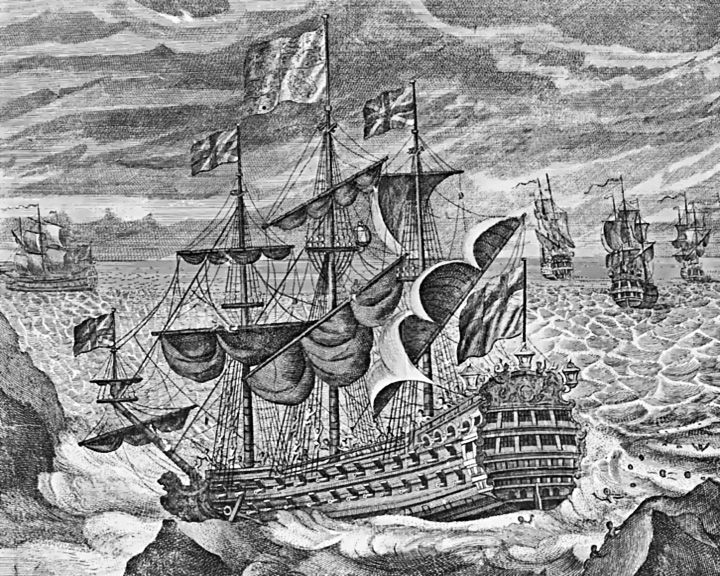
 (Another (Another Ark Royal, HMS — English galleon English flagship that fought against the Spanish Armada. During the reign of James VI and I, she was renamed Anne Royal. Several British aircraft carriers have been named Ark Royal. LAUNCHED: 1587 → FATE: Accidentally sunk in April of 1636; raised and broken up in 1638. |
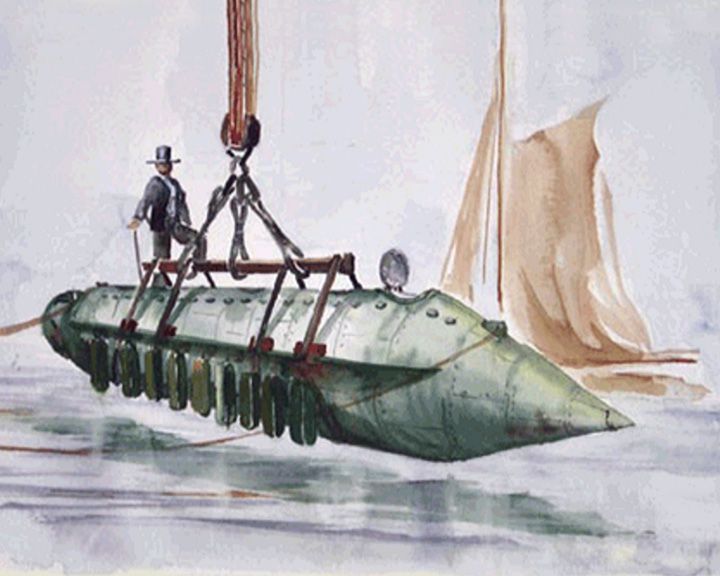
 Association, HMS — British second-rate ship of the line After serving with distinction at the capture of Gibraltar, she ended up lost in a storm and wrecked with 3 other ships with the loss of nearly 2,000 lives. The rediscovery of the Association and so many historical artefacts led to legislation such as the Protection of Wrecks Act to preserve British historic wreck sites. LAUNCHED: 1697 → FATE: Wrecked of the Isles of Scilly October 22, 1707. |
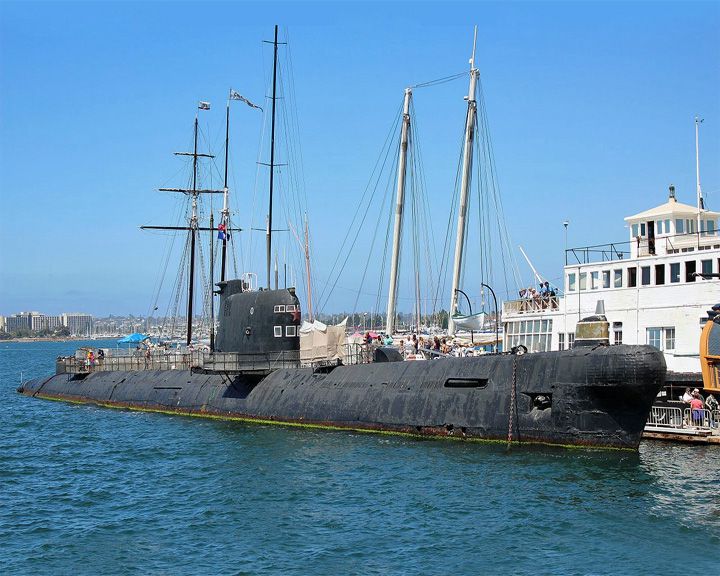 B-39 — Russian foxtrot-class submarine The Soviet Navy's largest non-nuclear submarines.. In 2012, she was used as a prop in the movie Phantom. Another B-39 is rusting in England (see Black Widow). LAUNCHED: 1967, April 18 → FATE: Decommissioned April 1994; now a museum ship at the Maritime Museum of San Diego, California. |
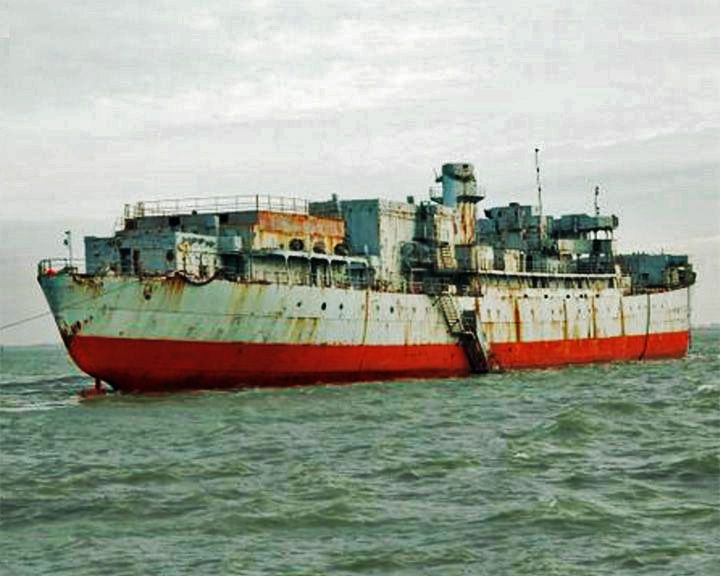
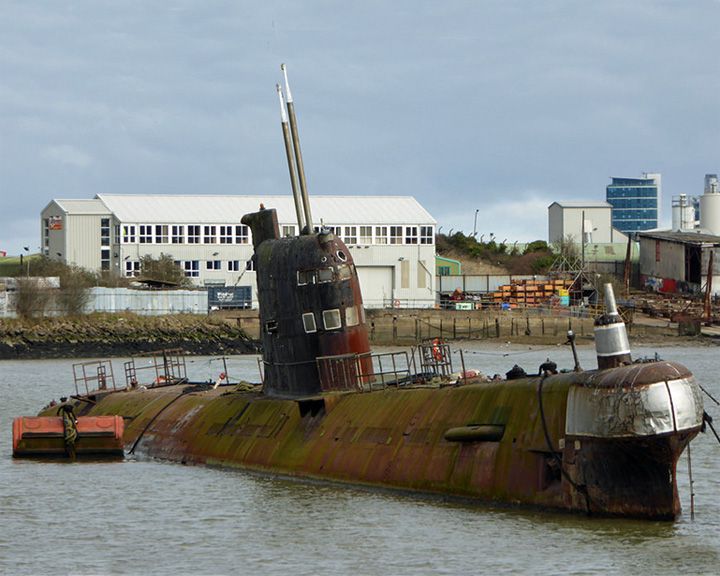 Black Widow — Russian foxtrot-class submarine The rusting boat had been a museum ship for several years in the early 2000s at Folkestone in England. Submarine U-475 Black Widow was a Soviet Navy submarine of the late 20th century. She was sold by the Soviet Navy in 1998 and became a museum ship. Another Foxtrot B-39 is moored at San Diego as a museum ship (see B-39). LAUNCHED: 1966, December 18 → FATE: Decommissioned in 1994 and sold; she is in a state of disrepair awaiting restoration at River Medway. |


|
Page 2
|
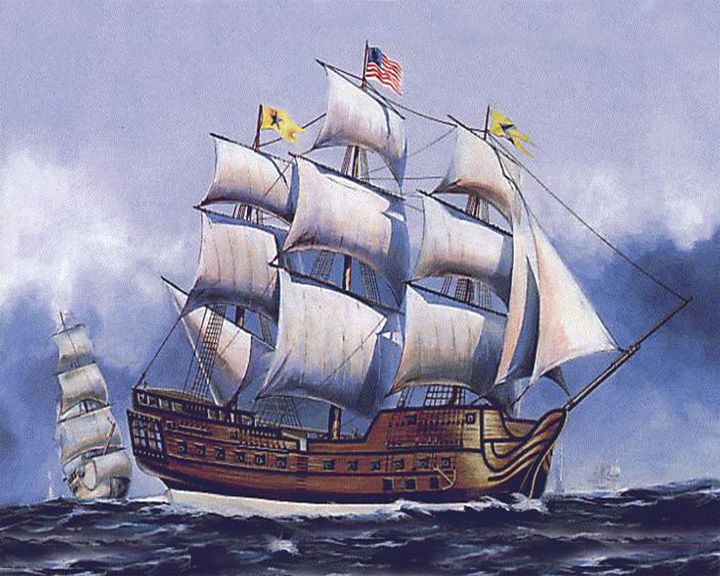 Bonhomme Richard, USS — American frigate Warship commanded by John Paul Jones. She defeated HMS Serapis in the Battle of Flamborough Head. LAUNCHED: 1766 → FATE: Sank in battle off the coast of Yorkshire September 25, 1779. |
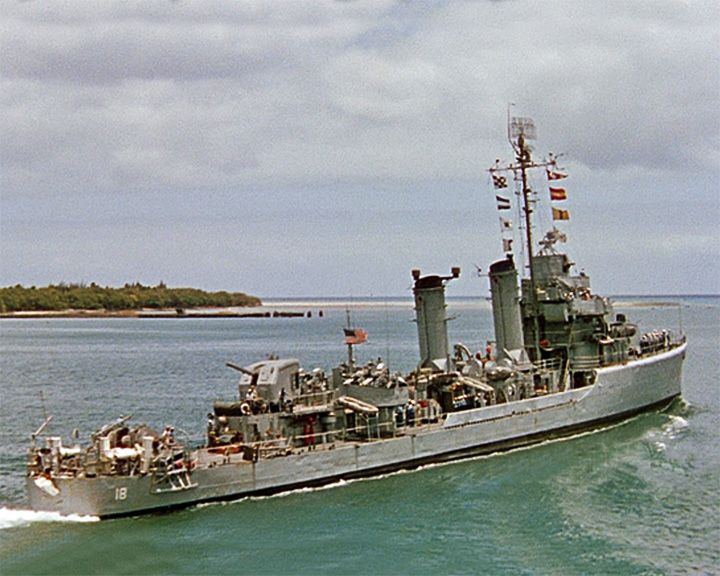 Caine, USS — American destroyer minesweeper The vessel captained by Queeg in the 1951 book The Cain Mutiny and the 1954 movie. In the movie, the USS Thompson (DD-627) was used as the USS Caine. LAUNCHED: 1951, novel, 1954 movie → FATE: Inconclusive. |
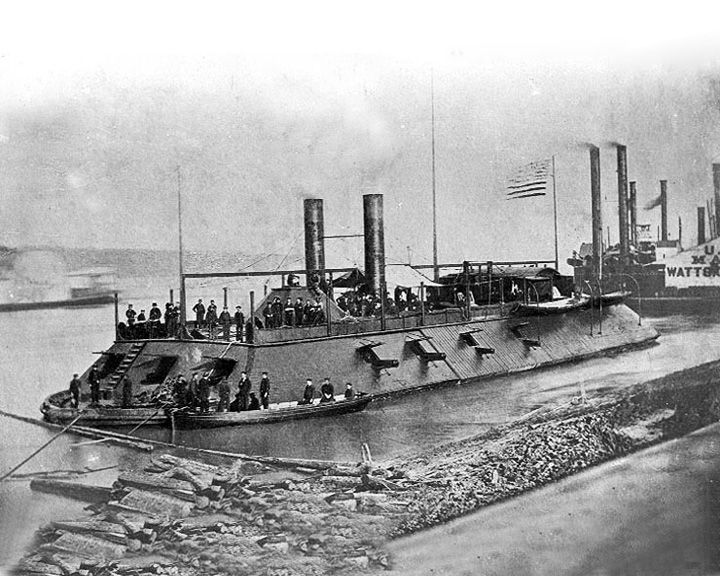 Cairo, USS — American ironclad gunboat First ship sunk by a naval mine and first vessel of the City class ironclads. Served with the Army's Western Gunboat Fleet during the American Civil War. Remnants of the gunboat are in a museum in the Vicksburg National Military Park. LAUNCHED: 1861 → FATE: Sunk by a naval mine in the Yazoo Riveron December 12, 1862. |
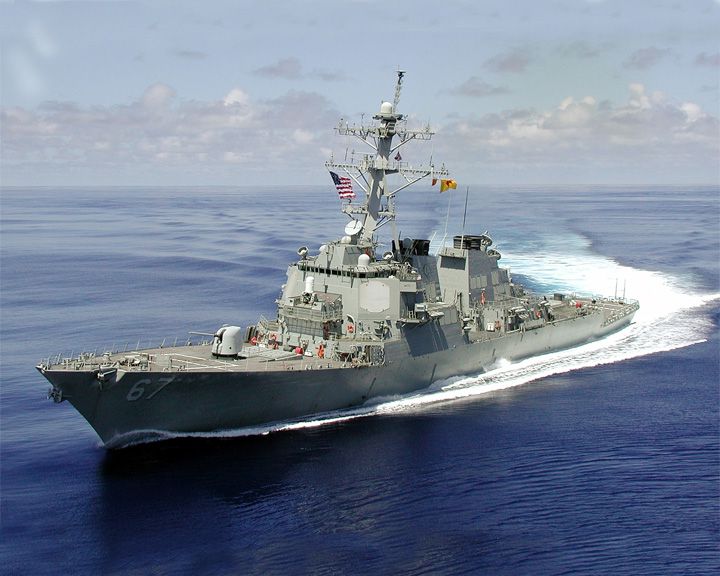 (Another (Another Cole, USS — American aegis-equipped guided missile destroyer In the news because of a suicide attack against it on October 12, 2000. Seventeen American sailors were killed in the incident while harbored in the Yemeni port of Aden. LAUNCHED: 1995, February 18 → FATE: Still in service. |
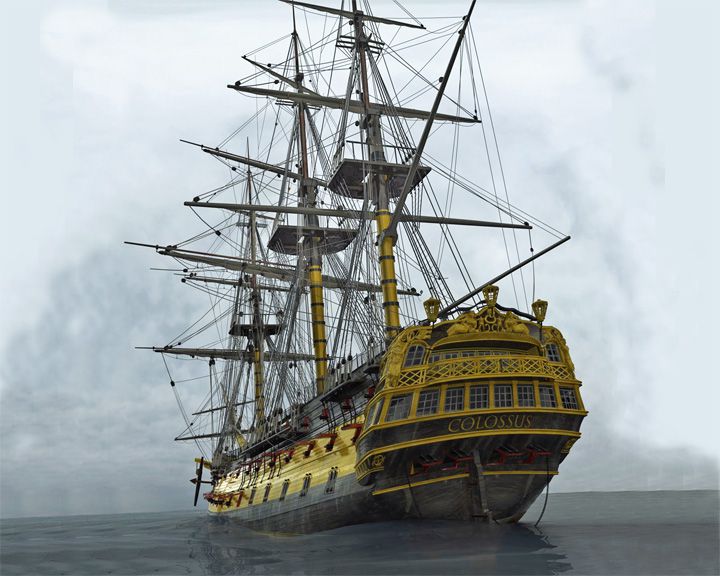 Colossus, HMS — British third-rate ship of the line After many battles and much glory, she lost her way and ran aground and sunk with one fatality. In 1974, fragments from the Colossus were discovered and reconstructed and are now displayed at the British Museum in London. LAUNCHED: 1787, April → FATE: Wrecked of the Isles of Scilly December 10, 1798. |
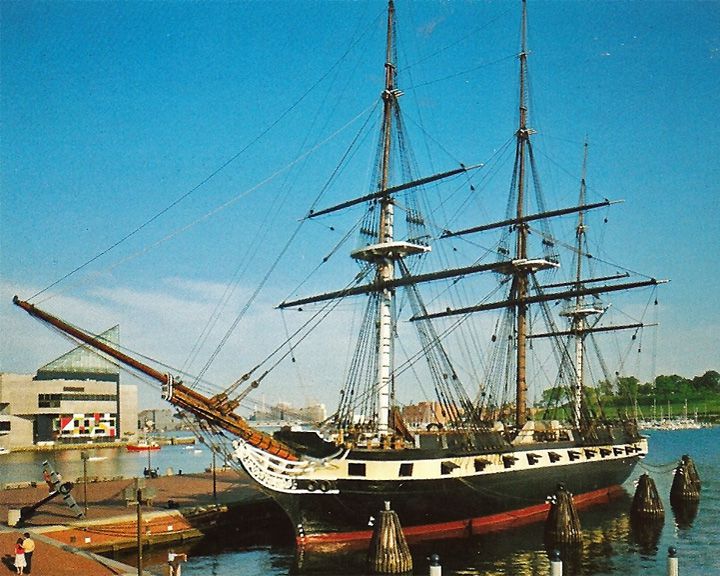 Constellation, USS — American sloop-of-war The last sail-only warship designed and built by the U.S. Navy. This flagship of the USN African Squadron from 1859-1861 disrupted the African slave trade off the coast of Africa. LAUNCHED: 1854, August 18 → FATE: On display at Annapolis, Maryland as a museum ship. |
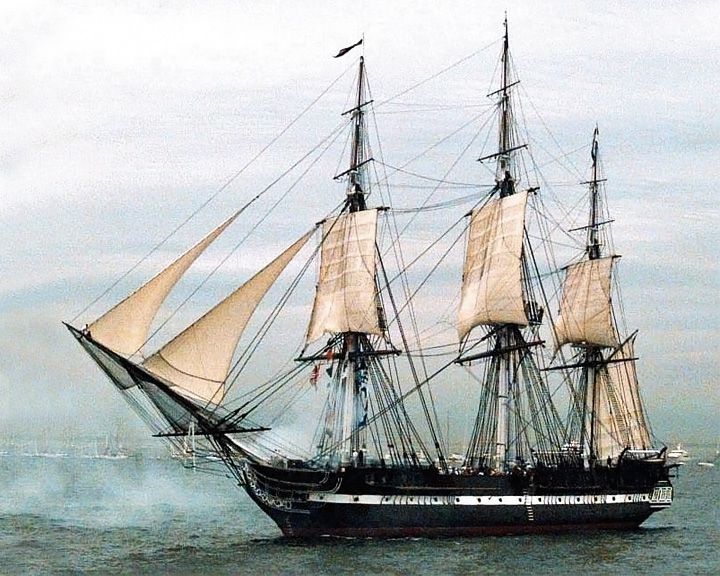 Constitution, USS — American three-masted heavy frigate Oldest commissioned ship afloat in the world. She was larger and more heavily armed than the standard frigates of the period. LAUNCHED: 1797, October 18 → FATE: On display at the Boston Navy Yard as a museum ship. |
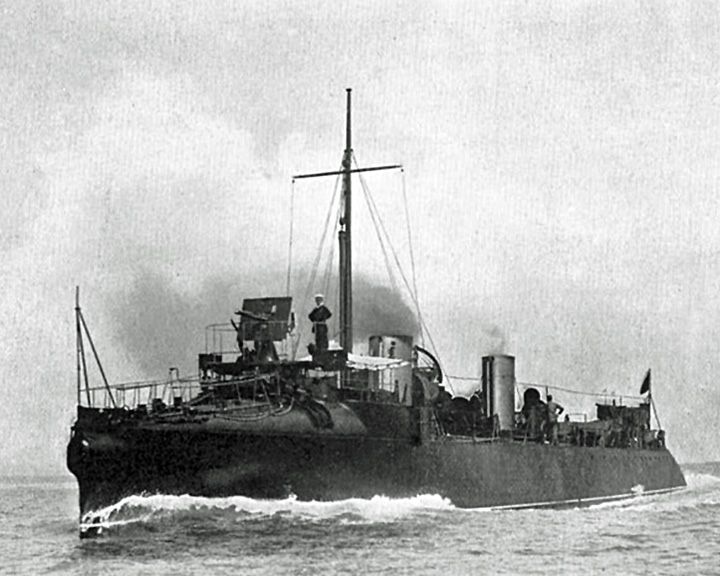 Darling, HMS — British torpedo boat destroyer First destroyer-type ship. Created to defend against torpedo boats. She was described at the time as the "fastest boat ever" having achieved a speed over 28 knots. LAUNCHED: 1893, November 18 → FATE: Scrapped in 1912. |
|
Page 3
|
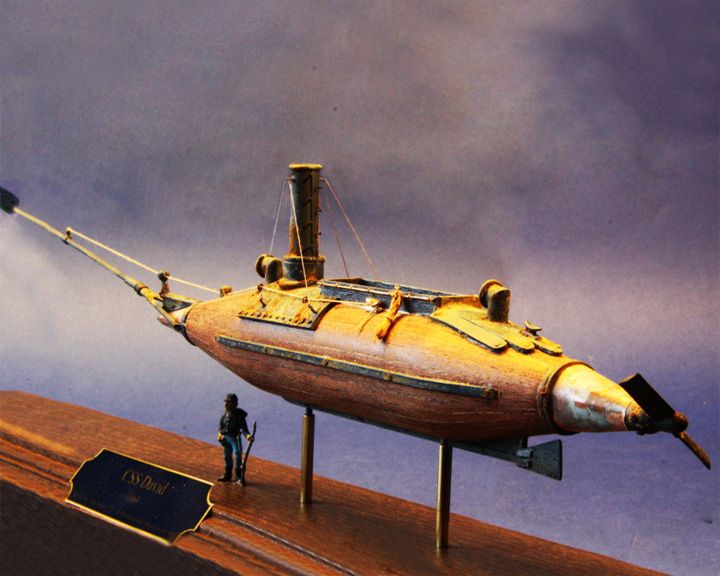 (Another (Another David, CSS — American Confederate torpedo boat A cigar-shaped boat with explosives on the end of a spar projecting forward from her bow. Surface vessel designed to operate very low in the water, resembling a submarine. LAUNCHED: 1863 → FATE: Unknown. |
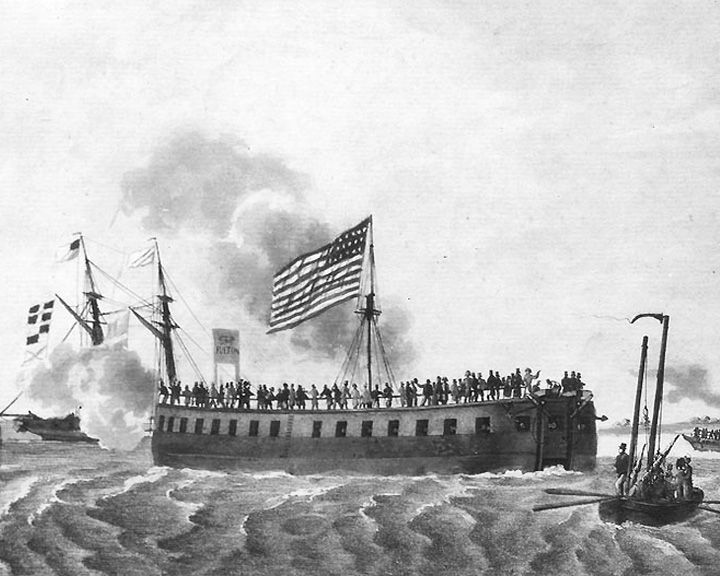 (Another (Another Demologos — American paddle steamers with a catamaran hull First warship to be propelled by a steam engine. Designed by Robert Fulton, with the steam engine between a double hull, no other ship like her was ever built. (See "Another IMAGE" for cross view of her structure.) LAUNCHED: 1815 → FATE: Accidentally blown up in the Brooklyn Navy Yard on June 4, 1829. |
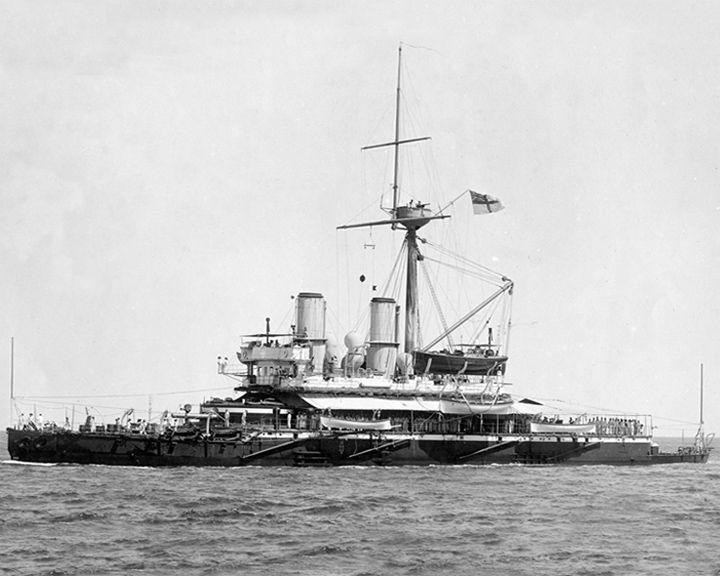

Devastastion, HMS — British Devastation-class ironclad The first ocean-going capital ship not carry sails, and the first with the entire main armament mounted on top of the hull rather than inside it. Originally conceived as a ocean-going breastwork monitor, she was redesignated as 2nd Class Turret ships in 1886 and finally as 2nd Class Battleships by the 1900. LAUNCHED: 1874 → FATE: Was scrapped in 1908. |
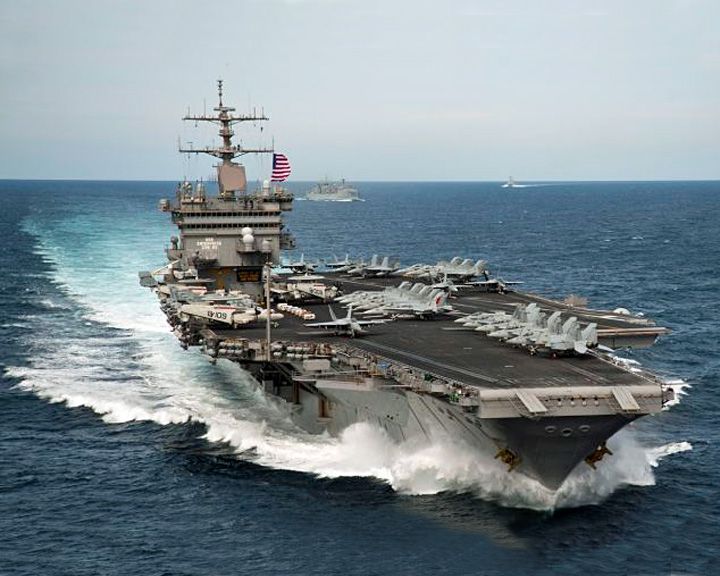 Enterprise, USS — American aircraft carrier World's first nuclear powered aircraft carrier and the eighth U.S. Naval vessel to bear the name. As one of the oldest carriers in the fleet, she was deactivated in 2012 at which time a Gerald R. Ford class carrier, CVN-80, will inherit the name Enterprise. LAUNCHED: 1960, September 18 → FATE: Put in storage in 2017. |
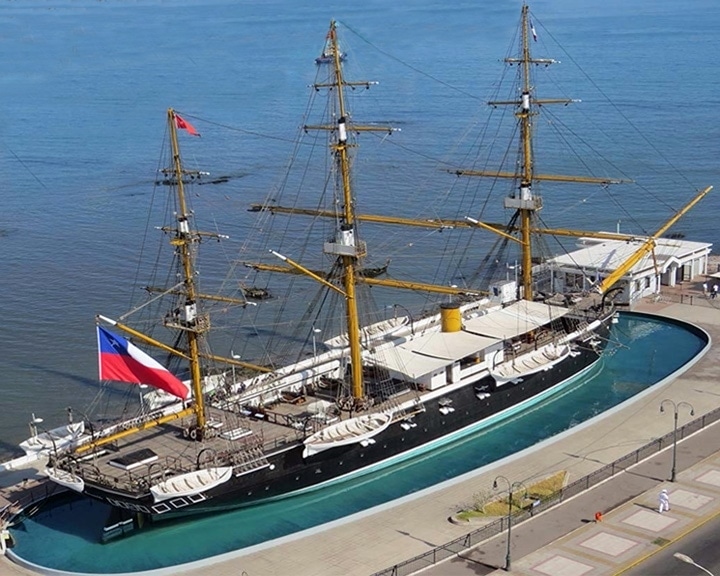 (Another (Another Esmeralda — Chilean wooden hull steam corvette Engaged the Peruvian ironclad Huáscar in the Battle of Iquique despite the material superiority of the Peruvian ship. A replica of Esmeralda is a museum ship in Iquique, Chile. LAUNCHED: 1855, June 26 → FATE: Rammed and sunk on 21 May 1879 at the Battle of Iquique during the War of the Pacific. |
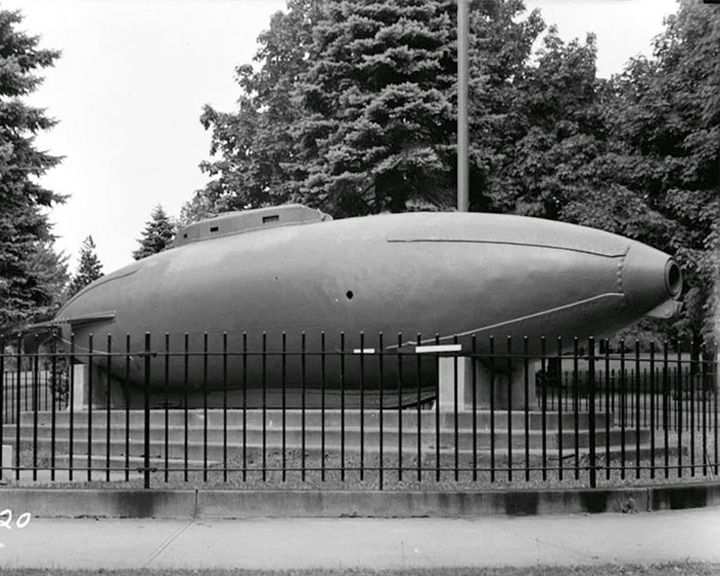 Fenian Ram — American submarine The second experimental submarine built by Irish-born inventor and educator John P. Holland. In 1916, she was exhibited in Madison Square Garden to raise funds for victims of the Easter Rising. LAUNCHED: 1881 → FATE: On exhibit at the Paterson Museum in Paterson, New Jersey. |
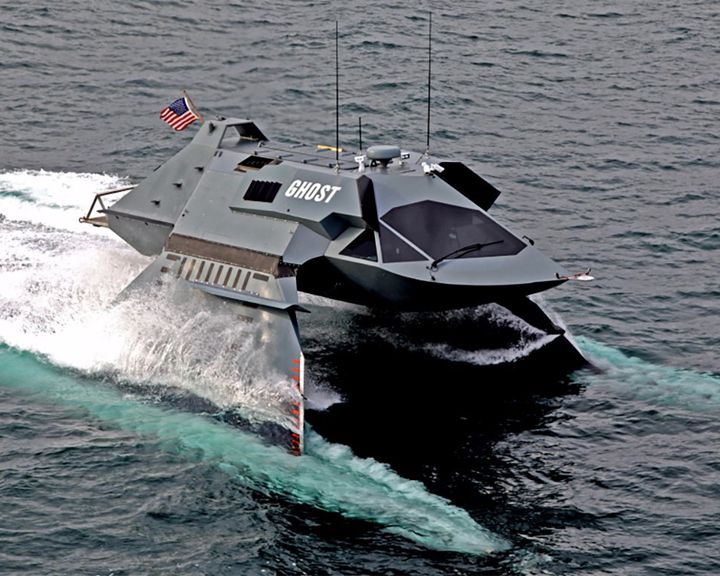 Ghost, stealth ship — American super-cavitating stealth ship A prototype ship for stealth operations designed by a private American company, Juliet Marine Systems. Designed to travel above the water's surface, her main hull is positioned atop by two long and narrow struts. LAUNCHED: 2009, (trials in 2011) → FATE: Its future is uncertain. |
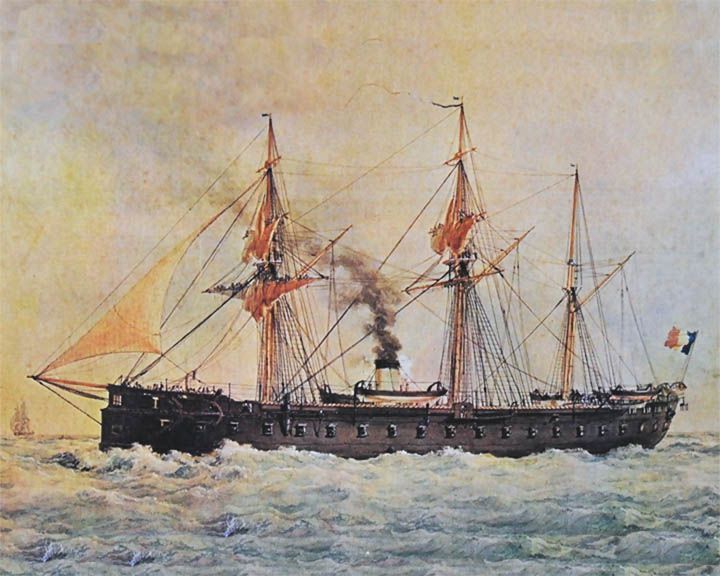 Gloire — French ocean-going ironclad First ocean-going ironclad, developed in response to navel gun technology, including the Paixhans gun, thus rendering obsolete traditional unarmoured wooden ships-of-the-line. She was constructed with light barquentine sails as well as a steam-powered screw. LAUNCHED: 1859, November 18 → FATE: Scrapped in 1883. |
|
Page 4
|
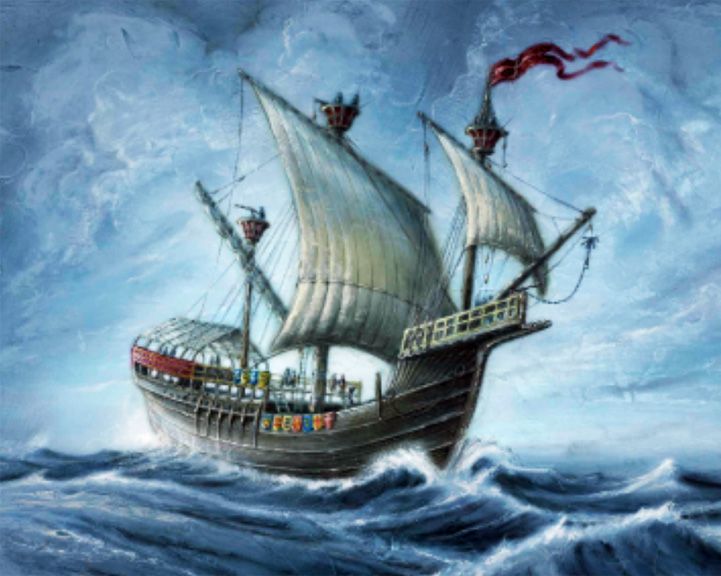 Gribshunden — Danish warship, one of the first carvel-built vessels and among the earliest armed with guns. She was the flagship of the King of Denmark, Hans, on her way to a political summit with the Swedish leader when she sank, killing a number of those aboard and the summit. In 2015, the wreckage attracted international attention when a near perfectly-preserved wooden figurehead of a mythical beast was brought to the surface. LAUNCHED: 1485 → FATE: In 1495, she sank after an accidental fire while in the Baltic Sea off the coast of Ronneby in southeastern Sweden. |
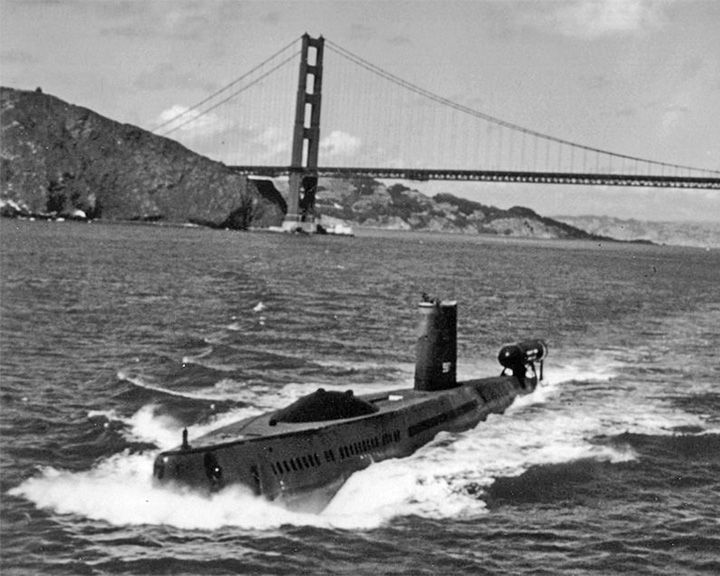 Halibut, USS — American attack submarine Unique nuclear-powered guided missile submarine, adapted for spying operations. In the 1970s, she was used on secret underwater espionage missions by the US against the Soviet Union including the underwater tapping of a Soviet communication line (see Operation Ivy Bells). LAUNCHED: 1959, January 9 → FATE: Moth-balled 1976, dismantled in 1994. |
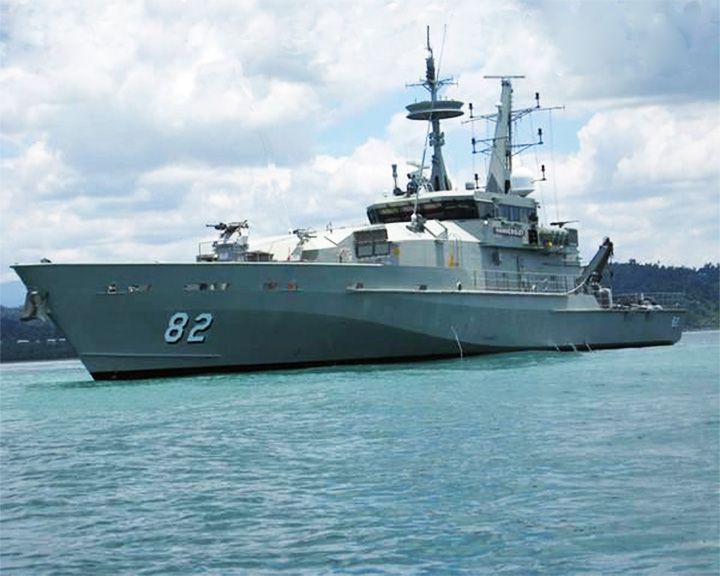 Hammersly, HMAS — Australian Armidale-class patrol boat Setting for the Australian television drama Sea Patrol, from 2007-2011. Several ships were used in filming; first portrayed by two real Fremantle-class patrol boats, then for the second season, two Armidale-class patrol boat were used to represent Hammersley LAUNCHED: 2007 → FATE: Inconclusive. |
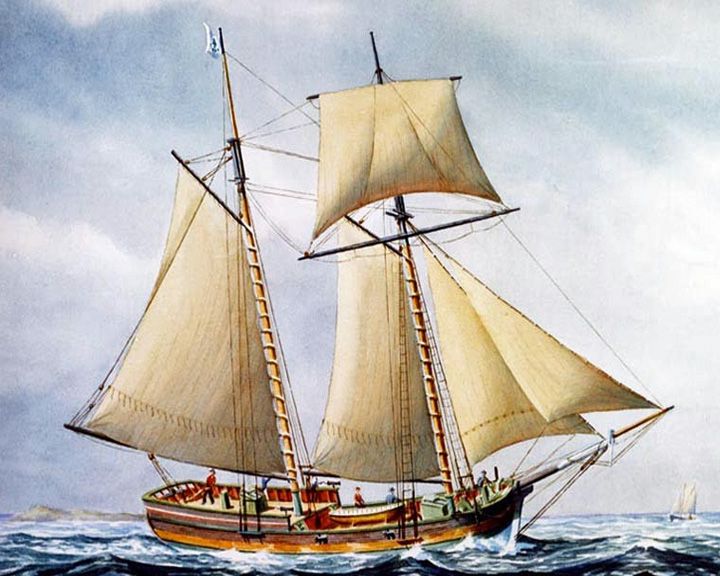 Hannah, USS — American schooner The first armed American naval vessel of the American Revolution and is claimed to be the founding vessel of the US Navy. The city of Beverly, Massachusetts and the town of Marblehead, Massachusetts each claim to have been the home port of the schooner. LAUNCHED: 1775, September 2 → FATE: Unknown. |
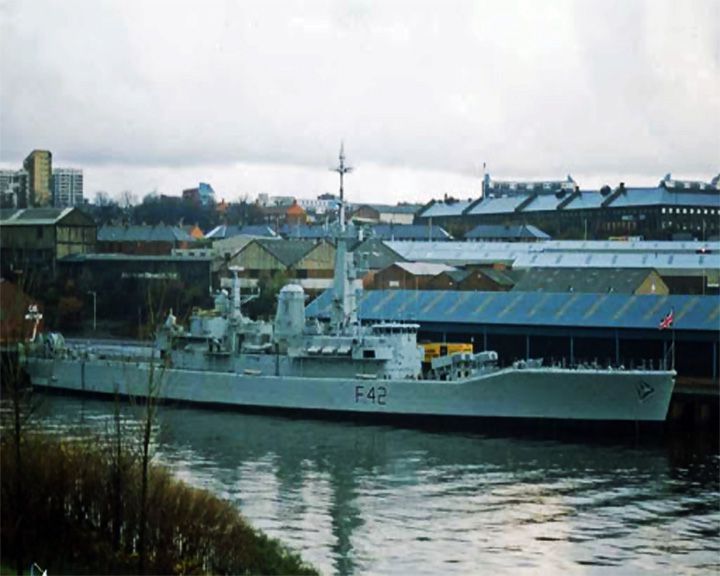 Hero, HMAS — British Leander-class frigate Setting for the popular British television series Warship, from 1973-1977. Seven different frigates played the role of HMS Hero, all were repainted with the pennant number F42 of HMS Phoebe, the main warship used for filming. LAUNCHED: 1973 → FATE: Inconclusive. |
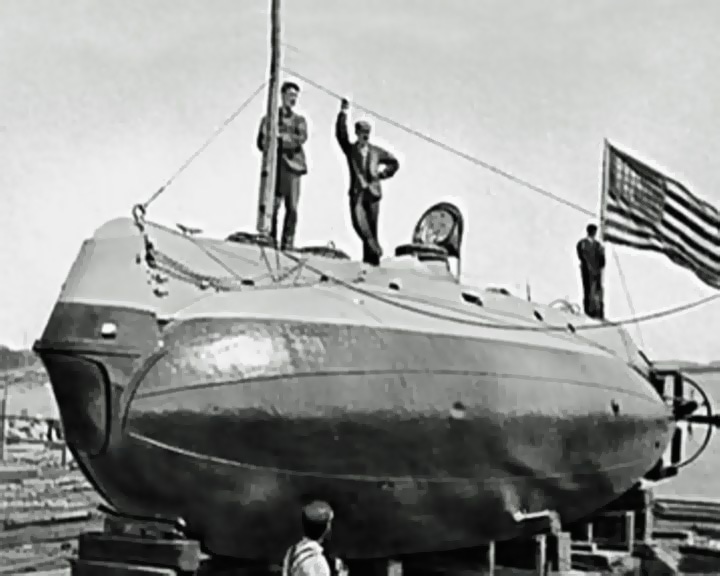 Holland, USS (SS-1) — American submarine First modern commissioned submarine for the US Navy. She proved valuable for experimental purposes in collecting data for submarines under construction or contemplation and for training officers and enlisted men. LAUNCHED: 1897, May 17 → FATE: On display in a park in Paterson, New Jersey until sold for scrap, 1932. |
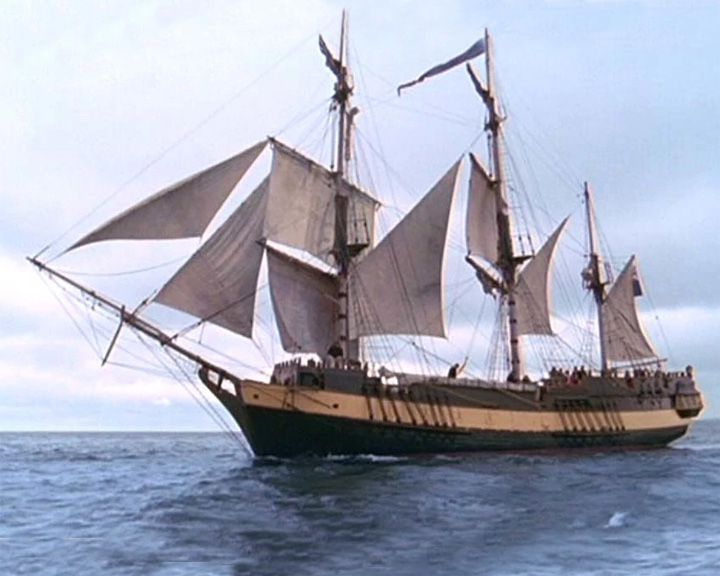 Hotspur, HMS — British sloop-of-war Ship of Horatio Hornblower in the book series and British TV series Hornblower and the Hotspur by C. S. Forester. In the TV series, she is captured by the French. After Hornblower and the crew later discover the ship, they succeed in retaking it. LAUNCHED: 1962, for the book; 1988 2003 for the TV series → FATE: Unknown. |
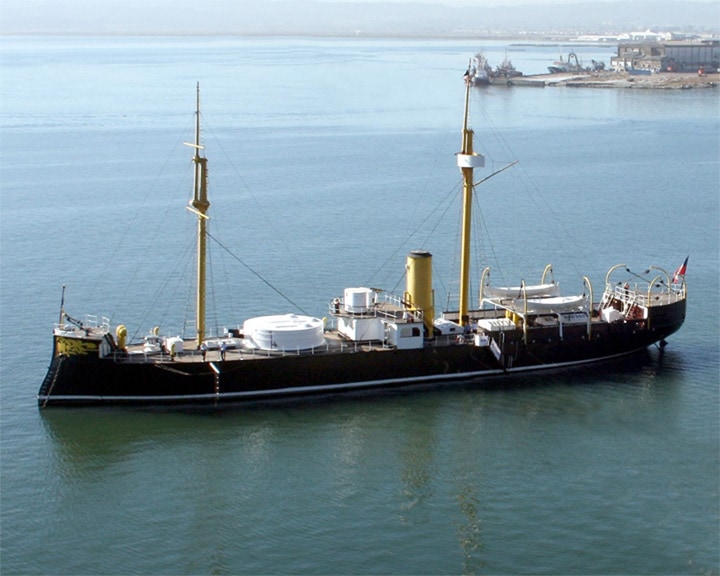 (Another (Another Huáscar — Peruvian iron-clad turret ship The flagship of the Peruvian Navy and participated in the Battle of Pacocha and the War of the Pacific of 1879–1883. She is the second oldest armored warship afloat and the oldest monitor afloat LAUNCHED: 1865, October 6 → FATE: She was restored and is a memorial ship anchored in Talcahuano, Chile. |
|
Page 5
|
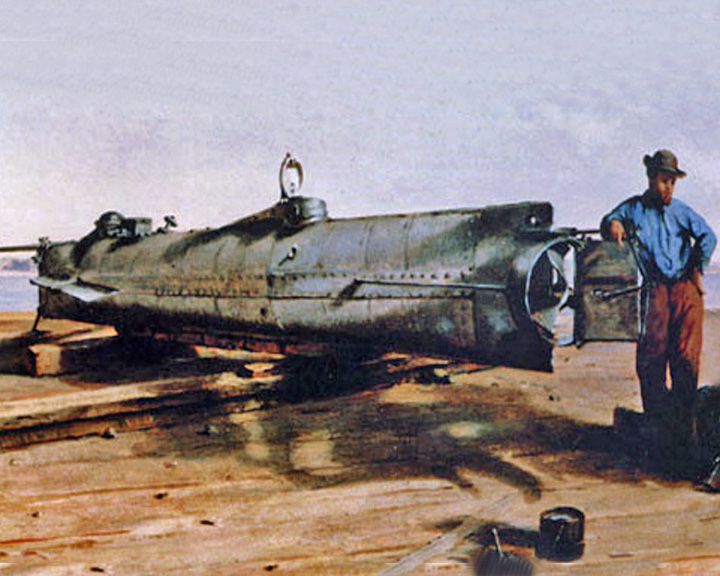 Hunley, H.L. — American Confederate submarine During the American Civil War, the first submarine to sink a ship. She a ttacked by embedding a barbed spar torpedo into the foe's hull and detonating it as she backed away. LAUNCHED: 1863, July → FATE: Sank after attacking and sinking USS Housatonic in Charleston Harbor, February 17, 1864. |
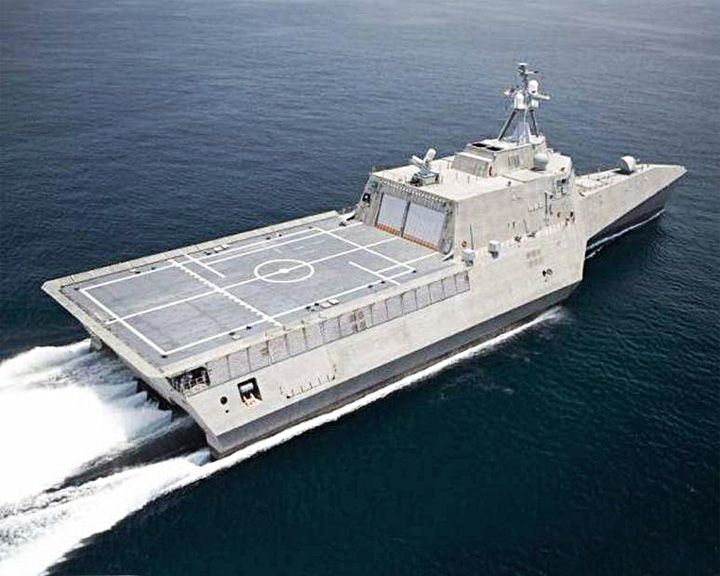 Independence, USS — American trimaran, small assault transport ship A versatile multi-hulled U.S. Navy ship designed for high speed. The ship is a trimaran design that can make more than 40 knots (74 km/h; 46 mph). LAUNCHED: 2008, April 18 → FATE: Currently in service. |
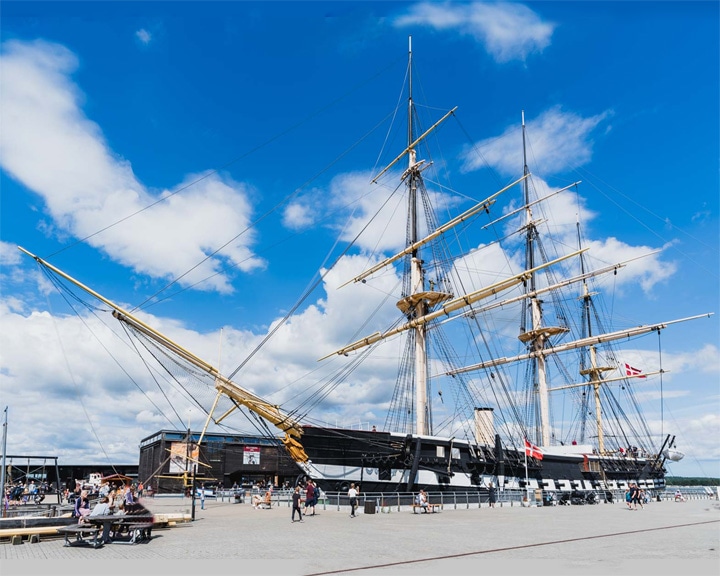 Jylland, HDMS — Danish screw-propelled steam frigate The world's largest wooden warship still in existence. She took part in the Battle of Heligoland May 9, 1864 LAUNCHED: 1860, November 20 → FATE: She is preserved as a museum ship in the small town of Eblet, Denmark. |
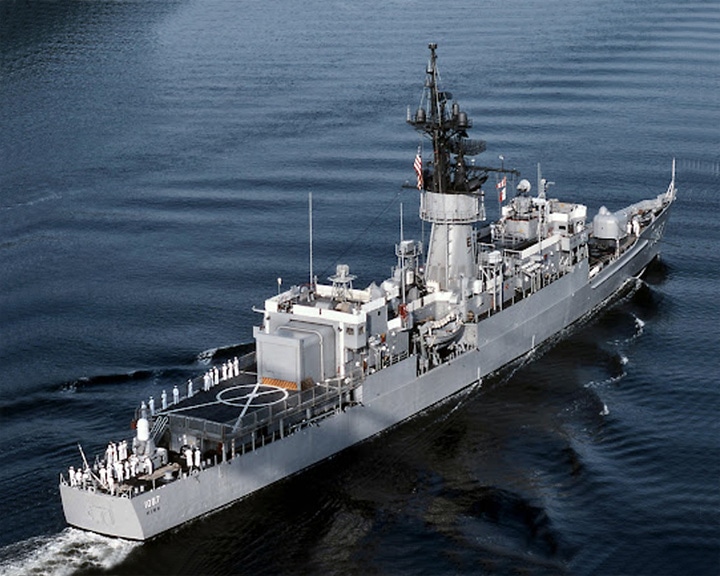 (Another (Another Kirk, USS — American destroyer escort, Knox-class She was sent to help evacuate Americans and fleeing refugees from South Vietnam, caring out one of the most significant humanitarian missions in U.S. military history.. During the evacuation, she was a makeshift landing pad for helicopters flown by South Vietnamese pilots fleeing with families and friends on board. LAUNCHED: 1971, September 25 → FATE: On 29 September 1999, the ship was purchased by Taiwan and renamed Fen Yang. |
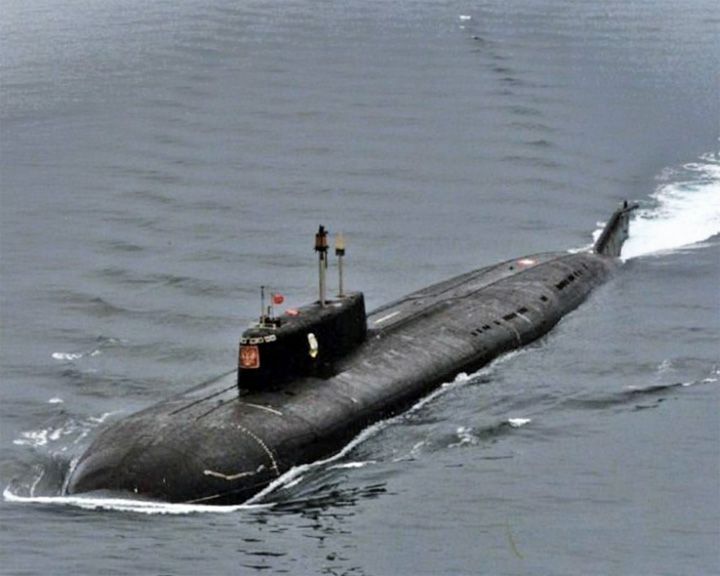 Kursk, K-141 — Russian nuclear submarine Sank with all 118 crew; Russia declined rescue offers even though rescue of some was possible. With the use of a giant barge, the she was eventually raised and the dead recovered and buried in Russia. LAUNCHED: 1994 → FATE: Sank in the Barents Sea on August 12, 2000. |
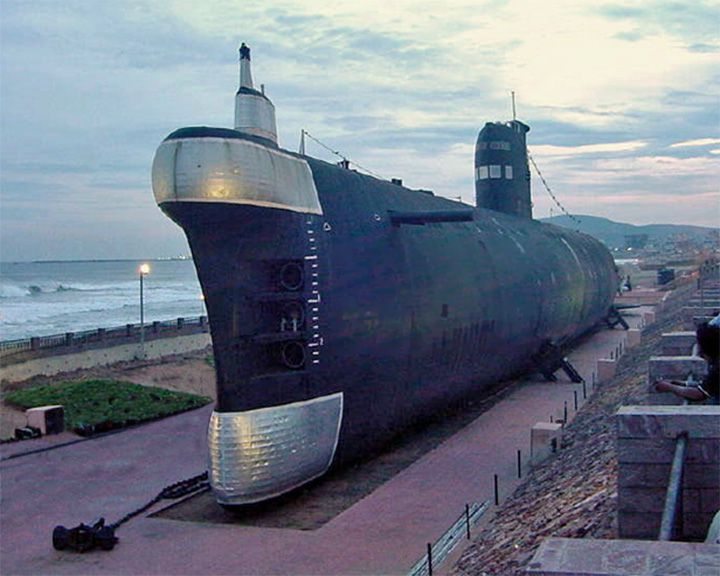 Kursura, INS — Indian Kalvari-class submarine (Russian built) A famous tourist attraction and one of the few submarine museums to be exhibited as it was in service. She was laid off for several years and cannibalized for spare parts for other submarines; then between 1980 to 1982 underwent a refit in the Soviet Union and made operational again in 1985. LAUNCHED: 1969, December 18 → FATE: Decommissioned on February 2001 and made into a museum ship August 2002 at Ramakrishna Mission Beach in Visakhapatnam, India. |
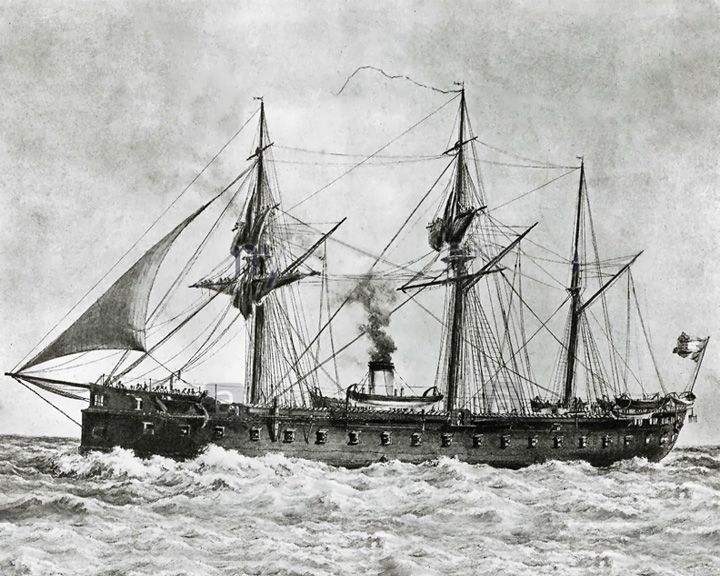 La Gloire — French battleship, steamer The first ocean-going ironclad battleship in history. The ship initiated the obsolescence of traditional unarmored wooden ships-of-the-line. LAUNCHED: 1859, November → FATE: Scrapped in 1883. |
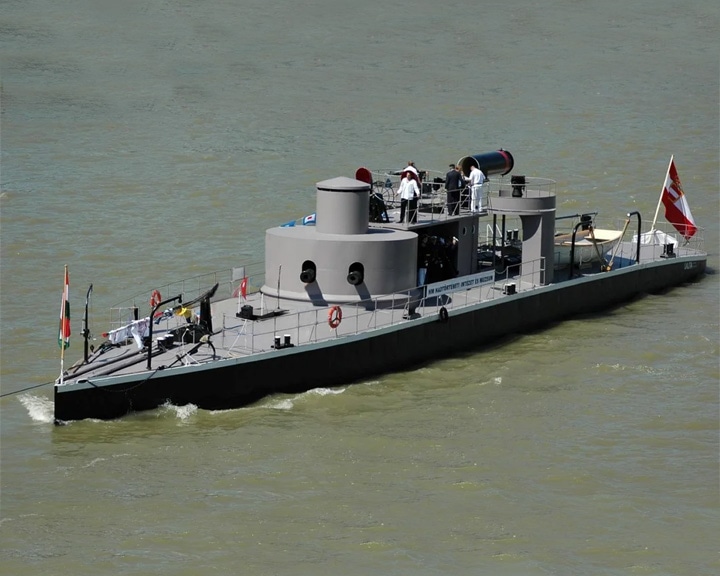 Leitha, SMS (later named Lajta) — Austro-Hungarian river monitor The first river monitor in Europe. The oldest and the only restored warship of the Austro-Hungarian Navy. In October 1914, her turret took a direct hit, all the crew inside being killed. LAUNCHED: 1872, October 13 → FATE: Restored in 2009, Lajta is currently moored on the Danube in Budapest as a museum ship |
|
Page 6
|
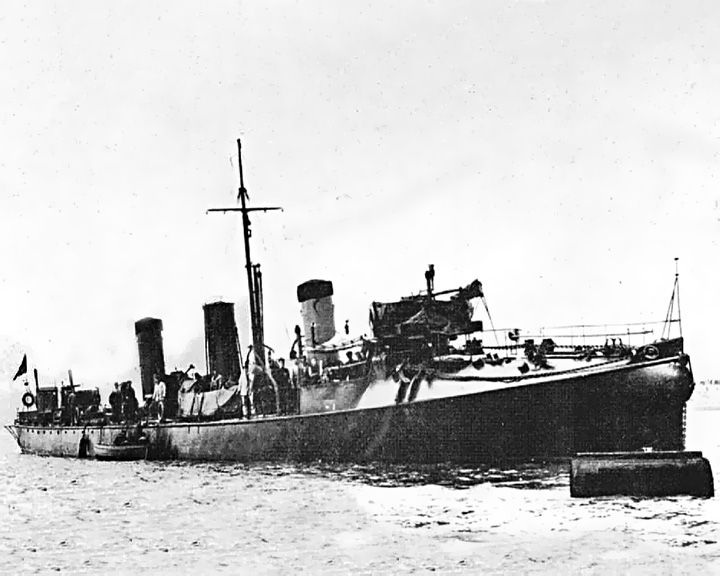 Lightning, HMS — British torpedo boat The first ship to launch self-propelled torpedos. She was used exclusively with HMS Vernon, a torpedo school ship at the Royal Navy's Torpedo Branch at Portsmouth, England. LAUNCHED: 1876 → FATE: Scrapped in 1896. |
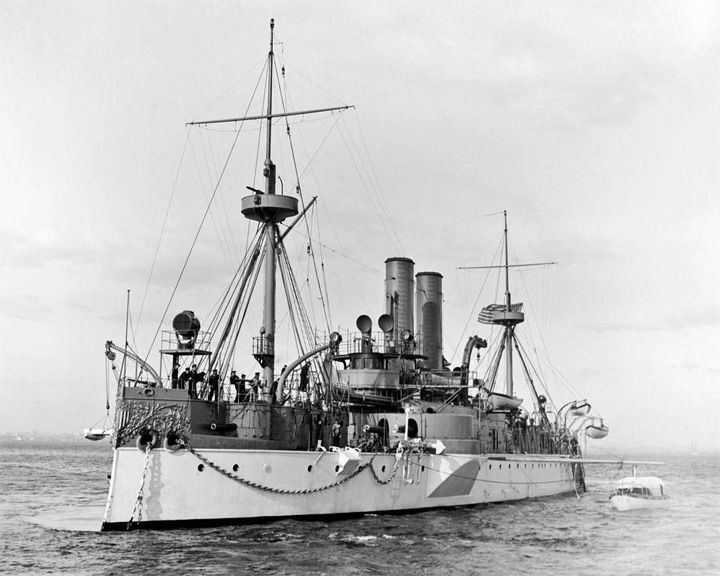 (Another (Another Maine, USS — American battleship Its sinking precipitated the Spanish-American War. Sent to protect U.S. interests during the Cuban revolt against Spain, she exploded without warning and sank, killing 274 men. LAUNCHED: 1889, November 18 → FATE: Sank in the Havana Harbor February 15, 1898. |
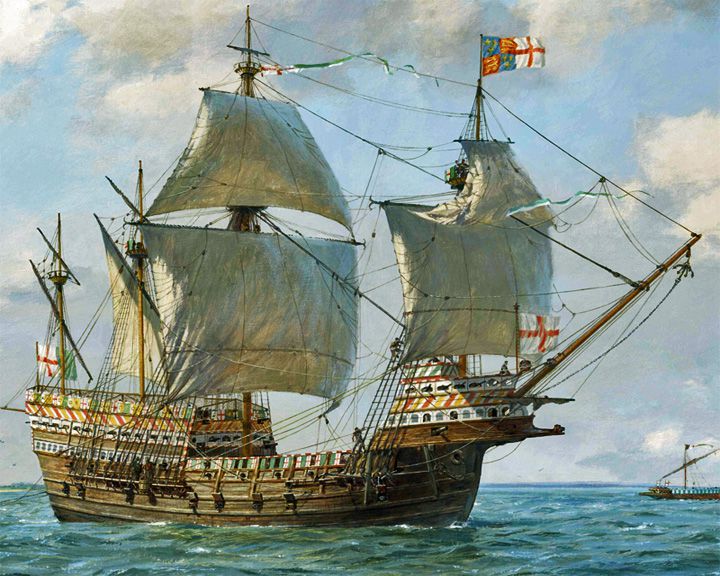 Mary Rose — English carrack-type warship One of the earliest ships built for war sporting the innovation of gun ports. The wreck of the Mary Rose was rediscovered in 1971 and salvaged in 1982. LAUNCHED: 1512 → FATE: Sank in the straits north of the Isle of Wight, 1545. |
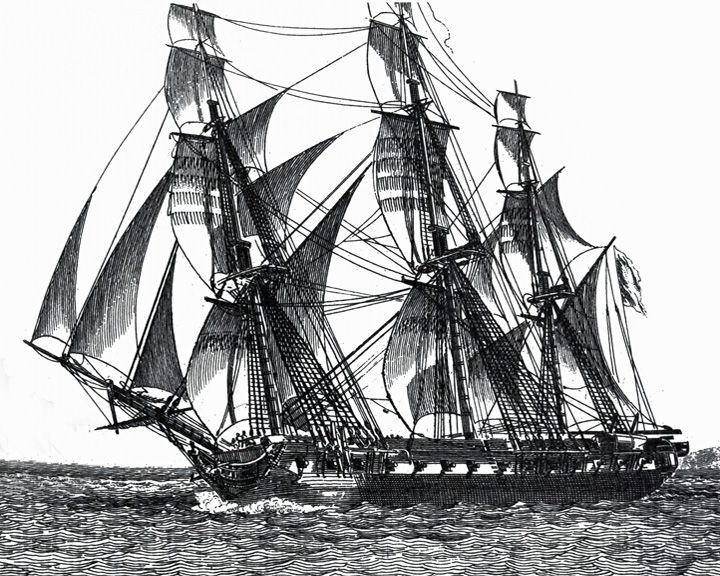 (Another (Another Medusa — French frigate Most famous sea disaster of the nineteenth century. After hitting a shoal, most of the 400 passengers were evacuated while 151 men took refuge on an improvised raft. After 13 days at sea, the raft was discovered with only 15 men still alive. The raft carrying people was the subject of a famous painting, The Raft of the Medusa by French artist Théodore Géricault. LAUNCHED: 1810 → FATE: Beached on Bank of Arguin in 1817. |
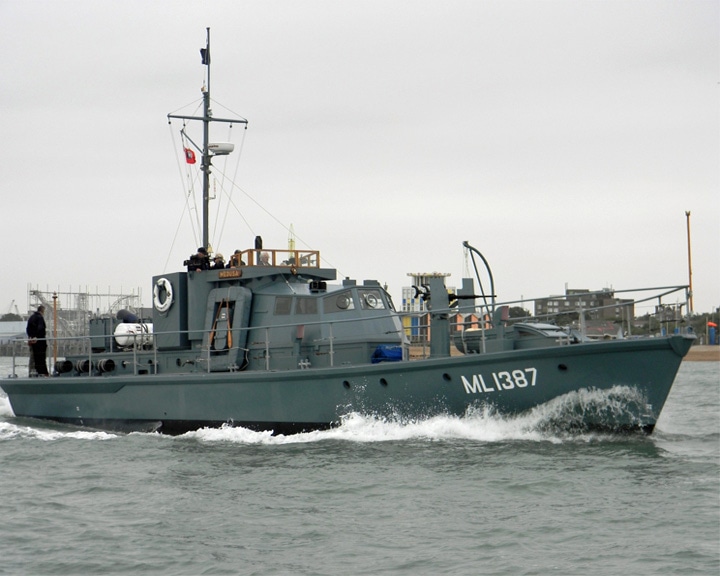 Medusa, HMS — British Harbour defence motor launch She served at D-Day as a Navigation Leader, marking German minefields to be cleared by minesweepers, and then staying at the entrance of the cleared channel to direct parts of the invasion force. For more, see Museum Ships. LAUNCHED: 1943 → FATE: On exhibit at Gosport in England. |
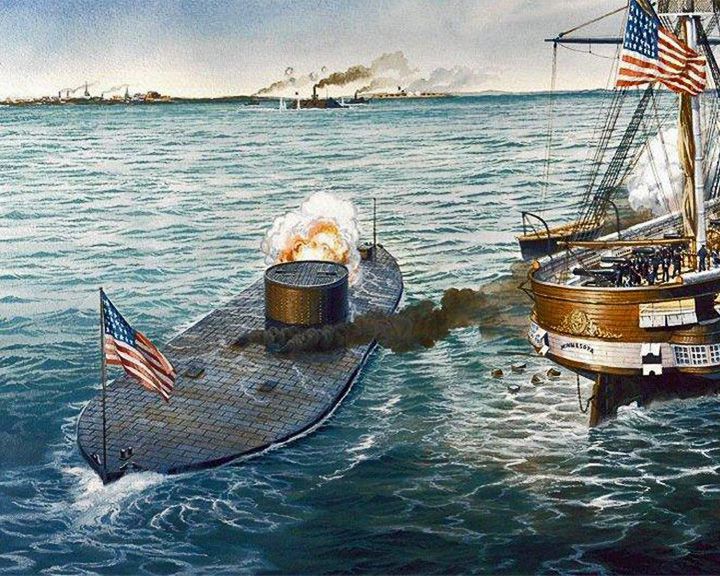 Monitor, USS — American ironclad warship With CSS Virginia, first naval battle between two ironclad warships at the Battle of Hampton Roads. She had a rotating gun turret. LAUNCHED: 1862, January 18 → FATE: Sank on December 31, 1862. |
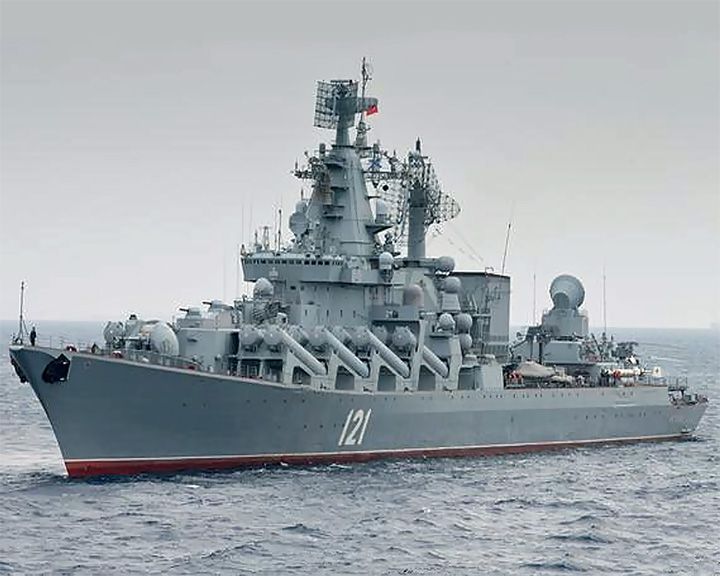 Moskva — Russian guided missile cruiser Flagship of the Russian Black Sea Fleet and helped lead the naval assault during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. The Russian Ministry of Defence said she sank after a fire caused a munitions explosion. LAUNCHED: 1979 → FATE: Sunk by Ukraine forces on April 14, 2022. |
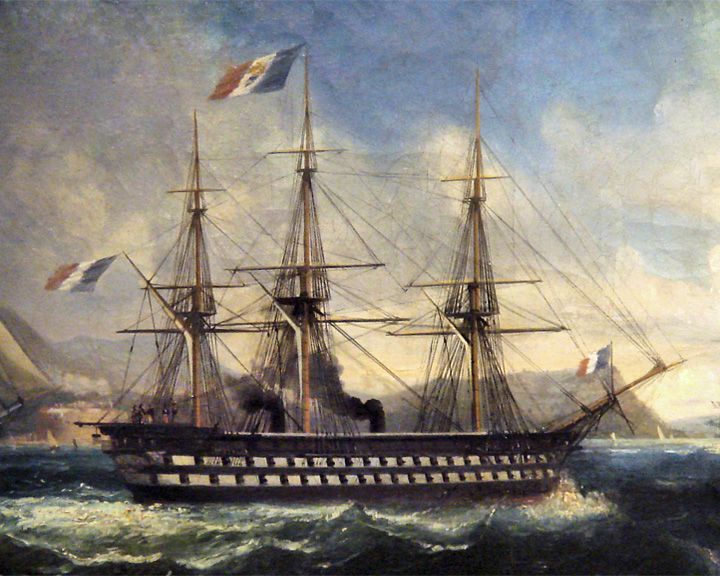 Napoléon, (Le) — French battleship, ship of the line First true steam and screw battleship in the world. She was the lead ship of a class of 9 battleships, all considered as very successful and built over a period of 10 years. LAUNCHED: 1850, May 18 → FATE: Sunk November 6, 1876. |
|
Page 7
|
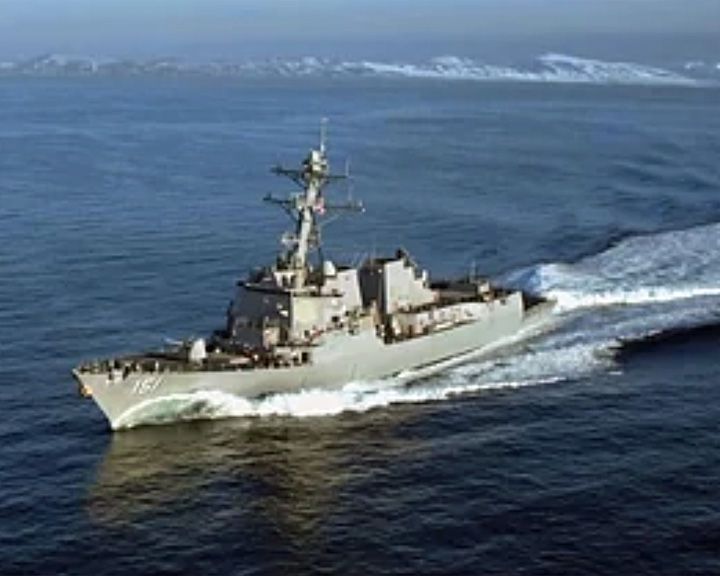 Nathan James, USS — American guided missile destroyer Fictional ship in the movie The Last Ship. She was portrayed by USS Halsey. LAUNCHED: 2014, movie release → FATE: Inconclusive. |
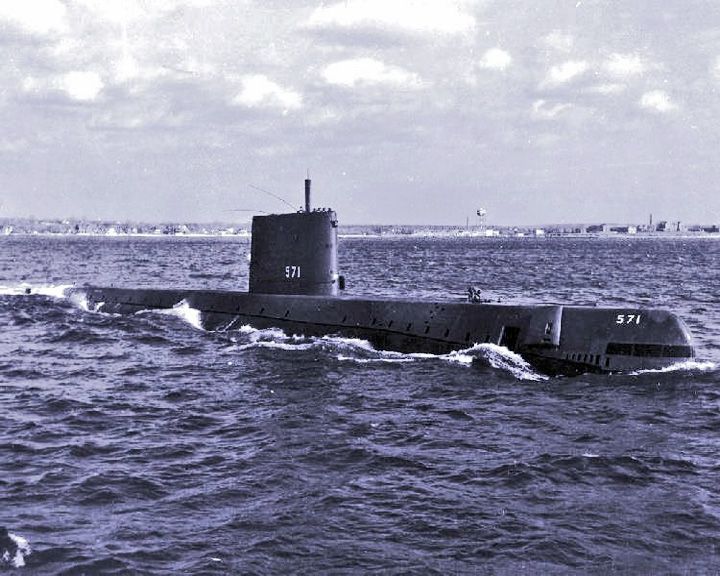 Nautilus, USS — American nuclear submarine World's first nuclear-powered submarine. She was the first vessel to cross under the North Pole. Also the namesake of another U.S. submarine that served in World War II. LAUNCHED: 1954, January 18 → FATE: On exhibit at the Naval Submarine Base New London in Groton, Connecticut. |
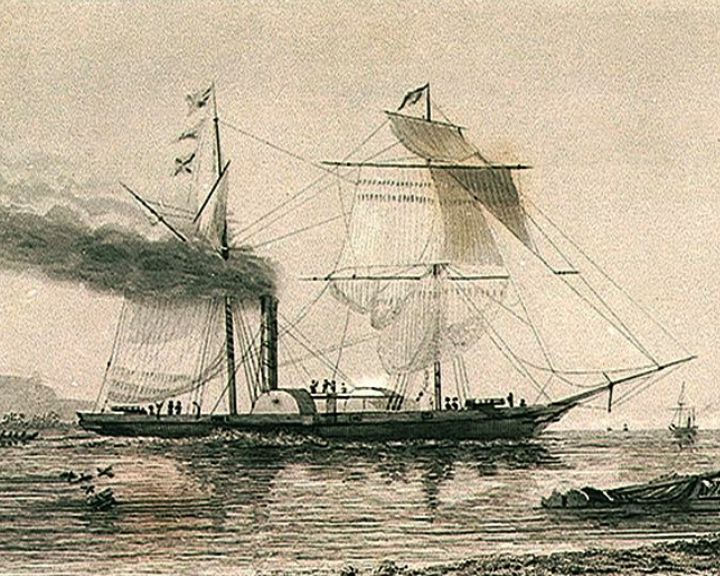 Nemesis — British steam and sail powered warship The first British ocean-going iron warship; also the first iron ship to sail around the Cape of Good Hope. She was greatly effective in the First Opium War. The Chinese referred to her as the "devil ship". LAUNCHED: 1839 → FATE: Ended up in Calcutta, 1855. |
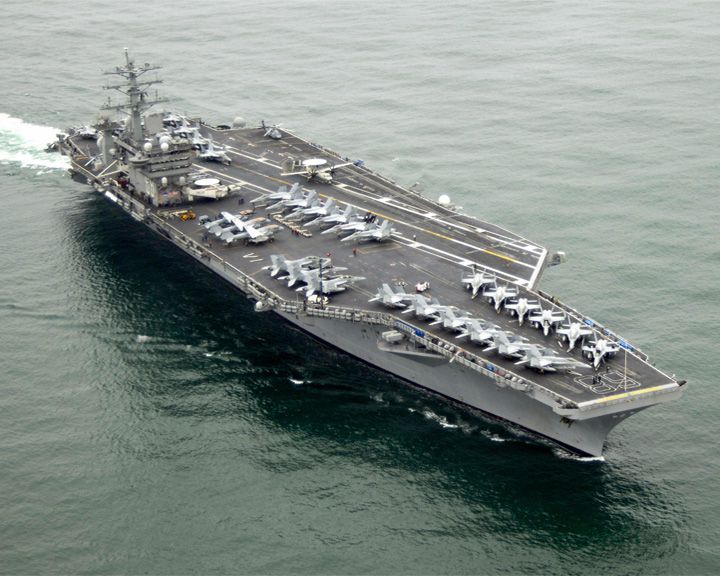 Nimitz, USS — American aircraft carrier; supercarrier Setting for the 1980 science fiction movie The Final Countdown. In May of 1981, one of her planes crashed on the flight deck, killing 14 crewmen. LAUNCHED: 1972, May → FATE: Still in service. |
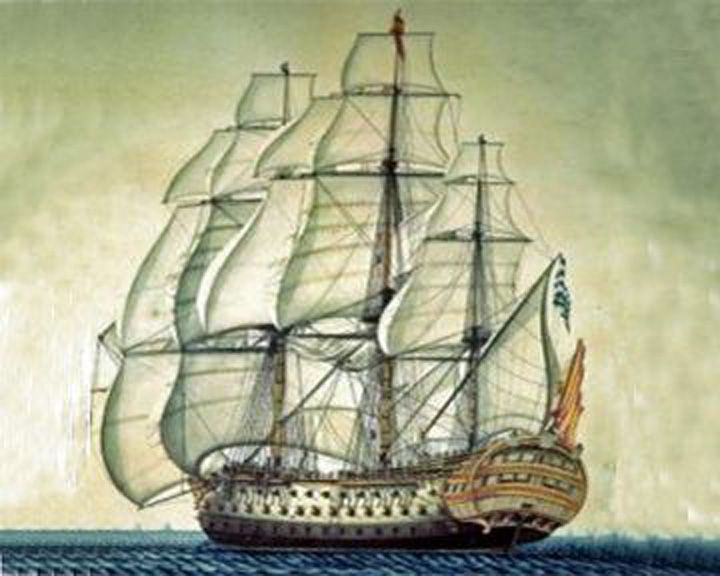 Nuestra Señora de las Mer — Spanish frigate Thought to be the wreck discovered by Odyssey Marine Exploration. Returning to Spain from South America with tons of gold, silver and jewels, she was blown up by the British off Cabo de Santa Maria, Portugal. LAUNCHED: 1786 → FATE: Sunk by the British on October 5, 1804. |
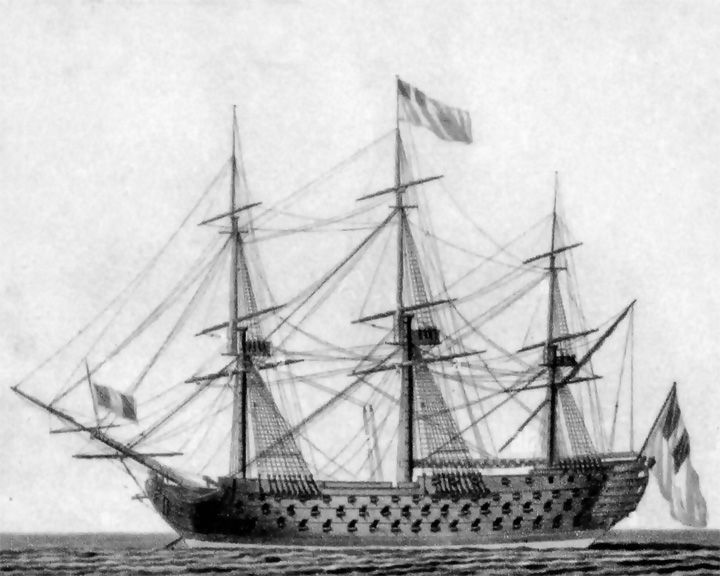 Orient — French ship of the line Famous for her role as flagship of the French fleet at the Battle of the Nile, 1798. During the battle, she caught fire and exploded, with an estimated loss of over 1,130 men; 760 are said to have survived. LAUNCHED: 1791, July 20 → FATE: She was destroyed by an explosion, August 1798. |
 (Another (Another Oriskany, USS — American aircraft carrier, Essex class The world's largest, and the U.S.'s first, artificial reef. She had multiple reconfigurations and updates. In 1966, a flare accidentally ignited on the hangar bay causing a catastrophic fire killing 44 crewmen. LAUNCHED: 1945, October 18 → FATE: Sunk as an artifical reef May 17, 2006. |
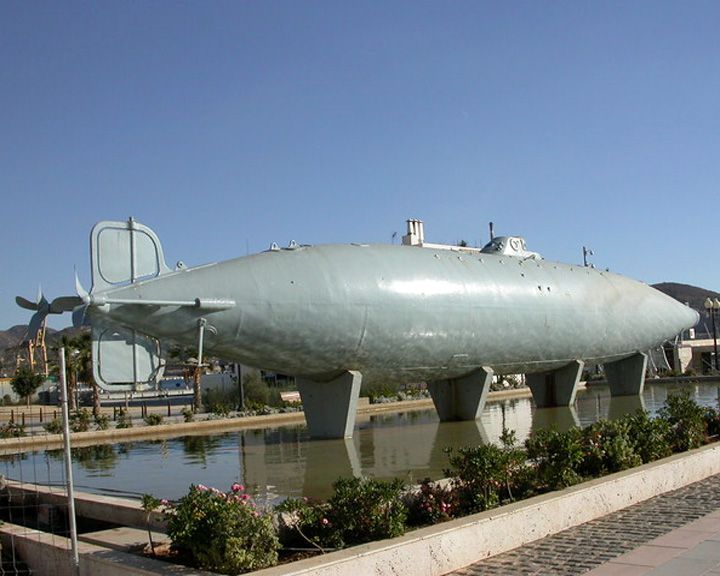 (Another (Another Peral — Spanish submarine The first fully capable military submarine and the first electric battery-powered submarine. She was also the fastest at the time. Since she lacked a means of charging batteries while underway, such as an internal combustion engine, she had very limited endurance and range. LAUNCHED: 1889 → FATE: Withdrawn from service in 1890 and is now preserved at the Cartagena Naval Museum. |
|
Page 8
|
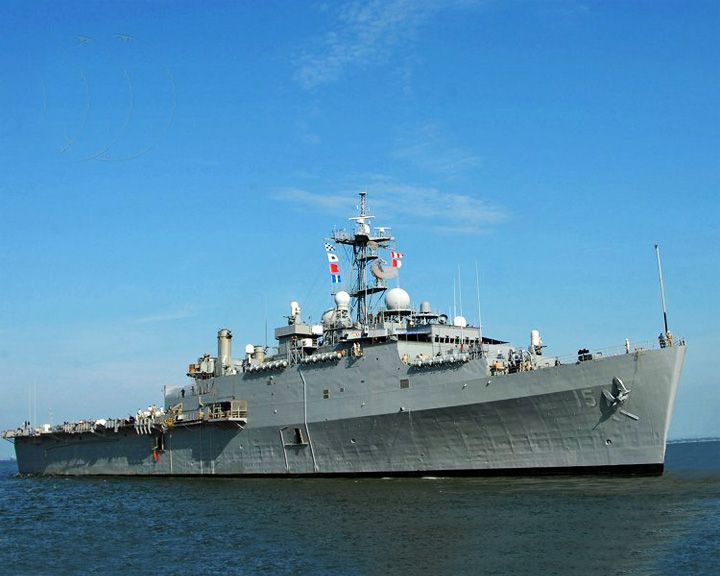 Ponce, USS — American amphibious assault ship First "Afloat Forward Staging Base" (AFSB) ship. She was refitted in 2012 to serve as floating port for helicopters and patrol craft. LAUNCHED: 1970, May 18 → FATE: Still in service. |
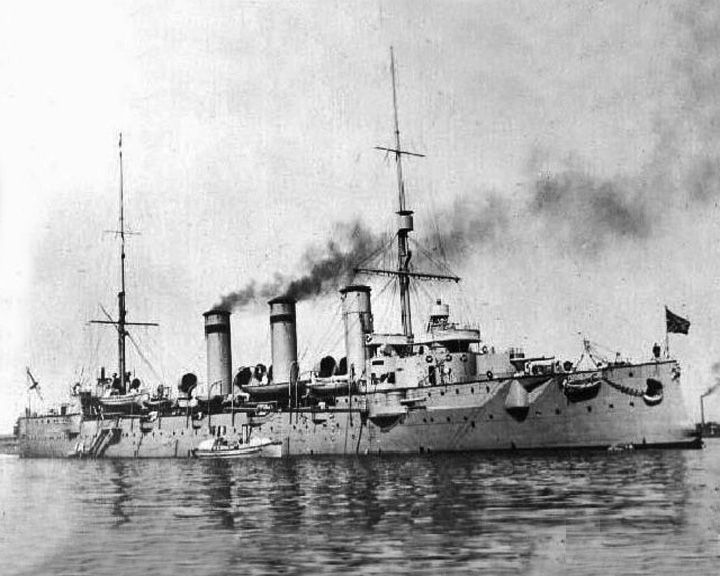 Potemkin — Russian battleship A rebellion of the crew against their cruel officers in 1905 signaled the coming of the Russian Revolution of 1917. Following the mutiny, now called Panteleimon, she accidentally sank a Russian submarine in 1909 and was badly damaged when she ran aground in 1911. LAUNCHED: 1904 → FATE: Scuttled by interventionists at Sevastopol April of 1919. |
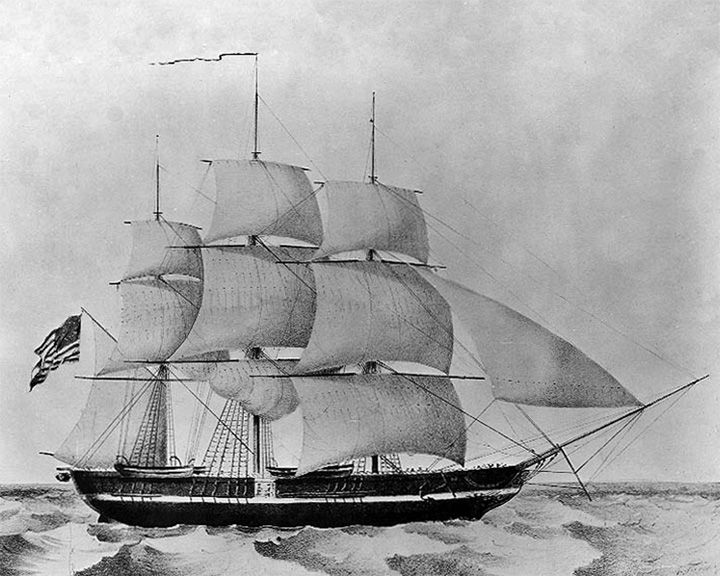 Prineton, USS — American screw steam warship First ship with screw propellers powered by an engine mounted entirely below the waterline. In 1844, during a pleasure cruise for dignitaries, a gun exploded killing 6 high-ranking federal officials and wounding 20 more, the worst such tragedy in American history. LAUNCHED: 1843, September 5 → FATE: Broken up at the Boston Navy Yard, October 1849. |
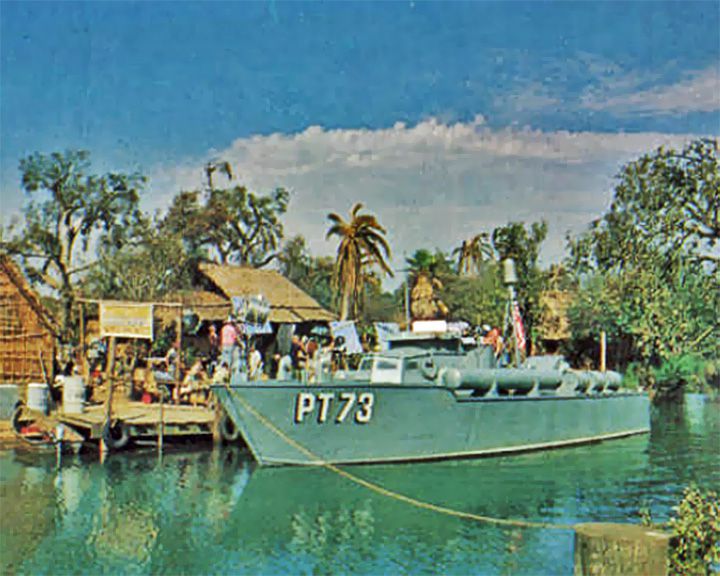 PT-73 — American PT boat Patrol boat in the TV sitcom McHale's Navy. The real-life PT-73 was built on August 12, 1942, and was destroyed by the crew in January, 1945. LAUNCHED: 1962, 1966 for the TV series → FATE: Inconlusive. |
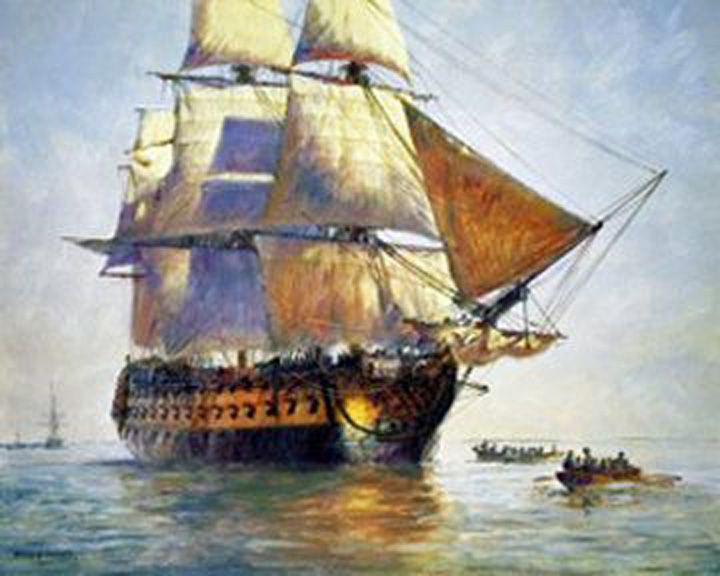 (Another (Another Queen Anne's Revenge — English sloop Flagship of pirate Blackbeard (Edward Thatch). As Conccord was captured by the French in 1711, and then as La Concord she was taken by pirates in 1717. LAUNCHED: 1710 → FATE: Run aground near Beaufort Inlet, North Carolina in May, 1718. |
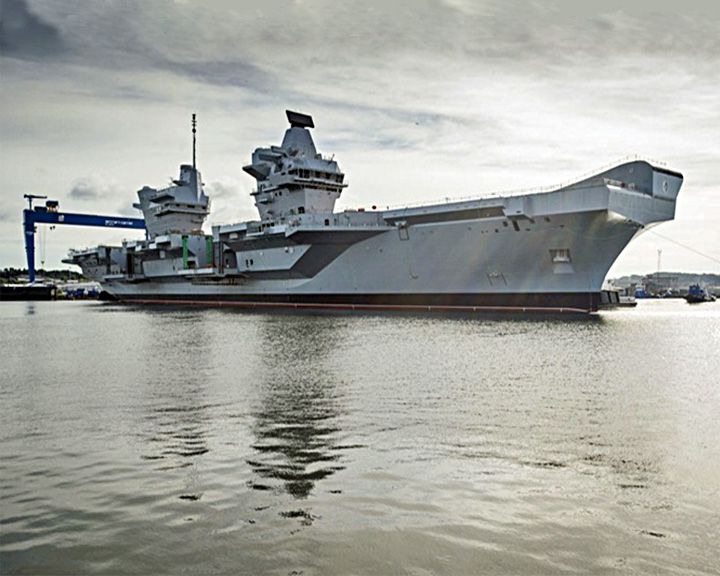 Queen Elizabeth, HMS — British aircraft carrier Largest warship ever built for the Royal Navy capable of carrying up to 40 aircraft. With no catapults and catch wires she carries only V/STOL aircraft, F-35B Lightning II fighters and Merlin helicopters. LAUNCHED: 2014, July 18 → FATE: In service 2017. |
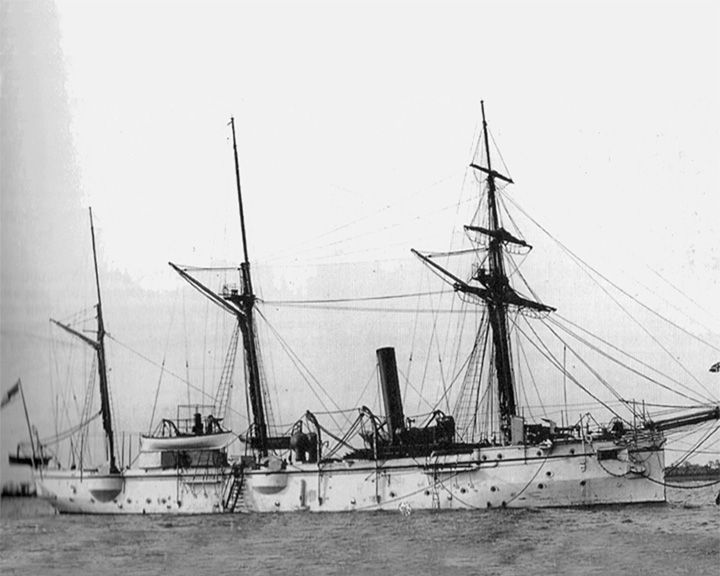 Rattler, HMS — British sloop made of wood with metal frame First warship to adopt a screw propellor. In March 1845, she beat HMS Alecto in a series of races, followed by a contest in which she towed Alecto backwards at a speed of 2 knots (3.7 km/h). LAUNCHED: 1843 → FATE: Broken up 1856. |
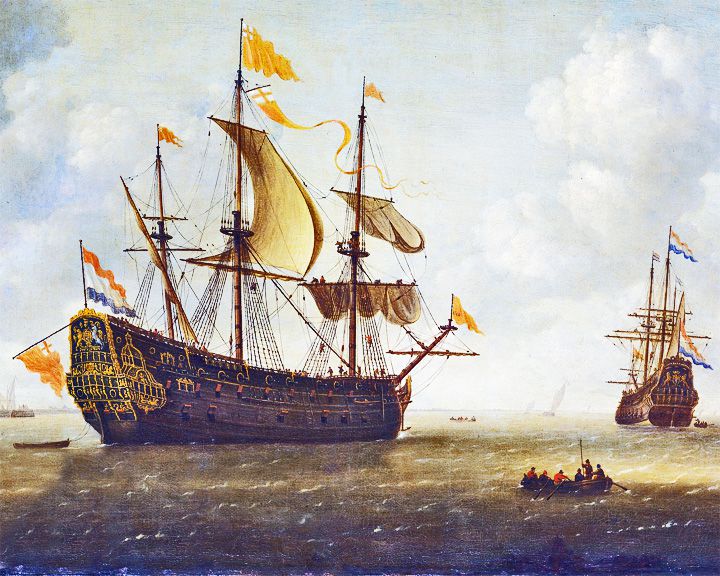 Royal Charles, HMS — British first-rate three-decker ship of the line During the English Restoration, she brought Charles II and his entourage from the Dutch Republic to England to reclaim his crown. At 1,229 tons, she was larger than Sovereign of the Seas, the first three-deck ship of the line. LAUNCHED: 1655, April 18 → FATE: Sold for scrap in 1673 by Dutch navy. |
|
Page 9
|
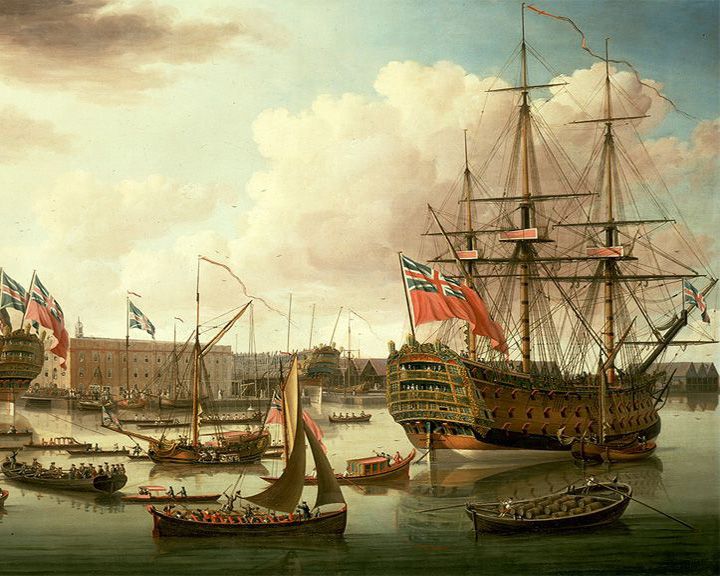 Royal George, HMS — English first-rate ship of the line One of the most serious maritime losses to occur in British water, sinking while undergoing routine maintenance taking more than 800 lives. She was the largest warship in the world at the time of launching. LAUNCHED: 1756, February 18 → FATE: Sank while anchored off Portsmouth August 29, 1782. |
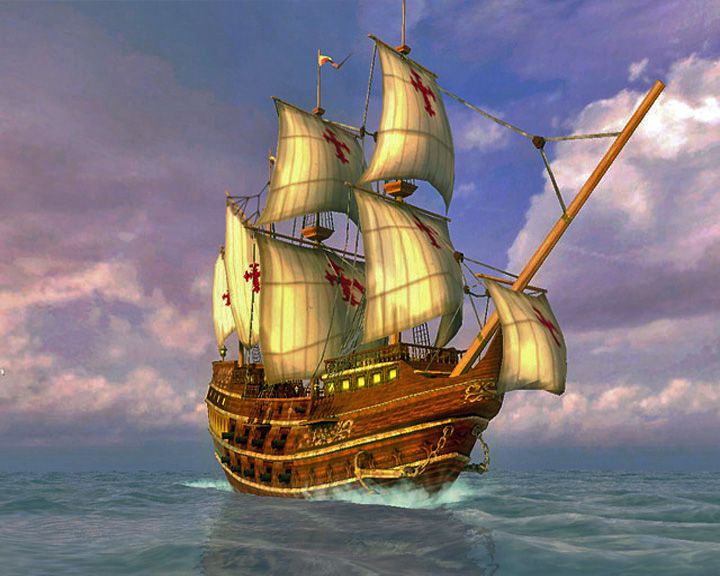 São Martinho — Portuguese galleon Flagship of Duke of Medina Sedonia, commander-in-chief of the Spanish Armada. In September 1588, she was among the few Armada ships to make it back to the port city of Santander, Spain, after suffering heavy damage by English ships. LAUNCHED: 1580 → FATE: 1589 perhaps. |
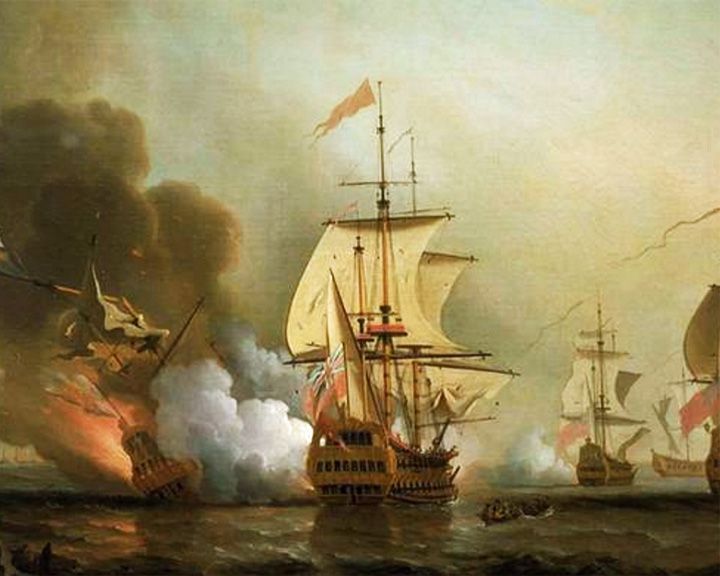 San José — Spanish galleon,60-gun Sunken treasure ship with 7 to 10 million Spanish pesos on board. She was discovered in 2015 with treasure estimated to be worth between 4-17 billion US dollars. LAUNCHED: 1696 → FATE: Sunk in battle off the coast of Cartagena, Colombia in 1708. |
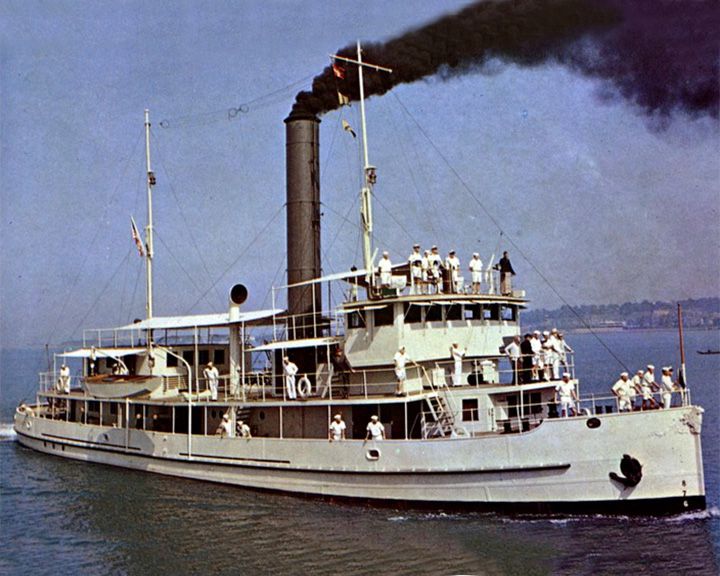 San Pablo — American gunboat Featured in the movie Sand Pebbles starring Steve McQueen. After filming was completed, she was sold and renamed the Nola D, received significant modifications, and eventually used as a base camp for a seismic exploration company. LAUNCHED: 1966, movie release; actual ship September, 1895 → FATE: As the Nola D, she was taken to Singapore and scrapped in 1975. |
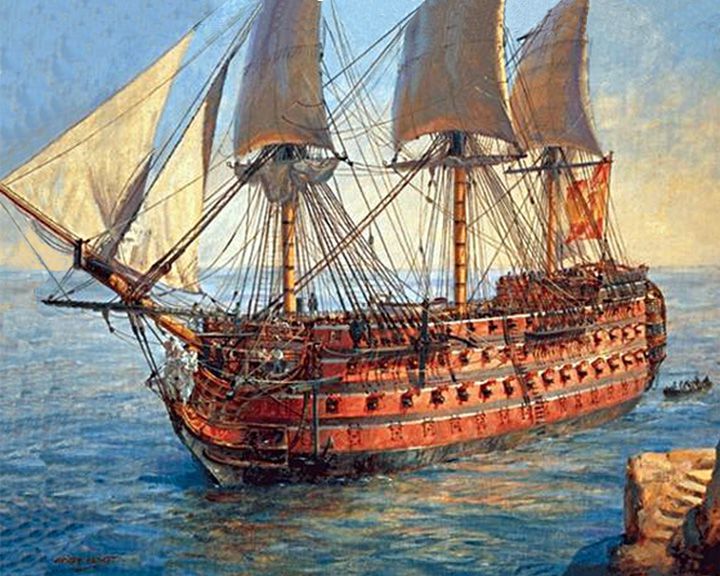 (Another (Another Santísima Trinidad — Spanish ship of the line, first-rate After refitting in 1804, the largest and heaviest-armed ship in the world with 140 guns on four decks. A full-size representation in on display in the harbour of Alicante, Spain as shown in "Another IMAGE". LAUNCHED: 1768 → FATE: Sank at the Battle of Trafalgar in October of 1805. |
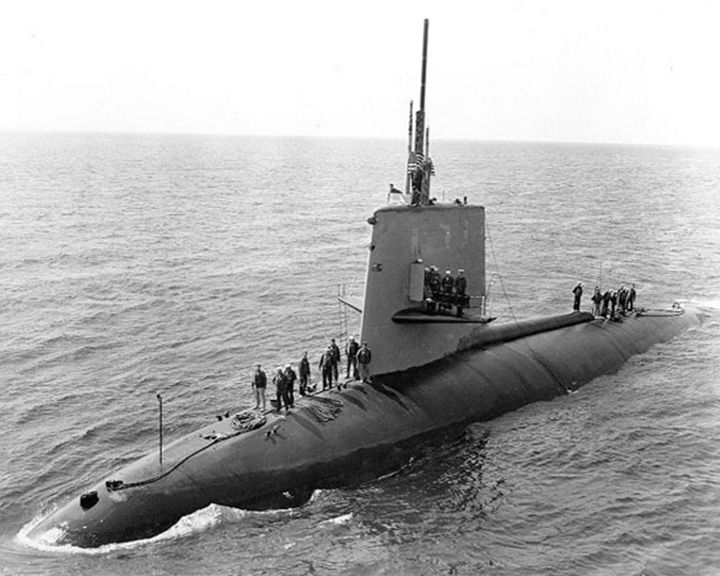 Scorpion, USS — American Skipjack-class nuclear submarine Went missing at sea with 99 crewmen, one of two nuclear submarines the U.S. Navy has lost, the other being USS Thresher (SSN-593). She carried two nuclear-tipped torpedoes. In November 2012, the submarine veterans asked the US Navy to reopen the investigation on the sinking. LAUNCHED: 1959, December 18 → FATE: Sank on May 22, 1968 in the Atlantic Ocean southwest of the Azores. |
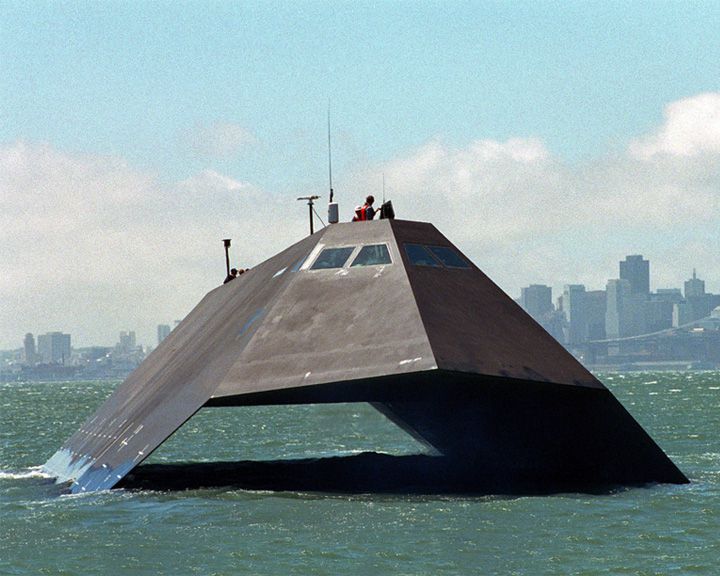 Sea Shadow — American stealth warship U.S. Navy experimental stealth ship, never intended to be mission capable and never commissioned. The ship was the inspiration for the stealth ship in the James Bond movie Tomorrow Never Dies. LAUNCHED: 1985, March → FATE: As of June, 2011 the ship is still being stored at Suisun Bay in northern California awaiting its fate. |
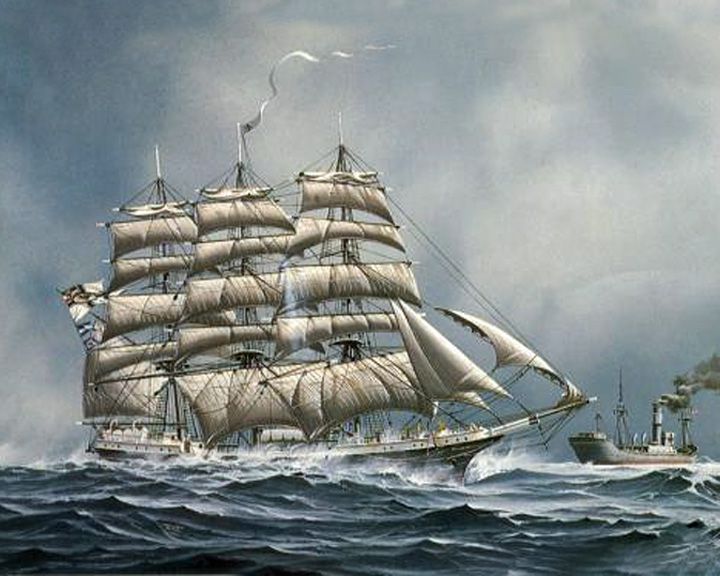 Seeadler, SMS — Scottish windjammer, three-masted; American owned One of the last sailing ships used in a war; as a German merchant raider disguised as a Norwegian wood carrier. she was originally named Pass of Balmaha before capture by a German submarine. LAUNCHED: 1888 → FATE: Wrecked on a reef at the island of Pacific, August 2, 1917. |
|
Page 10
|
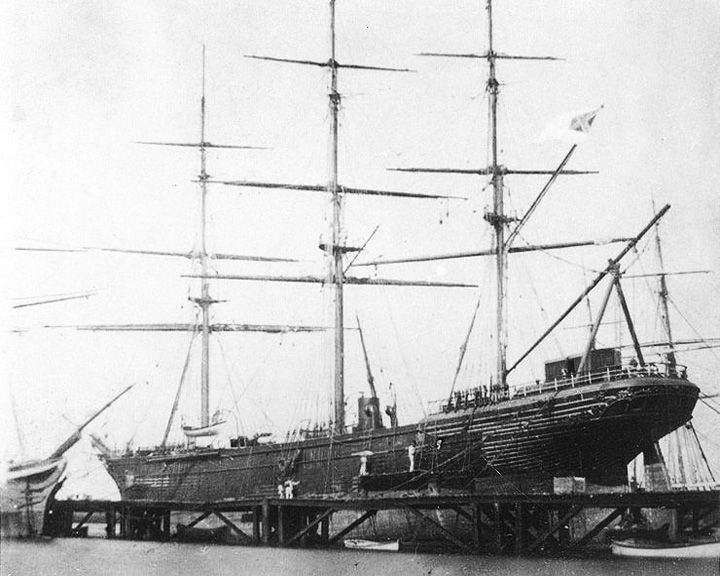 Shenandoah, CSS — American Confederate full-rigged ship, iron-clad During the US Civil War, she captured and/or sank 38 Union merchant vessels. She fired the last shot of the Civil War off the Aleutian Islands, then was surrendered to the British. She was sold to Majid bin Said, the first Sultan of Zanzibar who renamed her El Majidi after himself. LAUNCHED: 1863, August 18 → FATE: As El Majidi, beached during hurricane near Zanzibar in 1872. |
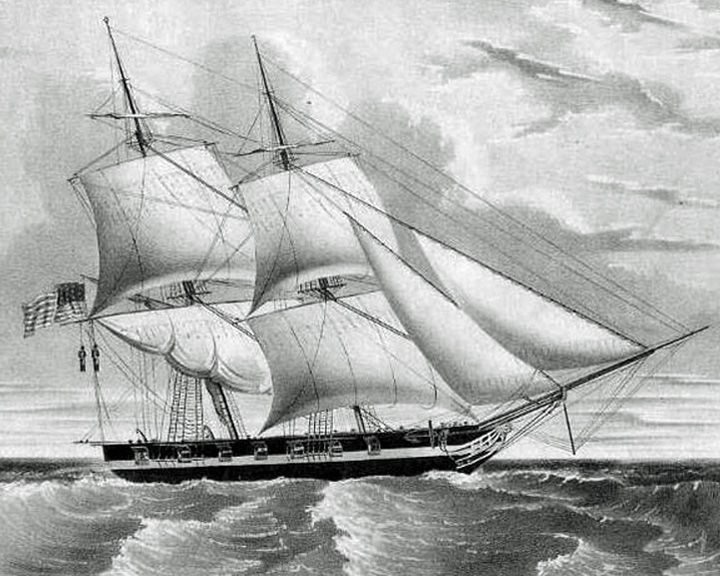 Somers, USS — American brig The only U.S. Navy ship upon which a conspiracy of mutiny took place. Known as the "Somers Affair", it was the basis for several books and dramatizations. December 1, 1842, three of the mutineers who intended to take over the ship and use it for piracy were found guilty of "intention to commit a mutiny," hanged and buried at sea. LAUNCHED: 1842, May 18 → FATE: Capsized and foundered in a sudden squall off Vera Cruz December of 1846. |
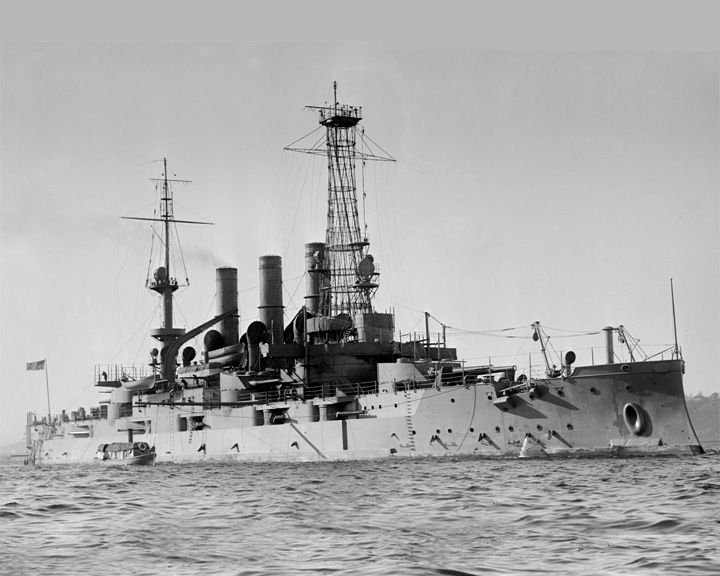 South Carolina, USS — American dreadnought, battleship The first American dreadnought and the first of any nation to have its main guns in a superfire arrangement. She was part of America's Great White Fleet that circumnavigated, December of 1907 to February of 1909. LAUNCHED: 1908, July 18 → FATE: Sold for scrap on April of 1924. |
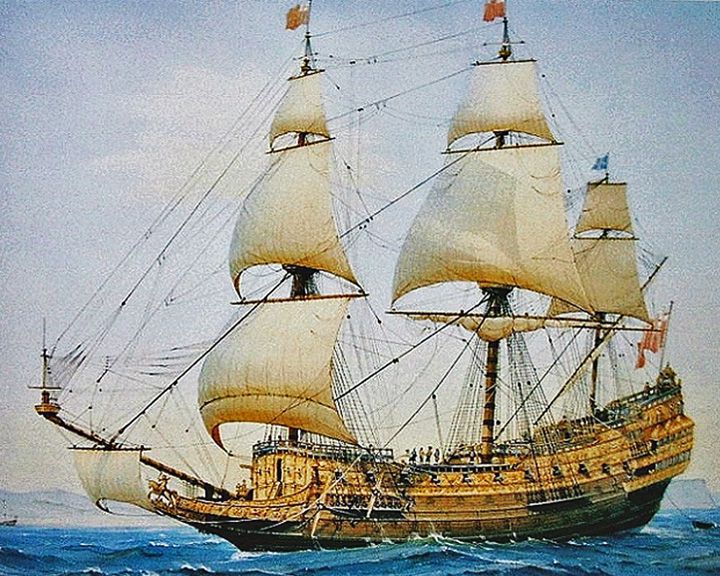 Sovereign of the Seas, HMS — English full-rigged warship The most extravagantly decorated warship in the early Royal Navy. She was armed with 102 bronze guns at the insistence of the king, Charles I of England. LAUNCHED: 1637, October 18 → FATE: Burnt to the water line January 27, 1697. |
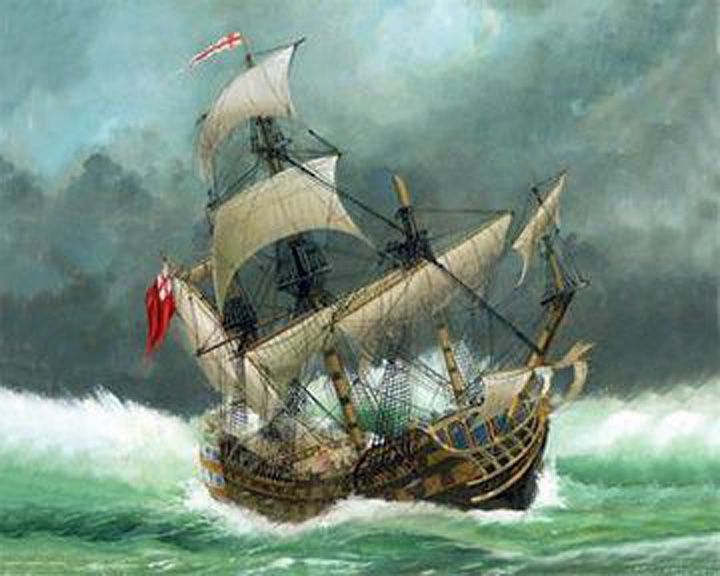 Sussex, HMS — English ship of the line, third-rate One of the most valuable wrecks ever with possibly 10 tons of gold coins and other valuables on board. Besides Sussex, 12 other ships of her flotilla sank with about 1,200 casualties making the disaster one of the worst in Royal Navy history. LAUNCHED: 1693, April 18 → FATE: Sank in a violent storm near the Strait of Gibraltar February 27, 1694. |
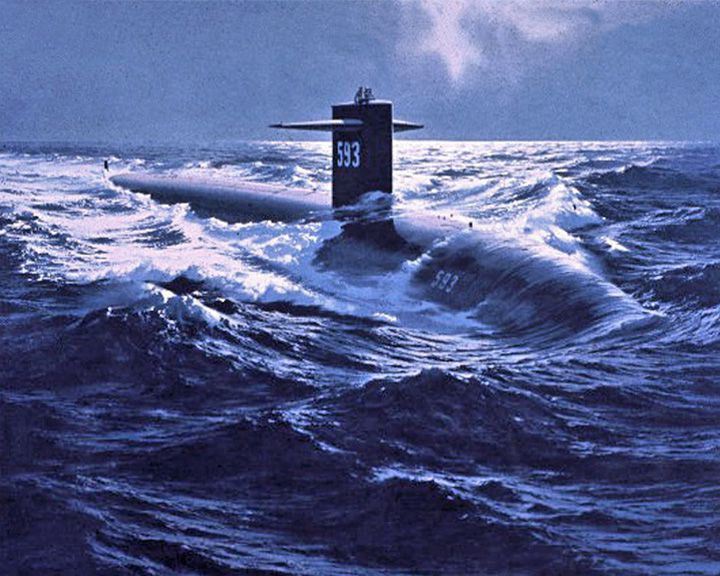 Thresher, USS — American nuclear submarine Lost at sea during deep-diving tests in 1963 with 129 crew. She was the lead ship of her class of nuclear-powered attack submarines and one of two nuclear submarines the U.S. Navy has lost, the other being USS Scorpion, SSN-589. LAUNCHED: 1960, July 18 → FATE: Sunk April 10, 1963. |
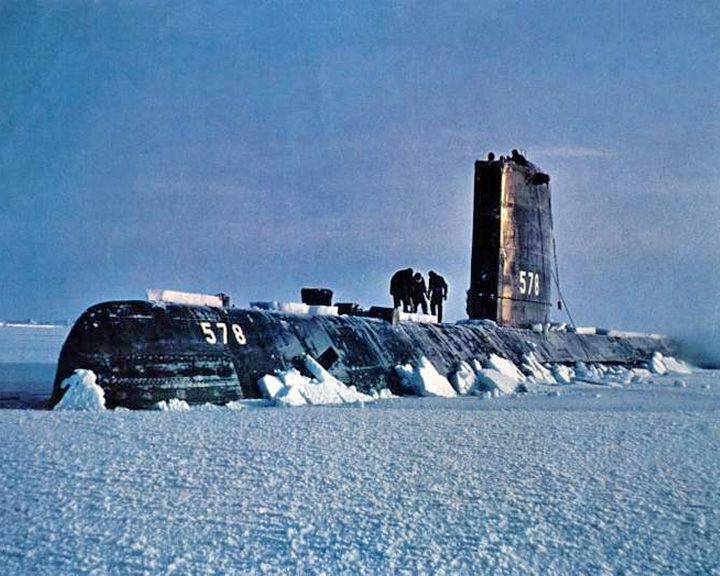 Tigerfish, USS — American attack submarine Fictional submarine in the movie Ice Station Zebra. She was portrayed in the movie by the diesel-electric submarine USS Ronquil when seen on the surface. LAUNCHED: 1968, movie release → FATE: Inconclusive. |
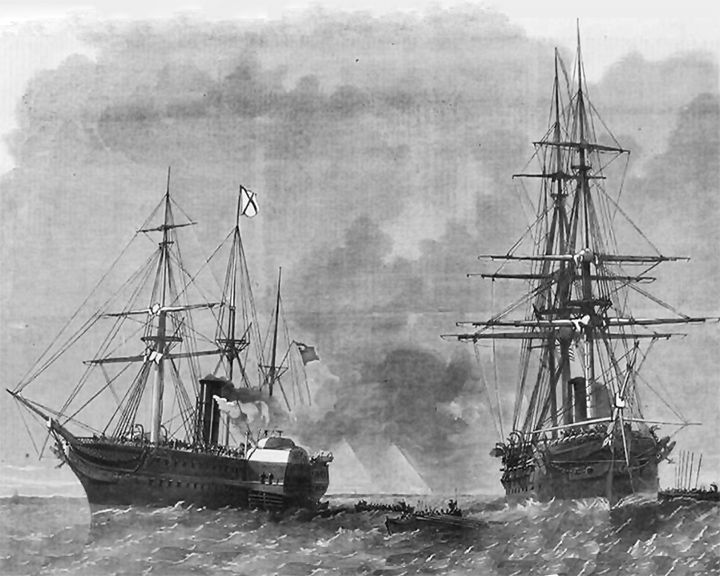 Trent, RMS — British paddle steamer serving as a packet boat Principle ship in the Trent affair in 1861 during the American Civil War. Her interception by USS San Jacinto and unlawfully capture of two Confederate diplomats almost led to war between the Britian and the United States. LAUNCHED: 1841 → FATE: Sold and broken up after 1865. |
|
Page 11
|
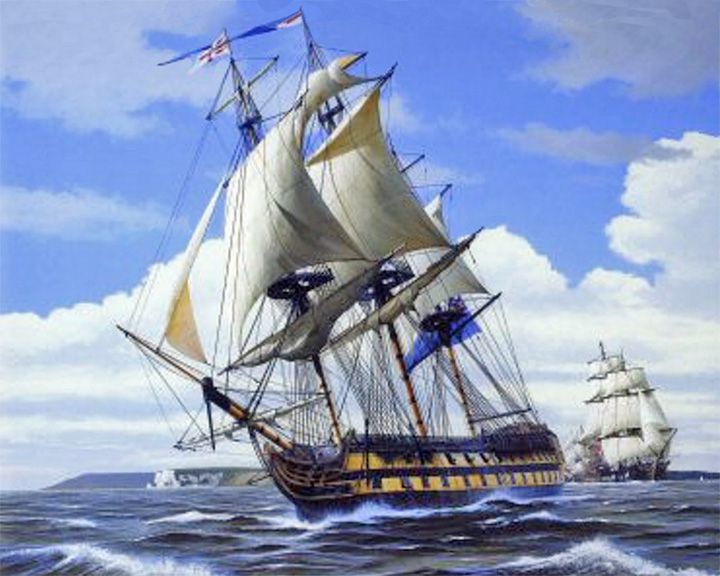 Vanguard, HMS — English ship of the line, 74-gun third-rate The flag ship of Horatio Nelson at the Battle of the Nile, 1798. Prince Alberto of Naples and Sicily, part of a royal entourage on board fleeing from Naples and the French, died on board. LAUNCHED: 1787, March 18 → FATE: Broken up in 1821. |
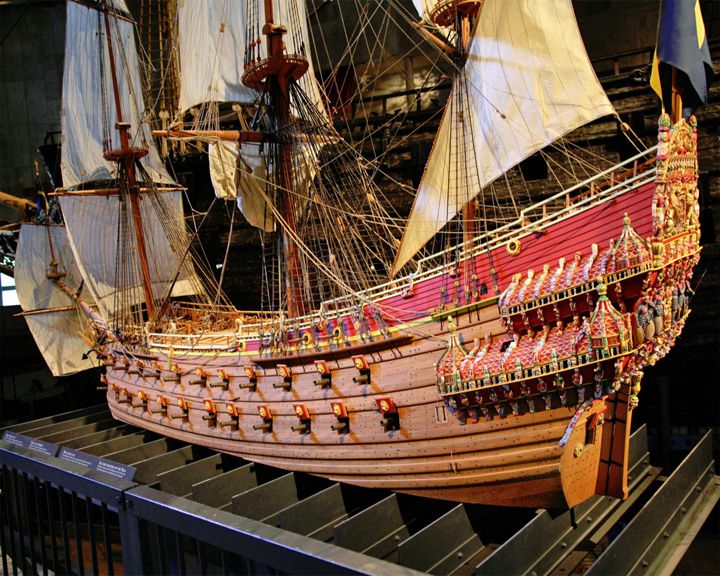 Vasa — Swedish wooden warship One of Sweden's most popular tourist attractions and a widely recognized symbol of the Swedish 'great power period'. During the 1961 recovery, thousands of artifacts and the remains of at least 15 people were found in and around the hull of the Vasa by marine archaeologists. LAUNCHED: 1627 → FATE: Sank on her maiden voyage in 1628 near Södermalm; salvaged in 1961 and now on display in the Vasa Museum in Stockholm. |
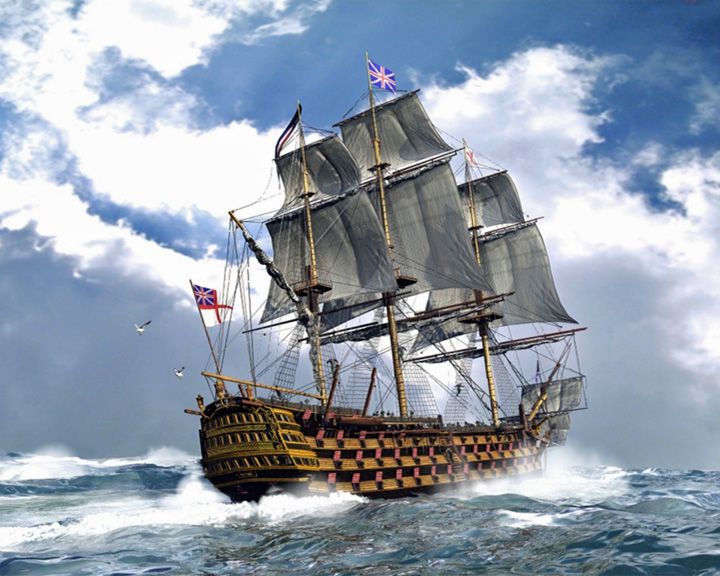 Victory, HMS — English first-rate ship of the line (Galleon) Lord Nelson's flagship at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805. She was refitted and repainted in 1800-1803, almost broken up in 1831, fitted up as a Naval School 1889, retired in 1904, and eventually restored. LAUNCHED: 1765, May 18 → FATE: Being restored at the HMNB, Portsmouth, England. |
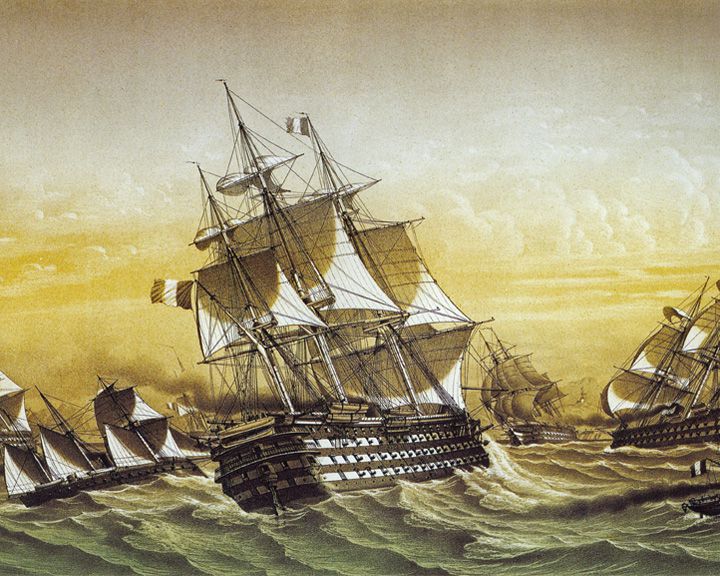 Ville de Paris — French ship of the line, large three-decker The flagship of the Comte de Grasse during the American Revolutionary War and the Siege of Yorktown. A ship of the line of the Royal Navy was named after her, HMS Ville de Paris, and launched in 1795. LAUNCHED: 1764 → FATE: Sank in September 1782 with other ships in a Central Atlantic hurricane. |
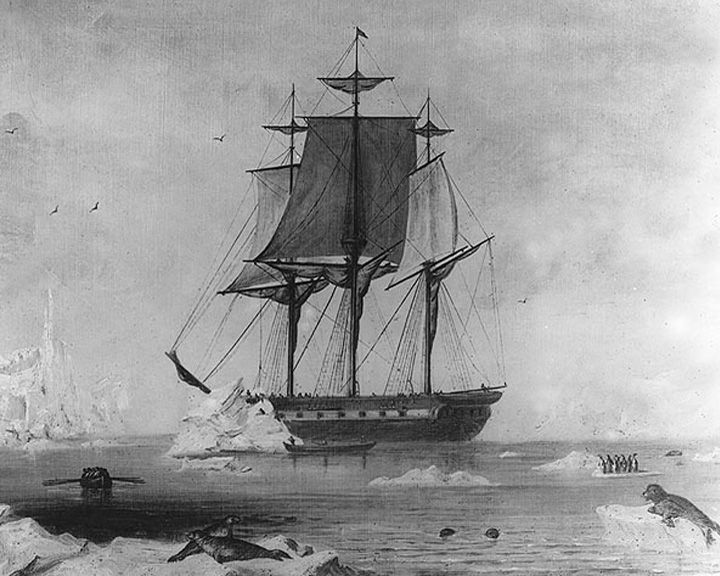 Vincennes, USS — American sloop of war First U.S. ship to circumnavigate the globe. She was the flagship for the U.S. Exploring Expedition of 1838. LAUNCHED: 1826 → FATE: Sold in October of 1867 at Boston, Massachusetts; fate unknown. |
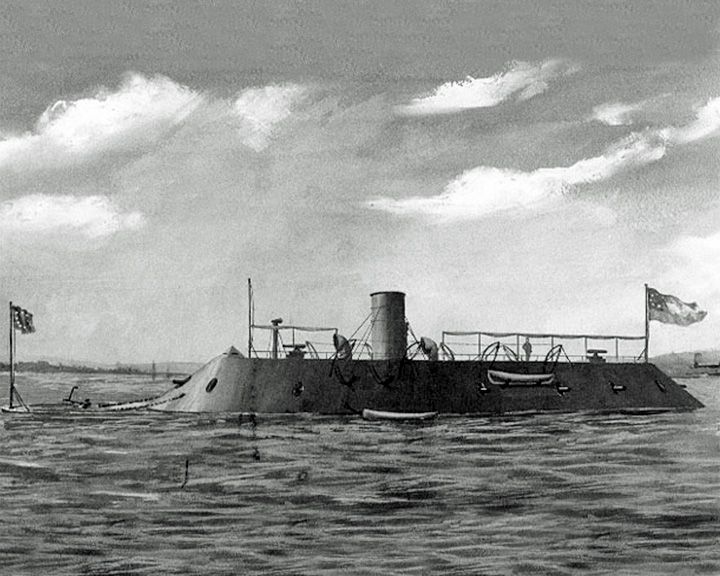 Virginia, CSS — Americant Confederat ironclad warship With USS Monitor, first naval battle between ironclad warships at the Battle of Hampton Roads. She was converted to an ironclad from a steam frigate. LAUNCHED: 1862, February → FATE: Destroyed by crew May 11, 1862. |
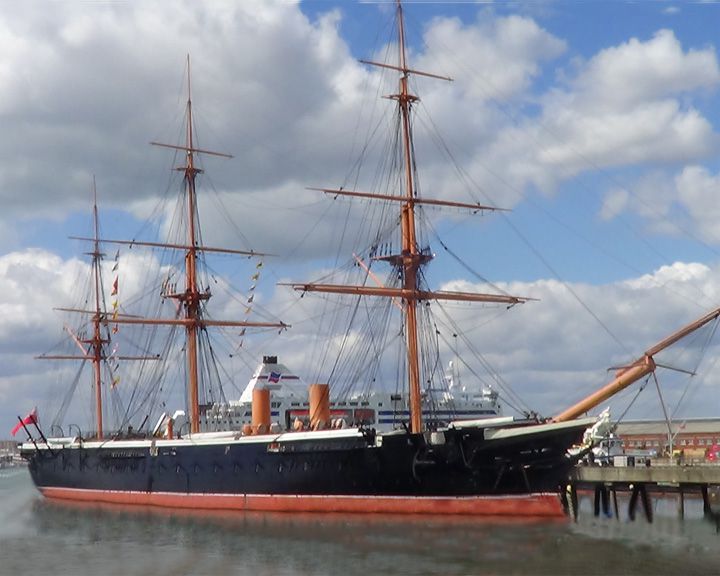 Warrior, HMS — British warship First British iron-hulled, armour-plated warship. She was the largest, fastest, most heavily armed and armored warship up to that time. LAUNCHED: 1860, December 18 → FATE: Currently berthed in Portsmouth, England as a museum. |
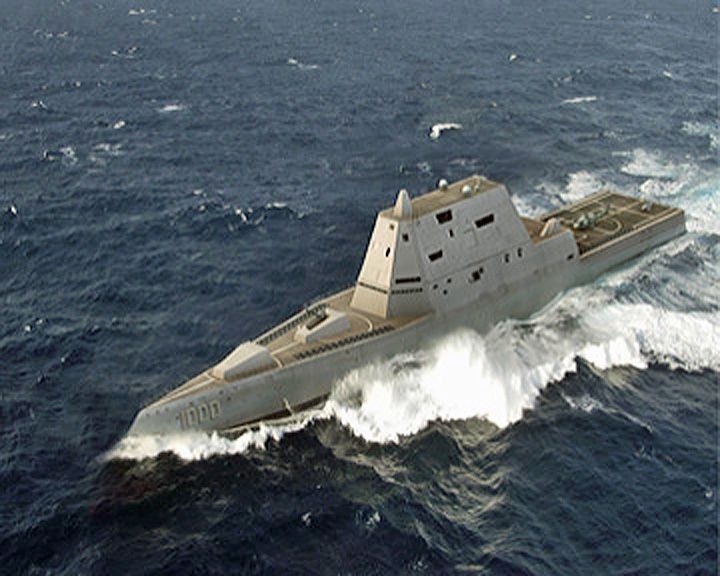 Zumwalt, USS — American guided missile destroyer Designed with stealth capabilities, having a radar cross-section akin to a fishing boat. Commanding officer is Captain James A. Kirk, coincidentially the same as the Star Trek captain. LAUNCHED: 2013, October → FATE: Currently at sea. |
The number of All Countries Warships, not in World Wars listed is 87 The contents of this page are available under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license and the GNU Free Documentation License (GFDL). |
|
|
First Ship on each page
| |
| Page | Ship Name (Country and Type) |
| 1. | Albert M. Boe (American liberty ship) |
| 2. | Bonhomme Richard, USS (American frigate) |
| 3. | David, CSS (American Confederate torpedo boat) |
| 4. | Gribshunden (Danish warship) |
| 5. | Hunley, H.L. (American Confederate submarine) |
| 6. | Lightning, HMS (British torpedo boat) |
| 7. | Nathan James, USS (American guided missile destroyer) |
| 8. | Ponce, USS (American amphibious assault ship) |
| 9. | Royal George, HMS (English first-rate ship of the line) |
| 10. | Shenandoah, CSS (American Confederate full-rigged ship) |
| 11. | Vanguard, HMS (English ship of the line) |
All Countries | |
| 1. | Albert M. Boe American liberty ship |
| 2. | Alligator American submarine |
| 3. | Ark Royal, HMS English galleon |
| 4. | Association, HMS British second-rate ship of the line |
| 5. | B-39 Russian foxtrot-class submarine |
| 6. | Black Widow Russian foxtrot-class submarine |
| 7. | Bonhomme Richard, USS American frigate |
| 8. | Caine, USS American destroyer minesweeper |
| 9. | Cairo, USS American ironclad gunboat |
| 10. | Cole, USS American aegis-equipped |
| 11. | Colossus, HMS British third-rate ship of the line |
| 12. | Constellation, USS American sloop-of-war |
| 13. | Constitution, USS American frigate |
| 14. | Darling, HMS British torpedo boat destroyer |
| 15. | David, CSS American Confederate torpedo boat |
| 16. | Demologos American paddle steamers |
| 17. | Devastastion, HMS British Devastation-class ironclad |
| 18. | Enterprise, USS American aircraft carrier |
| 19. | Esmeralda Chilean steam corvette |
| 20. | Fenian Ram American submarine |
| 21. | Ghost, stealth ship American super-cavitating |
| 22. | Gloire French ocean-going ironclad |
| 23. | Gribshunden Danish warship |
| 24. | Halibut, USS American attack submarine |
| 25. | Hammersly, HMAS Australian Armidale-class patrol boat |
| 26. | Hannah, USS American schooner |
| 27. | Hero, HMAS British Leander-class frigate |
| 28. | Holland, USS (SS-1) American submarine |
| 29. | Hotspur, HMS British sloop-of-war |
| 30. | Huáscar Peruvian iron-clad |
| 31. | Hunley, H.L. American Confederate submarine |
| 32. | Independence, USS American trimaran |
| 33. | Jylland, HDMS Danish screw-propelled steam frigate |
| 34. | Kirk, USS American destroyer escort, Knox-class |
| 35. | Kursk, K-141 Russian nuclear submarine |
| 36. | Kursura, INS Indian Kalvari-class |
| 37. | La Gloire French battleship |
| 38. | Leitha, SMS Austro-Hungarian river monitor |
| 39. | Lightning, HMS British torpedo boat |
| 40. | Maine, USS American battleship |
| 41. | Mary Rose English carrack-type |
| 42. | Medusa French frigate |
| 43. | Medusa, HMS British Harbour defence motor launch |
| 44. | Monitor, USS American ironclad warship |
| 45. | Moskva Russian guided missile cruiser |
| 46. | Napoléon, (Le) French battleship |
| 47. | Nathan James, USS American guided missile destroyer |
| 48. | Nautilus, USS American nuclear submarine |
| 49. | Nemesis British steam and sail powered warship |
| 50. | Nimitz, USS American aircraft carrier |
| 51. | Nuestra Señora de las Mer Spanish frigate |
| 52. | Orient French ship of the line |
| 53. | Oriskany, USS American aircraft carrier |
| 54. | Peral Spanish submarine |
| 55. | Ponce, USS American amphibious assault ship |
| 56. | Potemkin Russian battleship |
| 57. | Prineton, USS American screw steam warship |
| 58. | PT-73 American PT boat |
| 59. | Queen Anne's Revenge English sloop |
| 60. | Queen Elizabeth, HMS British aircraft carrier |
| 61. | Rattler, HMS British sloop made of wood with metal frame |
| 62. | Royal Charles, HMS British first-rate three-decker ship of the line |
| 63. | Royal George, HMS English first-rate ship of the line |
| 64. | São Martinho Portuguese galleon |
| 65. | San José Spanish galleon |
| 66. | San Pablo American gunboat |
| 67. | Santísima Trinidad Spanish ship of the line |
| 68. | Scorpion, USS American Skipjack-class nuclear submarine |
| 69. | Sea Shadow American stealth warship |
| 70. | Seeadler, SMS Scottish windjammer |
| 71. | Shenandoah, CSS American Confederate full-rigged ship |
| 72. | Somers, USS American brig |
| 73. | South Carolina, USS American dreadnought |
| 74. | Sovereign of the Seas, HMS English full-rigged |
| 75. | Sussex, HMS English ship of the line |
| 76. | Thresher, USS American nuclear submarine |
| 77. | Tigerfish, USS American attack submarine |
| 78. | Trent, RMS British paddle steamer |
| 79. | Vanguard, HMS English ship of the line |
| 80. | Vasa Swedish wooden warship |
| 81. | Victory, HMS English first-rate |
| 82. | Ville de Paris French ship of the line |
| 83. | Vincennes, USS American sloop of war |
| 84. | Virginia, CSS Americant Confederat ironclad warship |
| 85. | Warrior, HMS British warship |
| 86. | Zumwalt, USS American guided missile destroyer |
|
About the Data There are more than 400 ships in this database, but the initial list is only for famous ships names that begin with letters "A-B". For other listings, use the country and type tabs. Touching (or cursor over) a ship image produces an enlargement. Touch anywhere else (or move the cursor off the image) to close the larger image. Touching (or clicking on) any underlined name will link to a page with more information. Although submarines are usually called boats, they are grouped with ships here. Most of the information comes from Wikipedia. |
^
Other Pages in Names Galore: | |
Famous Cowboy Names Sports Team Names Other Name Lists | Name Generators Naming Fun Stories about Names |